Single-family rental portfolios offer direct ownership of residential properties, providing investors with tangible assets and potential for steady rental income. Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) enable investors to access diversified real estate holdings through publicly traded shares without the responsibilities of property management. Explore the advantages and challenges of each investment type to determine the best fit for your portfolio goals.
Why it is important
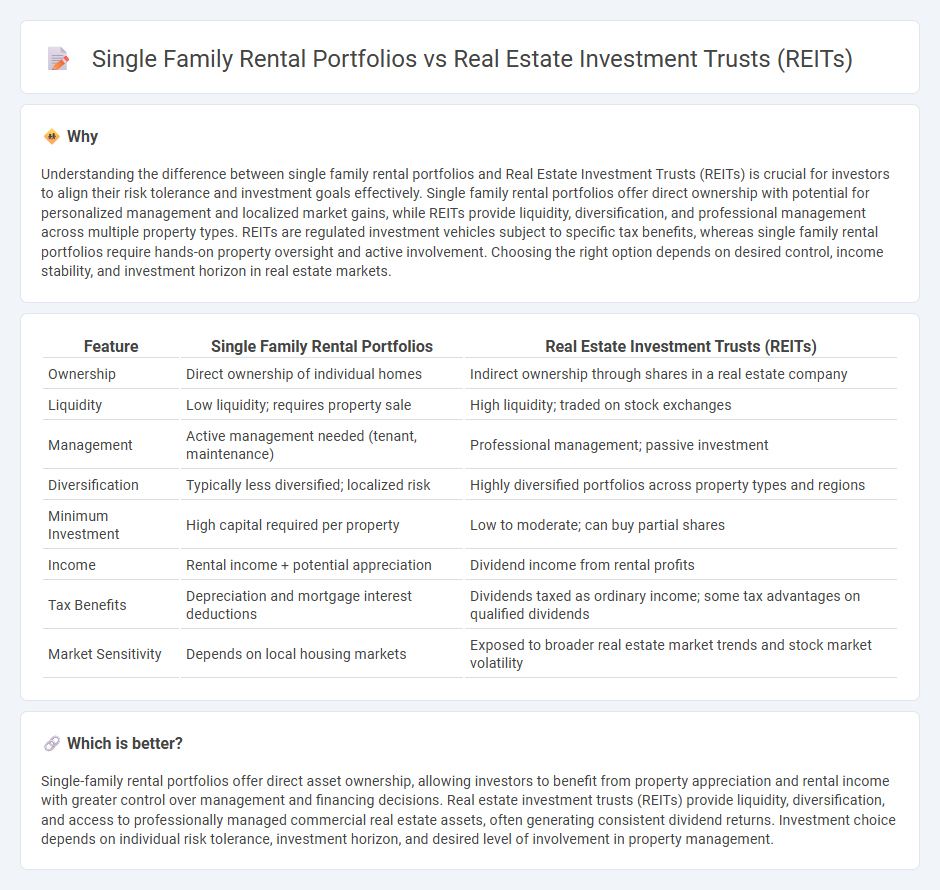
Understanding the difference between single family rental portfolios and Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) is crucial for investors to align their risk tolerance and investment goals effectively. Single family rental portfolios offer direct ownership with potential for personalized management and localized market gains, while REITs provide liquidity, diversification, and professional management across multiple property types. REITs are regulated investment vehicles subject to specific tax benefits, whereas single family rental portfolios require hands-on property oversight and active involvement. Choosing the right option depends on desired control, income stability, and investment horizon in real estate markets.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Single Family Rental Portfolios | Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Direct ownership of individual homes | Indirect ownership through shares in a real estate company |
| Liquidity | Low liquidity; requires property sale | High liquidity; traded on stock exchanges |
| Management | Active management needed (tenant, maintenance) | Professional management; passive investment |
| Diversification | Typically less diversified; localized risk | Highly diversified portfolios across property types and regions |
| Minimum Investment | High capital required per property | Low to moderate; can buy partial shares |
| Income | Rental income + potential appreciation | Dividend income from rental profits |
| Tax Benefits | Depreciation and mortgage interest deductions | Dividends taxed as ordinary income; some tax advantages on qualified dividends |
| Market Sensitivity | Depends on local housing markets | Exposed to broader real estate market trends and stock market volatility |
Which is better?
Single-family rental portfolios offer direct asset ownership, allowing investors to benefit from property appreciation and rental income with greater control over management and financing decisions. Real estate investment trusts (REITs) provide liquidity, diversification, and access to professionally managed commercial real estate assets, often generating consistent dividend returns. Investment choice depends on individual risk tolerance, investment horizon, and desired level of involvement in property management.
Connection
Single family rental portfolios and Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) are connected through their shared focus on residential property investments, with REITs often acquiring and managing large-scale single family rental homes to generate steady rental income. REITs leverage economies of scale and professional management to enhance the value and cash flow potential of single family rental portfolios, providing investors with diversified exposure to the residential real estate market. This integration allows for efficient capital deployment, increased liquidity, and risk diversification in the real estate investment sector.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Real estate investment trusts (REITs) offer higher liquidity compared to single-family rental portfolios due to their public market listings, allowing investors to buy and sell shares easily on stock exchanges. Single-family rental portfolios, while providing direct ownership and potential tax benefits, often entail longer holding periods and less flexibility in cashing out assets quickly. Explore detailed comparisons on liquidity metrics and investment strategies to make informed decisions.
Diversification
Real estate investment trusts (REITs) offer investors access to diversified portfolios of income-generating properties across various sectors, which reduces the risk associated with single asset ownership. Single-family rental portfolios concentrate investment in residential properties within specific locations, potentially exposing investors to market fluctuations in those areas. Explore the advantages of diversification strategies to optimize your real estate investment goals.
Management structure
Real estate investment trusts (REITs) operate under a centralized management structure with professional teams handling acquisitions, leasing, and asset management across diverse property types, ensuring operational efficiencies and scalability. In contrast, single family rental portfolios often rely on decentralized management, where individual owners or small firms oversee property maintenance, tenant relations, and financial operations, which can lead to more personalized but less scalable management. Explore further to understand how these management differences impact investment returns and risk profiles.
Source and External Links
Real Estate Investment Trust - Wikipedia - A real estate investment trust (REIT) is a company that owns and operates income-producing real estate, offering benefits such as reduced taxes and regular income streams.
What's a REIT (Real Estate Investment Trust)? - Nareit - REITs are companies that own or finance income-producing real estate, providing investors with income streams and diversification.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) - Charles Schwab - REITs allow investors to participate in real estate markets through liquid stock exchange listings, offering high dividend yields due to special tax structures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com