Senior living cohabitation offers shared housing arrangements that emphasize social interaction and flexible lifestyle choices for older adults, often resulting in lower living costs and enhanced companionship. Age-restricted communities provide structured environments designed exclusively for residents aged 55 and above, featuring amenities tailored to senior needs and strict community guidelines to maintain age-related residency requirements. Explore the key differences and benefits of these senior living options to determine the best fit for you or your loved one.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between senior living cohabitation and age-restricted communities is crucial for making informed real estate decisions tailored to lifestyle, health needs, and legal regulations. Senior living cohabitation often involves shared housing with personalized care options, while age-restricted communities impose age limits and offer specific amenities designed for active older adults. Real estate investors and buyers benefit from recognizing these distinctions to align property features, market demand, and investment potential accurately. This knowledge also aids in navigating zoning laws and enhances the value proposition in senior housing markets.
Comparison Table
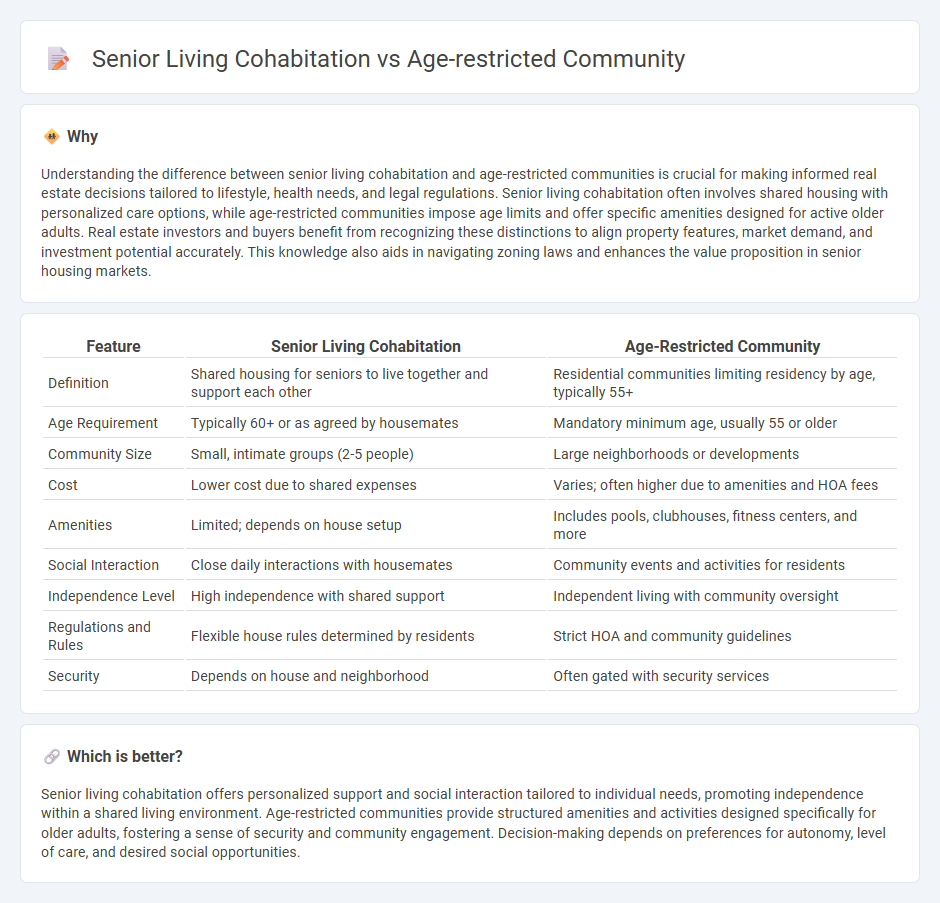
| Feature | Senior Living Cohabitation | Age-Restricted Community |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared housing for seniors to live together and support each other | Residential communities limiting residency by age, typically 55+ |
| Age Requirement | Typically 60+ or as agreed by housemates | Mandatory minimum age, usually 55 or older |
| Community Size | Small, intimate groups (2-5 people) | Large neighborhoods or developments |
| Cost | Lower cost due to shared expenses | Varies; often higher due to amenities and HOA fees |
| Amenities | Limited; depends on house setup | Includes pools, clubhouses, fitness centers, and more |
| Social Interaction | Close daily interactions with housemates | Community events and activities for residents |
| Independence Level | High independence with shared support | Independent living with community oversight |
| Regulations and Rules | Flexible house rules determined by residents | Strict HOA and community guidelines |
| Security | Depends on house and neighborhood | Often gated with security services |
Which is better?
Senior living cohabitation offers personalized support and social interaction tailored to individual needs, promoting independence within a shared living environment. Age-restricted communities provide structured amenities and activities designed specifically for older adults, fostering a sense of security and community engagement. Decision-making depends on preferences for autonomy, level of care, and desired social opportunities.
Connection
Senior living cohabitation and age-restricted communities share a focus on providing tailored housing solutions that promote social interaction and accessibility for older adults. Age-restricted communities often incorporate cohabitation models, such as shared living spaces or cooperative housing, to foster companionship and reduce isolation among seniors. Both concepts prioritize safety features, amenities, and services designed to enhance quality of life while addressing the unique needs of the aging population.
Key Terms
Age Restrictions
Age-restricted communities enforce strict age limits, typically requiring residents to be 55 years or older, ensuring a lifestyle tailored to active adults. Senior living cohabitation may accommodate various age groups but prioritizes services and support for elderly individuals, focusing less on rigid age policies. Discover the key differences and benefits of each living arrangement to make an informed decision.
Independent Living
Age-restricted communities specifically limit residency to individuals aged 55 and older, fostering a vibrant, age-similar environment with amenities tailored to independent lifestyles. Senior living cohabitation offers a broader range of options, often combining independent living with assisted services to accommodate varying levels of care needs. Explore the distinctions further to determine which independent living solution aligns best with your lifestyle preferences and care requirements.
Shared Housing
Age-restricted communities typically enforce minimum age limits, fostering social environments for adults 55+ or 62+, while senior living cohabitation emphasizes shared housing arrangements where older adults live together, sharing resources and companionship. Shared housing provides cost-effective, flexible living options with opportunities for mutual support, reducing isolation and enhancing quality of life. Explore more about how shared housing models are transforming senior living and fostering community connections.
Source and External Links
Age-restricted community - Age-restricted communities are residential areas that often have age limitations, typically requiring at least 80% of residents to be over a certain age, frequently 55 years old.
Are 55+ Communities Legal? - Age-restricted communities are legal if they meet specific requirements, including the 80/20 rule, clear designation as age-restricted, and age verification for residents.
Age-Restricted Communities - Age-restricted communities provide homes tailored for older adults, offering options like single-family homes, manufactured homes, and condominiums.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com