Modular homes offer customizable, factory-built construction with high durability and quicker build times compared to traditional homes, ideal for those seeking efficiency and scalability in real estate investment. Tiny homes emphasize minimalist living, cost-efficiency, and mobility, appealing to homeowners prioritizing affordability and environmental sustainability. Explore the key differences and benefits of modular and tiny homes to determine the best fit for your real estate goals.
Why it is important
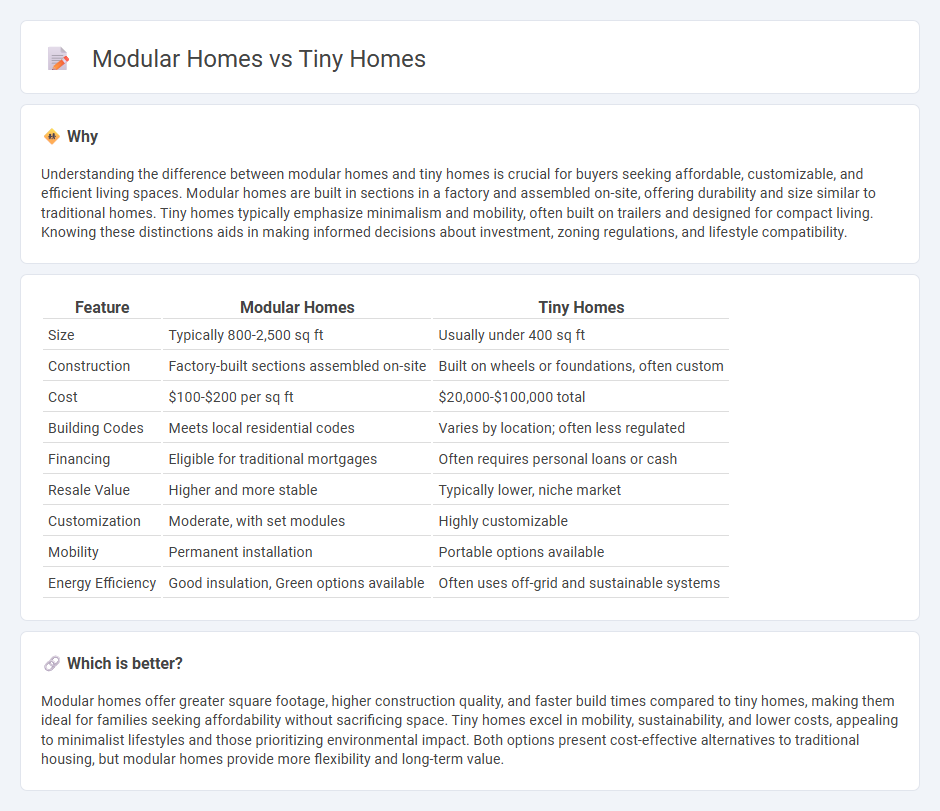
Understanding the difference between modular homes and tiny homes is crucial for buyers seeking affordable, customizable, and efficient living spaces. Modular homes are built in sections in a factory and assembled on-site, offering durability and size similar to traditional homes. Tiny homes typically emphasize minimalism and mobility, often built on trailers and designed for compact living. Knowing these distinctions aids in making informed decisions about investment, zoning regulations, and lifestyle compatibility.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Modular Homes | Tiny Homes |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Typically 800-2,500 sq ft | Usually under 400 sq ft |
| Construction | Factory-built sections assembled on-site | Built on wheels or foundations, often custom |
| Cost | $100-$200 per sq ft | $20,000-$100,000 total |
| Building Codes | Meets local residential codes | Varies by location; often less regulated |
| Financing | Eligible for traditional mortgages | Often requires personal loans or cash |
| Resale Value | Higher and more stable | Typically lower, niche market |
| Customization | Moderate, with set modules | Highly customizable |
| Mobility | Permanent installation | Portable options available |
| Energy Efficiency | Good insulation, Green options available | Often uses off-grid and sustainable systems |
Which is better?
Modular homes offer greater square footage, higher construction quality, and faster build times compared to tiny homes, making them ideal for families seeking affordability without sacrificing space. Tiny homes excel in mobility, sustainability, and lower costs, appealing to minimalist lifestyles and those prioritizing environmental impact. Both options present cost-effective alternatives to traditional housing, but modular homes provide more flexibility and long-term value.
Connection
Modular homes and tiny homes both emphasize efficient, cost-effective living with streamlined construction processes that reduce waste and build time. Modular homes are factory-built in sections and assembled on-site, allowing for customization and scalability, while tiny homes focus on compact, minimalistic design to maximize space within a smaller footprint. Both housing types appeal to eco-conscious buyers seeking sustainable, affordable alternatives to traditional real estate development.
Key Terms
Permanency
Tiny homes typically offer more flexibility in location and are often designed for temporary or semi-permanent living, emphasizing mobility and minimal land impact. Modular homes provide a permanent housing solution with higher structural standards, built in factory conditions and assembled on-site, ensuring durability and long-term stability. Discover more about the permanency aspects to choose the best option for your housing needs.
Building Codes
Tiny homes often face challenges with building codes because many municipalities classify them as recreational vehicles or accessory structures, limiting permanent residency options. Modular homes must comply with the same local building codes as traditional homes, ensuring higher standards for safety, insulation, and structural integrity. Explore deeper insights into how building codes impact the viability and legality of tiny vs. modular homes.
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations play a crucial role in determining where tiny homes and modular homes can be placed, often dictating minimum size requirements and land use restrictions. Tiny homes frequently face stricter zoning challenges due to their smaller footprint and classification as accessory structures, whereas modular homes are generally treated like traditional houses and benefit from more flexible zoning allowances. Explore more about how local zoning laws impact the feasibility of tiny versus modular home installations.
Source and External Links
Clever Tiny Homes - One of North America's largest tiny home builders offering high-quality, cost-efficient tiny homes with spacious designs including large windows and lofty ceilings, available as Tiny Homes on Wheels or ADUs on Foundations and shipped nationwide.
Incredible Tiny Homes - A builder focused on affordable, sustainable tiny homes designed for simplified lifestyles, with an emphasis on quality and customer guidance through their buying process.
Tumbleweed Tiny Homes For Sale - Offers certified green tiny homes with affordable monthly payments starting at $809, catering to diverse buyers across the U.S. with financing options and homes used for living, rentals, or business purposes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com