Vertical farming buildings maximize urban space by integrating advanced agricultural technology with sustainable architecture to produce fresh crops year-round while reducing food miles. Cultural centers foster community engagement and preserve local heritage through versatile event spaces that support arts, education, and social gatherings. Explore how these innovative real estate developments shape vibrant and resilient cities.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between vertical farming buildings and cultural centers is essential in real estate as it influences zoning regulations, property valuation, and land use planning. Vertical farming buildings optimize agricultural production within urban environments, requiring specialized infrastructure and sustainability considerations. Cultural centers focus on community engagement, arts, and social activities, affecting design and spatial requirements. Accurate knowledge informs investment decisions and maximizes property utility aligned with market demands.
Comparison Table
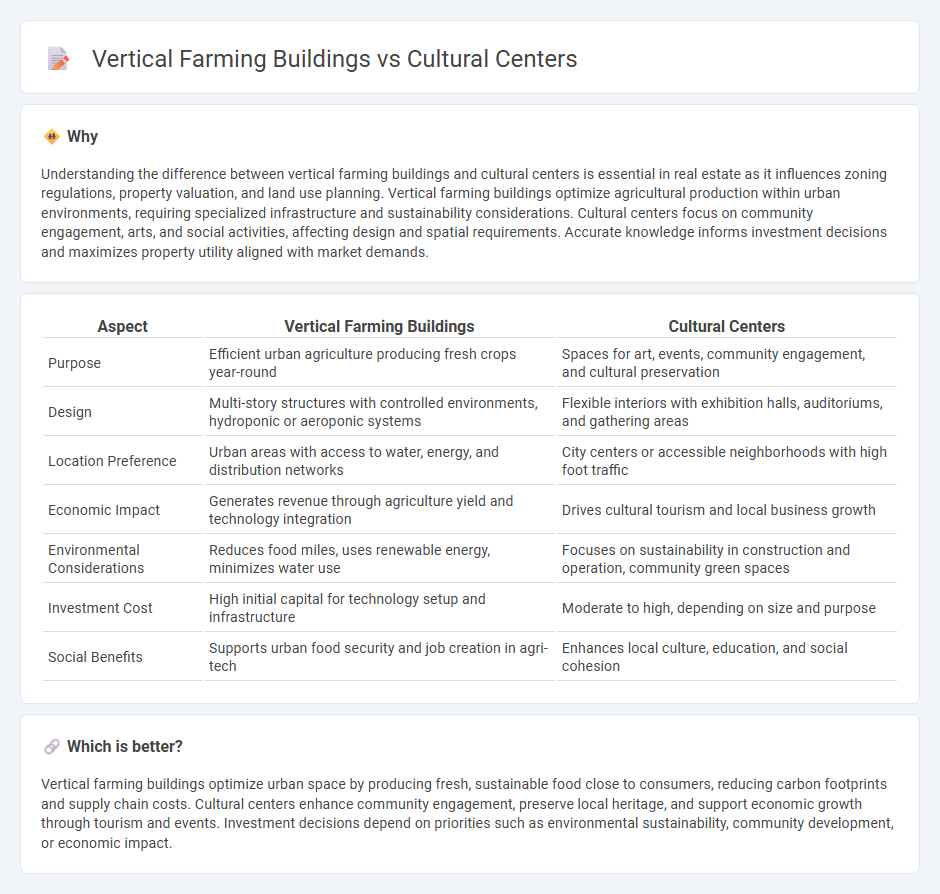
| Aspect | Vertical Farming Buildings | Cultural Centers |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Efficient urban agriculture producing fresh crops year-round | Spaces for art, events, community engagement, and cultural preservation |
| Design | Multi-story structures with controlled environments, hydroponic or aeroponic systems | Flexible interiors with exhibition halls, auditoriums, and gathering areas |
| Location Preference | Urban areas with access to water, energy, and distribution networks | City centers or accessible neighborhoods with high foot traffic |
| Economic Impact | Generates revenue through agriculture yield and technology integration | Drives cultural tourism and local business growth |
| Environmental Considerations | Reduces food miles, uses renewable energy, minimizes water use | Focuses on sustainability in construction and operation, community green spaces |
| Investment Cost | High initial capital for technology setup and infrastructure | Moderate to high, depending on size and purpose |
| Social Benefits | Supports urban food security and job creation in agri-tech | Enhances local culture, education, and social cohesion |
Which is better?
Vertical farming buildings optimize urban space by producing fresh, sustainable food close to consumers, reducing carbon footprints and supply chain costs. Cultural centers enhance community engagement, preserve local heritage, and support economic growth through tourism and events. Investment decisions depend on priorities such as environmental sustainability, community development, or economic impact.
Connection
Vertical farming buildings and cultural centers are connected through their shared role in urban revitalization and sustainable community development. By integrating vertical farms within cultural centers, cities maximize land use efficiency and promote local food production while fostering cultural engagement. This synergy supports environmental sustainability, economic growth, and social well-being in densely populated urban areas.
Key Terms
Zoning regulations
Zoning regulations play a crucial role in differentiating cultural centers and vertical farming buildings, as the former often falls under commercial or institutional zoning categories, while the latter typically requires agricultural or mixed-use zoning to accommodate specialized infrastructure and environmental controls. Cultural centers prioritize public accessibility and community engagement spaces, which influence zoning codes related to parking, noise, and public safety, whereas vertical farming buildings must adhere to regulations on light, water usage, and waste management to support sustainable urban agriculture. Explore the detailed zoning requirements for these distinct building types to understand how urban planning shapes their development and operational viability.
Community engagement
Cultural centers foster community engagement by providing inclusive spaces for art, education, and social interaction, often becoming local hubs of heritage and creativity. Vertical farming buildings, while primarily designed for sustainable agriculture, increasingly incorporate community gardens, workshops, and educational programs to connect urban residents with food production. Discover how these spaces uniquely enhance community bonds and urban life.
Adaptive reuse
Adaptive reuse transforms cultural centers and vertical farming buildings by repurposing existing structures to meet contemporary needs while preserving historical and architectural integrity. Cultural centers benefit from adaptive reuse by maintaining heritage and fostering community engagement, while vertical farming buildings optimize space and resources for sustainable urban agriculture. Explore how adaptive reuse bridges tradition and innovation in urban development.
Source and External Links
Cultural center - A cultural center is an organization or complex that promotes culture and arts, ranging from community arts organizations to government-sponsored institutions, with examples worldwide including the Bibliotheca Alexandrina in Egypt and the Perth Cultural Centre in Australia.
Cultural Centers at Purdue University - Purdue hosts several cultural centers such as the Asian American and Asian Resource and Cultural Center, Black Cultural Center, and Latino Cultural Center, each providing education, support, and cultural programming for their communities.
Indy Art Center - The Indy Art Center in Indianapolis is a vibrant hub for artistic expression and cultural enrichment, offering free public exhibitions and community-focused arts programs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com