Upzoning increases allowable building density in specific areas to encourage urban growth and housing supply, often leading to taller structures and mixed-use developments. Planned Unit Development (PUD) offers flexible land-use regulations that integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces under a customized zoning plan, enhancing community design and functionality. Explore how upzoning and PUDs shape modern urban landscapes and real estate investment opportunities.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between upzoning and planned unit development (PUD) is crucial for real estate investors to maximize property value and comply with local regulations. Upzoning allows for increased density or changes in land use, often leading to higher property values through expanded development potential. Planned Unit Development offers more flexible design standards and mixed-use opportunities, enabling tailored community planning and efficient land use. Recognizing these distinctions helps navigate zoning laws, optimize project feasibility, and enhance investment returns.
Comparison Table
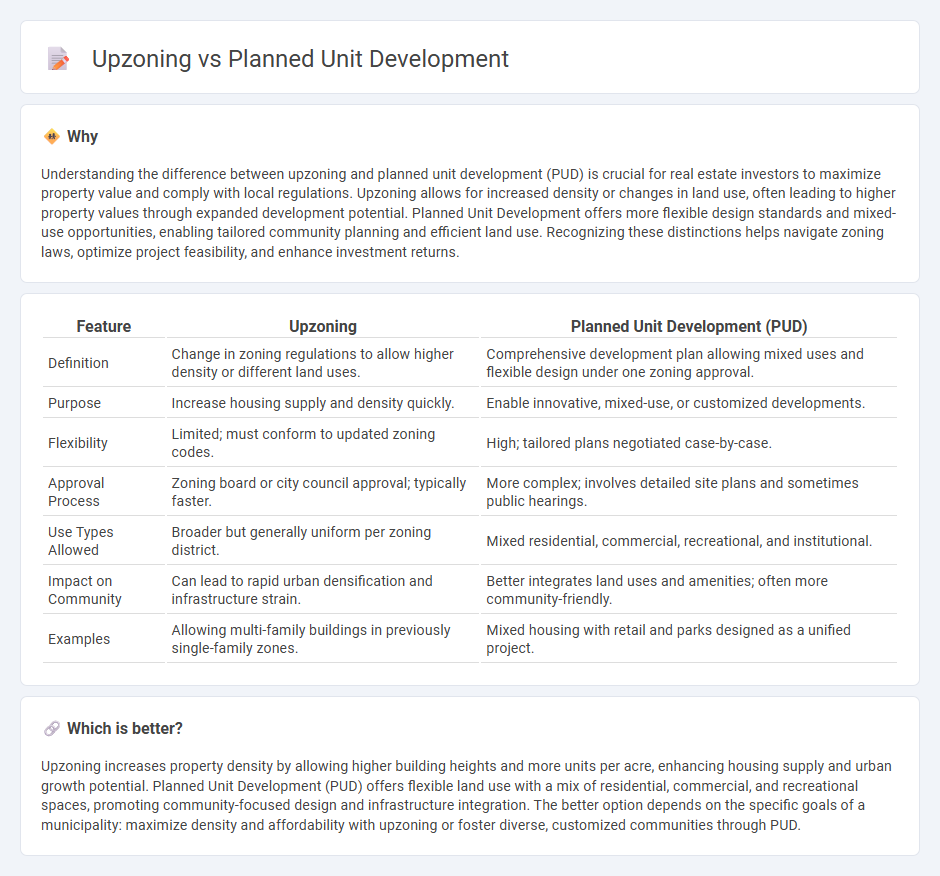
| Feature | Upzoning | Planned Unit Development (PUD) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Change in zoning regulations to allow higher density or different land uses. | Comprehensive development plan allowing mixed uses and flexible design under one zoning approval. |
| Purpose | Increase housing supply and density quickly. | Enable innovative, mixed-use, or customized developments. |
| Flexibility | Limited; must conform to updated zoning codes. | High; tailored plans negotiated case-by-case. |
| Approval Process | Zoning board or city council approval; typically faster. | More complex; involves detailed site plans and sometimes public hearings. |
| Use Types Allowed | Broader but generally uniform per zoning district. | Mixed residential, commercial, recreational, and institutional. |
| Impact on Community | Can lead to rapid urban densification and infrastructure strain. | Better integrates land uses and amenities; often more community-friendly. |
| Examples | Allowing multi-family buildings in previously single-family zones. | Mixed housing with retail and parks designed as a unified project. |
Which is better?
Upzoning increases property density by allowing higher building heights and more units per acre, enhancing housing supply and urban growth potential. Planned Unit Development (PUD) offers flexible land use with a mix of residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, promoting community-focused design and infrastructure integration. The better option depends on the specific goals of a municipality: maximize density and affordability with upzoning or foster diverse, customized communities through PUD.
Connection
Upzoning increases allowable building density or height, enabling developers to construct larger or more diverse projects within a given zoning district. Planned unit development (PUD) leverages upzoning by integrating mixed-use, residential, and commercial components in a flexible design framework that maximizes land use efficiency. Both tools work synergistically to promote higher-density, multifunctional urban environments that accommodate growth and enhance community amenities.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Planned Unit Development (PUD) offers flexible zoning regulations allowing mixed land uses and customized site planning to accommodate community needs, whereas upzoning primarily increases permitted density or building height within existing zoning districts. PUDs enable developers to deviate from standard zoning rules by negotiating design standards and land uses, often resulting in more integrated urban environments. Explore these zoning regulation strategies further to understand their implications for urban growth and development.
Density
Planned Unit Developments (PUDs) offer flexible zoning that allows for varied density within a single project by integrating residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, often resulting in higher density through clustered housing and mixed-use designs. Upzoning increases residential density by changing zoning laws to allow more units per acre, typically promoting taller buildings and more compact living spaces but with less design flexibility than PUDs. Explore the key differences in density management between PUDs and upzoning for better urban planning insights.
Land Use
Planned Unit Development (PUD) offers flexible land use by allowing developers to design cohesive communities with mixed uses, deviating from strict zoning codes to encourage innovation and integration. Upzoning increases allowable density or changes land use categories, enabling more intensive development such as taller buildings or multi-family housing but with less design flexibility than PUDs. Explore how both strategies can effectively optimize land use planning in urban development projects.
Source and External Links
Planned Unit Development - A Planned Unit Development (PUD) allows developers to bypass traditional zoning rules, creating mixed-use developments with flexibility in land use and building arrangements.
Planned Unit Developments (PUDs) | West Des Moines, IA - PUDs are used as an alternative zoning tool for creative and innovative developments that cannot be achieved under standard zoning regulations.
Planned unit development - A PUD is a flexible, non-Euclidean zoning strategy that facilitates mixed land uses, open spaces, and sustainable development within a defined area.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com