Vertical farming real estate maximizes urban agricultural space by integrating high-tech, sustainable farming systems within multi-story buildings, offering a transformative alternative to traditional office building usage. These innovative structures contribute to local food production, reduce supply chain costs, and minimize environmental impact compared to conventional office real estate. Explore how vertical farming real estate reshapes urban landscapes and investment opportunities.
Why it is important
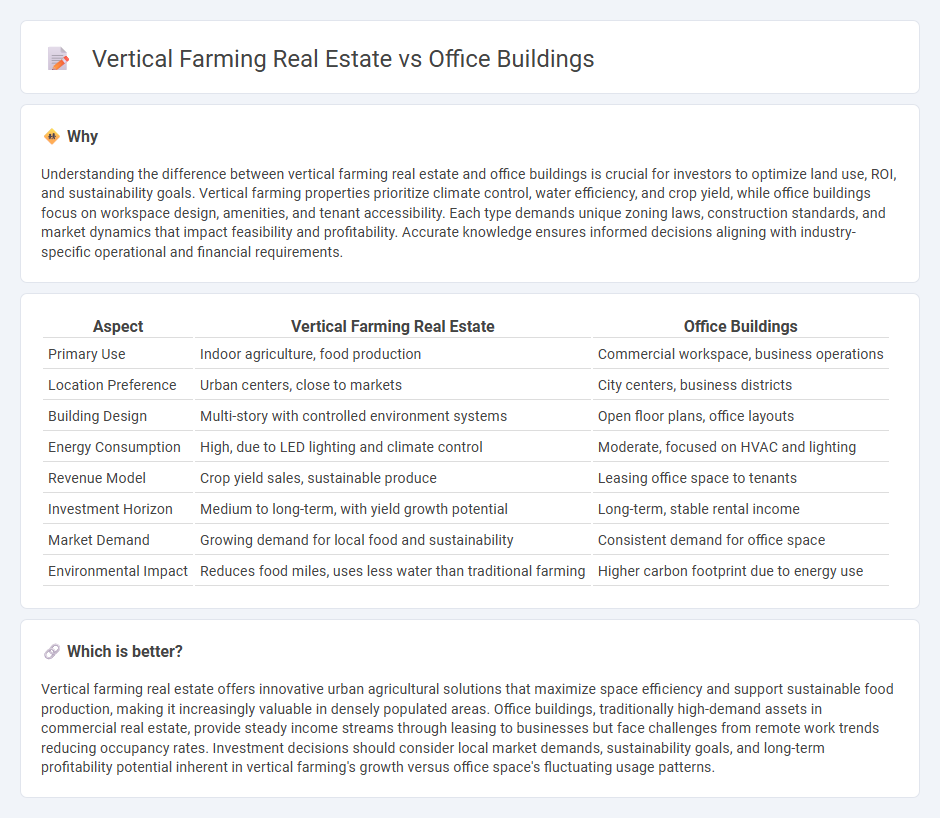
Understanding the difference between vertical farming real estate and office buildings is crucial for investors to optimize land use, ROI, and sustainability goals. Vertical farming properties prioritize climate control, water efficiency, and crop yield, while office buildings focus on workspace design, amenities, and tenant accessibility. Each type demands unique zoning laws, construction standards, and market dynamics that impact feasibility and profitability. Accurate knowledge ensures informed decisions aligning with industry-specific operational and financial requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Vertical Farming Real Estate | Office Buildings |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Indoor agriculture, food production | Commercial workspace, business operations |
| Location Preference | Urban centers, close to markets | City centers, business districts |
| Building Design | Multi-story with controlled environment systems | Open floor plans, office layouts |
| Energy Consumption | High, due to LED lighting and climate control | Moderate, focused on HVAC and lighting |
| Revenue Model | Crop yield sales, sustainable produce | Leasing office space to tenants |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long-term, with yield growth potential | Long-term, stable rental income |
| Market Demand | Growing demand for local food and sustainability | Consistent demand for office space |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces food miles, uses less water than traditional farming | Higher carbon footprint due to energy use |
Which is better?
Vertical farming real estate offers innovative urban agricultural solutions that maximize space efficiency and support sustainable food production, making it increasingly valuable in densely populated areas. Office buildings, traditionally high-demand assets in commercial real estate, provide steady income streams through leasing to businesses but face challenges from remote work trends reducing occupancy rates. Investment decisions should consider local market demands, sustainability goals, and long-term profitability potential inherent in vertical farming's growth versus office space's fluctuating usage patterns.
Connection
Vertical farming real estate integrates cutting-edge agricultural technology within multi-story office buildings, optimizing urban space usage for food production. These mixed-use developments enhance sustainability by reducing supply chain distances and promoting green infrastructure. Incorporating vertical farms into office buildings boosts energy efficiency, air quality, and employee well-being, driving innovative property value and urban resilience.
Key Terms
Zoning regulations
Zoning regulations distinctly affect office buildings and vertical farming real estate, with commercial zoning often favoring office developments due to established urban planning priorities. Vertical farming requires specialized zoning adaptations to integrate agriculture within urban environments, demanding allowances for water use, waste management, and artificial lighting. Explore more to understand how evolving zoning laws shape the future of urban real estate and sustainable agriculture.
Lease structures
Office buildings commonly utilize triple net leases where tenants cover property taxes, insurance, and maintenance, creating predictable expenses for landlords. Vertical farming real estate often features flexible lease structures that accommodate technology upgrades and variable utility costs, reflecting the unique operational demands. Explore detailed comparisons to optimize lease agreements tailored for vertical farming or office spaces.
Infrastructure requirements
Office buildings demand robust electrical systems, advanced HVAC for climate control, and extensive networking infrastructure to support daily business operations. Vertical farming real estate requires specialized infrastructure such as LED lighting, hydroponic or aeroponic systems, controlled environment agriculture (CEA) technology, and water recycling capabilities to optimize crop growth. Explore comprehensive insights on infrastructure needs for these distinct property types to enhance real estate investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Tampa, FL Office Space for Rent - Offers insights into the office space market in Tampa, including 154 buildings with over 31,931,990 square feet of office space.
Brandon, FL Office Space for Rent - Provides listings for office space rentals in Brandon, featuring various properties and their availability.
Brandon, FL Office Space for Lease - Lists numerous office spaces available for lease in Brandon, including options for coworking and traditional office rentals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com