Single family rental portfolios comprise residential properties designed for individual households, offering stable income with lower tenant turnover and simplified property management. Mixed-use property portfolios integrate residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial spaces, providing diversified revenue streams and potential for higher returns amid variable market demands. Explore the advantages and challenges of both portfolio types to determine the ideal real estate investment strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between single-family rental portfolios and mixed-use property portfolios is crucial for investors to tailor risk management and return expectations accurately. Single-family rentals typically offer steady cash flow with lower tenant turnover, while mixed-use properties combine residential and commercial tenants, potentially increasing income diversity but also operational complexity. This knowledge helps in optimizing portfolio diversification, aligning investment strategies with market trends, and maximizing long-term asset value. Recognizing these differences is essential for effective financial planning and property management in real estate investments.
Comparison Table
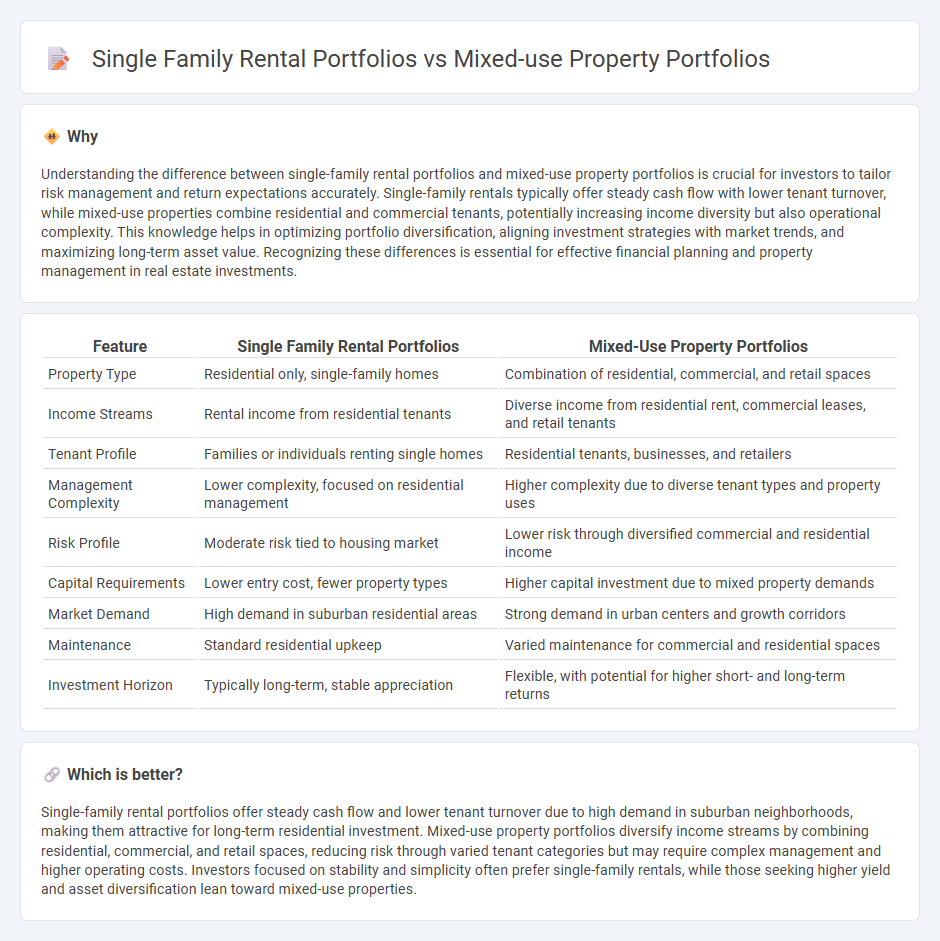
| Feature | Single Family Rental Portfolios | Mixed-Use Property Portfolios |
|---|---|---|
| Property Type | Residential only, single-family homes | Combination of residential, commercial, and retail spaces |
| Income Streams | Rental income from residential tenants | Diverse income from residential rent, commercial leases, and retail tenants |
| Tenant Profile | Families or individuals renting single homes | Residential tenants, businesses, and retailers |
| Management Complexity | Lower complexity, focused on residential management | Higher complexity due to diverse tenant types and property uses |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk tied to housing market | Lower risk through diversified commercial and residential income |
| Capital Requirements | Lower entry cost, fewer property types | Higher capital investment due to mixed property demands |
| Market Demand | High demand in suburban residential areas | Strong demand in urban centers and growth corridors |
| Maintenance | Standard residential upkeep | Varied maintenance for commercial and residential spaces |
| Investment Horizon | Typically long-term, stable appreciation | Flexible, with potential for higher short- and long-term returns |
Which is better?
Single-family rental portfolios offer steady cash flow and lower tenant turnover due to high demand in suburban neighborhoods, making them attractive for long-term residential investment. Mixed-use property portfolios diversify income streams by combining residential, commercial, and retail spaces, reducing risk through varied tenant categories but may require complex management and higher operating costs. Investors focused on stability and simplicity often prefer single-family rentals, while those seeking higher yield and asset diversification lean toward mixed-use properties.
Connection
Single family rental portfolios and mixed-use property portfolios are connected through their shared investment strategies aimed at diversifying income streams and mitigating market risks. Both portfolio types leverage residential components to provide stable cash flow while mixed-use properties integrate commercial spaces that enhance overall asset value and portfolio resilience. Investors often blend these assets to optimize returns by capitalizing on different demand drivers and occupancy trends within the real estate market.
Key Terms
Diversification
Mixed-use property portfolios offer enhanced diversification by combining residential, commercial, and retail spaces, reducing dependency on a single market segment. Single-family rental portfolios, while providing stable income through residential demand, are more susceptible to neighborhood-specific risks and limited cash flow sources. Explore how strategic diversification in mixed-use properties can optimize portfolio resilience and growth potential.
Cash Flow Stability
Mixed-use property portfolios provide diversified income streams by combining residential, commercial, and retail tenants, which enhances cash flow stability and reduces vacancy risks. Single-family rental portfolios often experience variable cash flows influenced by local market dynamics and tenant turnover but offer predictable, steady income in stable neighborhoods. Explore detailed analyses to understand how each portfolio type impacts long-term cash flow stability and investment performance.
Asset Management Complexity
Mixed-use property portfolios encompass residential, commercial, and retail spaces, requiring intricate asset management strategies to address diverse tenant needs, variable lease structures, and distinct maintenance schedules. Single-family rental portfolios offer more uniform management due to standardized property types and tenant agreements but may lack diversification benefits. Explore further to understand how asset management complexities impact investment performance in these portfolio types.
Source and External Links
Mixed Use Real Estate Investing | Marsh & Partners - Mixed-use properties combine retail, office, entertainment, and residential spaces in one development, offering high portfolio diversification and tax benefits, while often outperforming other property types during downturns due to the sense of community they foster.
Why You Should Invest in Mixed-Use Property - Val-Chris Investments - Mixed-use properties include types like Main Street (retail below, residential above), Live and Work spaces, Office with Residential units, and Mixed-Use Hotels, integrating commercial and residential uses to generate business and community engagement.
Investing in Mixed Use Property: Benefits and Insights | MRI Software - Mixed-use developments are growing globally, combining residential, commercial, and retail spaces to meet tenant demand for convenience and sustainability, while allowing landlords to diversify income and build vibrant communities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com