House hacking involves living in a property while renting out portions to cover mortgage costs, offering financial benefits and easier entry into real estate investing. Landlording focuses on owning rental properties solely for generating passive income, with responsibilities including tenant management and property maintenance. Discover more about the advantages and challenges of house hacking versus landlording to find the best strategy for your real estate goals.
Why it is important
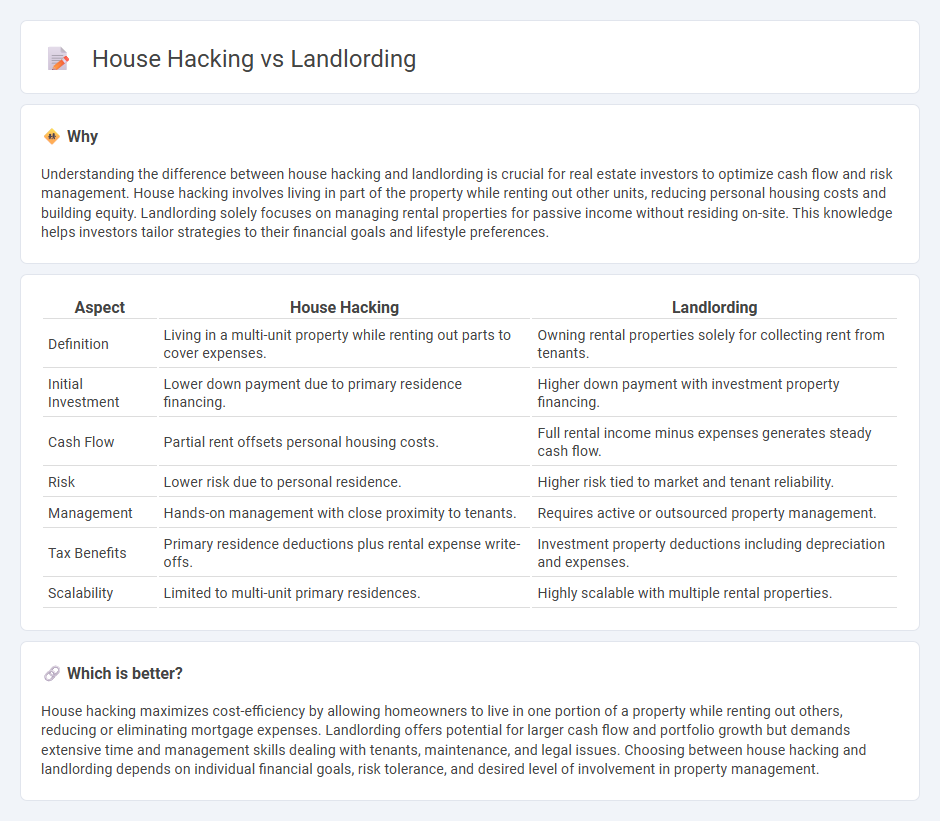
Understanding the difference between house hacking and landlording is crucial for real estate investors to optimize cash flow and risk management. House hacking involves living in part of the property while renting out other units, reducing personal housing costs and building equity. Landlording solely focuses on managing rental properties for passive income without residing on-site. This knowledge helps investors tailor strategies to their financial goals and lifestyle preferences.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | House Hacking | Landlording |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Living in a multi-unit property while renting out parts to cover expenses. | Owning rental properties solely for collecting rent from tenants. |
| Initial Investment | Lower down payment due to primary residence financing. | Higher down payment with investment property financing. |
| Cash Flow | Partial rent offsets personal housing costs. | Full rental income minus expenses generates steady cash flow. |
| Risk | Lower risk due to personal residence. | Higher risk tied to market and tenant reliability. |
| Management | Hands-on management with close proximity to tenants. | Requires active or outsourced property management. |
| Tax Benefits | Primary residence deductions plus rental expense write-offs. | Investment property deductions including depreciation and expenses. |
| Scalability | Limited to multi-unit primary residences. | Highly scalable with multiple rental properties. |
Which is better?
House hacking maximizes cost-efficiency by allowing homeowners to live in one portion of a property while renting out others, reducing or eliminating mortgage expenses. Landlording offers potential for larger cash flow and portfolio growth but demands extensive time and management skills dealing with tenants, maintenance, and legal issues. Choosing between house hacking and landlording depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and desired level of involvement in property management.
Connection
House hacking involves living in a property while renting out portions to generate income, effectively lowering personal housing costs and building equity. Landlording extends this concept by managing rental properties exclusively for income, requiring skills in tenant management and property maintenance. Both strategies leverage real estate investment to create passive income streams and build wealth through property ownership.
Key Terms
Passive Income
Landlording generates passive income by renting out entire properties, requiring property management skills and tenant oversight. House hacking involves living in one unit while renting out others, which reduces personal housing costs and builds equity simultaneously. Discover detailed strategies to maximize passive income through landlording and house hacking now.
Owner-Occupied
Owner-occupied strategies emphasize maximizing property use by residing in one unit while leveraging rental income from others; house hacking typically involves this approach within multi-unit dwellings or single-family homes with rentable spaces. Landlording strictly refers to managing rental properties without the owner's residence, often requiring more hands-on management and offering unique tax benefits different from owner-occupied investments. Explore detailed comparisons and financial implications to determine the best fit for your investment goals.
Rental Property
Landlording involves owning rental properties and managing tenants to generate consistent income, whereas house hacking typically means living in one part of a property while renting out other sections to offset living expenses. Rental properties as a landlording strategy require active management skills, including tenant screening, maintenance, and lease agreements. Explore more to understand which approach suits your investment goals and lifestyle best.
Source and External Links
Landlording 101 - This webpage provides a comprehensive guide to managing rental properties, including leasing processes and the importance of outsourcing certain tasks.
5 Do's and Don'ts of Landlording - Offers tips on how to avoid common mistakes when owning and operating rental properties, emphasizing the need for thorough preparation and understanding of the process.
Basics of Landlording - Provides resources and advice to help protect rental property investments by understanding relevant laws, avoiding legal disputes, and maintaining good tenant relationships.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com