Dynamic pricing in real estate adjusts property prices in real-time based on demand, supply, and market trends, optimizing revenue and occupancy rates. Market-based pricing relies on comparable sales and current market conditions to set property values more traditionally and steadily. Discover how these pricing strategies can impact your investment returns and property management by exploring their differences in depth.
Why it is important
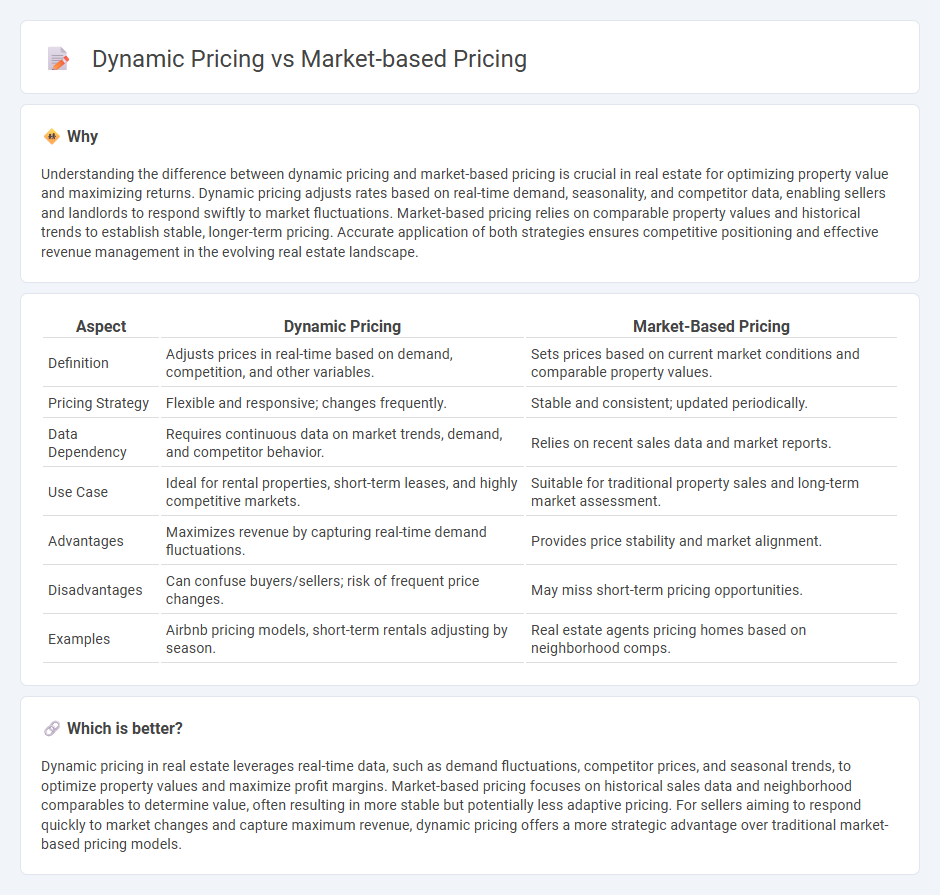
Understanding the difference between dynamic pricing and market-based pricing is crucial in real estate for optimizing property value and maximizing returns. Dynamic pricing adjusts rates based on real-time demand, seasonality, and competitor data, enabling sellers and landlords to respond swiftly to market fluctuations. Market-based pricing relies on comparable property values and historical trends to establish stable, longer-term pricing. Accurate application of both strategies ensures competitive positioning and effective revenue management in the evolving real estate landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dynamic Pricing | Market-Based Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjusts prices in real-time based on demand, competition, and other variables. | Sets prices based on current market conditions and comparable property values. |
| Pricing Strategy | Flexible and responsive; changes frequently. | Stable and consistent; updated periodically. |
| Data Dependency | Requires continuous data on market trends, demand, and competitor behavior. | Relies on recent sales data and market reports. |
| Use Case | Ideal for rental properties, short-term leases, and highly competitive markets. | Suitable for traditional property sales and long-term market assessment. |
| Advantages | Maximizes revenue by capturing real-time demand fluctuations. | Provides price stability and market alignment. |
| Disadvantages | Can confuse buyers/sellers; risk of frequent price changes. | May miss short-term pricing opportunities. |
| Examples | Airbnb pricing models, short-term rentals adjusting by season. | Real estate agents pricing homes based on neighborhood comps. |
Which is better?
Dynamic pricing in real estate leverages real-time data, such as demand fluctuations, competitor prices, and seasonal trends, to optimize property values and maximize profit margins. Market-based pricing focuses on historical sales data and neighborhood comparables to determine value, often resulting in more stable but potentially less adaptive pricing. For sellers aiming to respond quickly to market changes and capture maximum revenue, dynamic pricing offers a more strategic advantage over traditional market-based pricing models.
Connection
Dynamic pricing in real estate leverages real-time market data to adjust property prices based on demand fluctuations, inventory levels, and competitor pricing. Market-based pricing reflects these ongoing changes by setting property values aligned with current supply and buyer interest, ensuring competitive positioning. Both strategies depend on continuous data analysis to optimize pricing for maximum profitability and faster sales in fluctuating markets.
Key Terms
Comparative Market Analysis (CMA)
Market-based pricing relies on Comparative Market Analysis (CMA) to evaluate competitors' pricing structures, ensuring a business sets prices aligned with current market trends and demands. Dynamic pricing, on the other hand, adjusts prices in real-time based on factors such as customer behavior, inventory levels, and competitor activity, often utilizing advanced algorithms beyond traditional CMA. Explore these strategies deeper to understand how CMA impacts pricing decisions in fluctuating markets.
Real-time Data Analytics
Market-based pricing relies on competitor prices and market demand to set product values, while dynamic pricing uses real-time data analytics to adjust prices instantly based on consumer behavior, inventory levels, and external factors. Real-time data analytics enables businesses to capture granular insights, such as customer browsing patterns and purchase history, allowing for flexible, responsive pricing strategies that maximize revenue and market competitiveness. Explore how integrating advanced analytics can transform your pricing approach and drive higher profitability.
Demand-Supply Fluctuation
Market-based pricing adjusts prices based on prevailing market conditions and competitor pricing, reflecting the overall supply and demand balance. Dynamic pricing continuously modifies prices in real-time according to fluctuations in demand and supply, often using advanced algorithms and data analytics for immediate response. Explore how businesses leverage these strategies to maximize revenue and adapt to market changes.
Source and External Links
Market-based pricing definition - Market-based pricing is the strategy of setting prices closely aligned to current market prices of similar products, allowing for higher or lower prices depending on product differentiation, quality perception, product life cycle stage, and branding efforts.
Pricing Strategy Examples and Guide: Cost-Based Pricing - Market-based pricing incorporates competitor pricing and market conditions, commonly used in commodity markets, but may overlook buyer willingness to pay and can face data reliability issues.
What Is Market Pricing? Definition, Advantages and Tips - Market pricing sets prices relative to competitors' prices and consumer expectations, with three approaches: matching market prices, pricing below market to attract budget buyers, or pricing above market for differentiated or prestige products.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com