Tiny house communities prioritize compact, affordable living spaces that foster a sense of community and sustainability through minimal environmental impact. Eco-villages emphasize holistic, self-sufficient lifestyles with renewable energy, organic agriculture, and communal decision-making to promote environmental harmony. Explore the distinctive benefits and values of tiny house communities and eco-villages to find the best fit for your sustainable living goals.
Why it is important
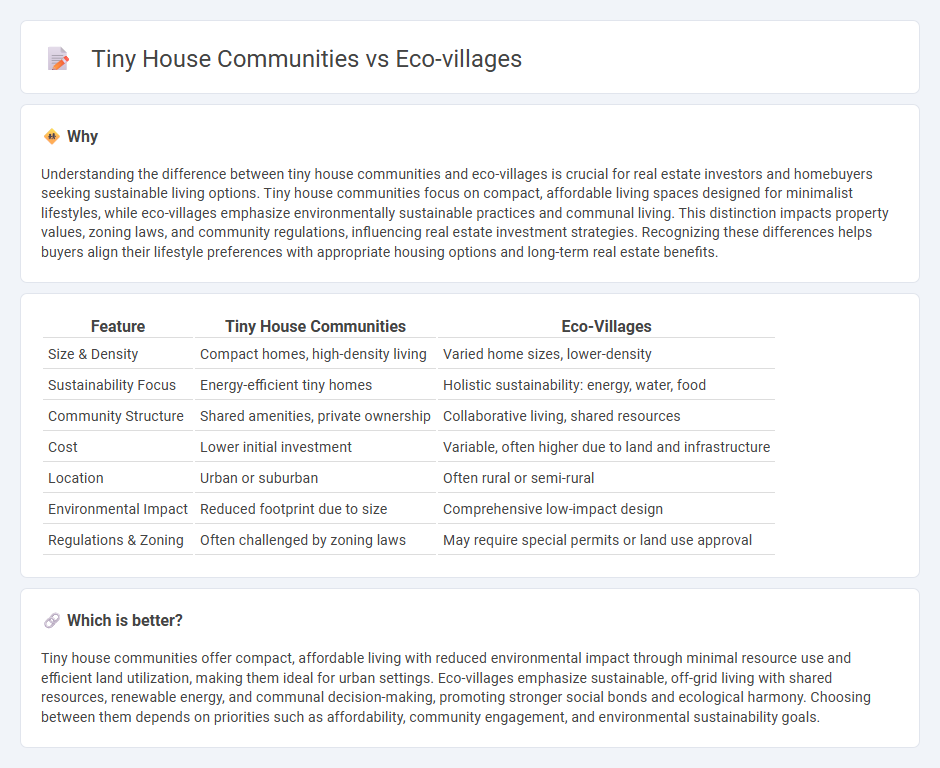
Understanding the difference between tiny house communities and eco-villages is crucial for real estate investors and homebuyers seeking sustainable living options. Tiny house communities focus on compact, affordable living spaces designed for minimalist lifestyles, while eco-villages emphasize environmentally sustainable practices and communal living. This distinction impacts property values, zoning laws, and community regulations, influencing real estate investment strategies. Recognizing these differences helps buyers align their lifestyle preferences with appropriate housing options and long-term real estate benefits.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tiny House Communities | Eco-Villages |
|---|---|---|
| Size & Density | Compact homes, high-density living | Varied home sizes, lower-density |
| Sustainability Focus | Energy-efficient tiny homes | Holistic sustainability: energy, water, food |
| Community Structure | Shared amenities, private ownership | Collaborative living, shared resources |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Variable, often higher due to land and infrastructure |
| Location | Urban or suburban | Often rural or semi-rural |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced footprint due to size | Comprehensive low-impact design |
| Regulations & Zoning | Often challenged by zoning laws | May require special permits or land use approval |
Which is better?
Tiny house communities offer compact, affordable living with reduced environmental impact through minimal resource use and efficient land utilization, making them ideal for urban settings. Eco-villages emphasize sustainable, off-grid living with shared resources, renewable energy, and communal decision-making, promoting stronger social bonds and ecological harmony. Choosing between them depends on priorities such as affordability, community engagement, and environmental sustainability goals.
Connection
Tiny house communities and eco-villages are interconnected through their shared focus on sustainable living, minimal environmental impact, and communal resource management. Both models emphasize compact, energy-efficient housing designs that reduce carbon footprints while fostering strong social cohesion among residents. Integration of renewable energy sources, permaculture gardening, and waste reduction systems highlight their commitment to ecological responsibility within real estate development.
Key Terms
Sustainable Infrastructure
Eco-villages emphasize holistic sustainable infrastructure integrating renewable energy systems, permaculture agriculture, and waste recycling technology to create self-sufficient living environments. Tiny house communities prioritize compact, energy-efficient homes with minimalist resource use, often incorporating solar panels and rainwater harvesting to reduce ecological footprints. Discover how these innovative models reshape sustainable living by exploring their unique infrastructure strategies.
Zoning Regulations
Eco-villages often face complex zoning regulations due to their larger scale and intentional community structures, which can include shared resources and communal spaces, while tiny house communities typically navigate zoning laws related to minimum dwelling sizes and land use density. Understanding how local governments classify residential zones and their adaptability to non-traditional housing models is crucial for successful development. Explore detailed zoning insights to assess feasibility and compliance for both eco-villages and tiny house communities.
Community Governance
Eco-villages implement participatory community governance models emphasizing consensus decision-making and sustainable living practices, ensuring equal stakeholder involvement. Tiny house communities often adopt flexible governance structures, such as homeowner associations or cooperative models, focusing on cost-efficiency and personal autonomy. Explore the distinctive governance frameworks of eco-villages and tiny house communities to better understand their impact on communal living.
Source and External Links
Ecovillages From Around the World for Sustainable Living - Earth.Org - Ecovillages are intentional or traditional communities aiming to be socially, culturally, ecologically, and economically sustainable, minimizing environmental and social impacts while fostering local participation, with more than 1,100 such villages worldwide.
5 of the World's Coolest EcoVillages - The World Economic Forum - Findhorn EcoVillage in Scotland exemplifies an ecovillage with low ecological footprint, sustainable architecture, renewable energy, and community programs promoting sustainability, aiming for carbon neutrality by 2030.
Ecovillage - Wikipedia - Ecovillages prioritize sustainability via renewable energy, organic farming, green building, and alternative transport, while fostering strong social bonds through collaboration, consensus, and shared responsibilities for resilient, sustainable living.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com