Modular construction offers efficient, factory-built components assembled on-site, enabling faster completion and higher quality control compared to traditional methods. Tiny homes maximize space with minimal square footage, appealing to those seeking affordability and sustainable living options. Explore the benefits and differences of modular construction and tiny homes to determine which fits your real estate goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between modular construction and tiny homes is crucial for real estate investors seeking efficient property development options. Modular construction offers scalable and customizable building solutions with faster completion times, while tiny homes emphasize minimalistic living and cost efficiency on a smaller scale. Real estate professionals benefit from knowing these distinctions to accurately appraise properties, forecast market trends, and advise clients on investment potential. This knowledge supports optimized decision-making in residential and commercial property acquisitions or developments.
Comparison Table
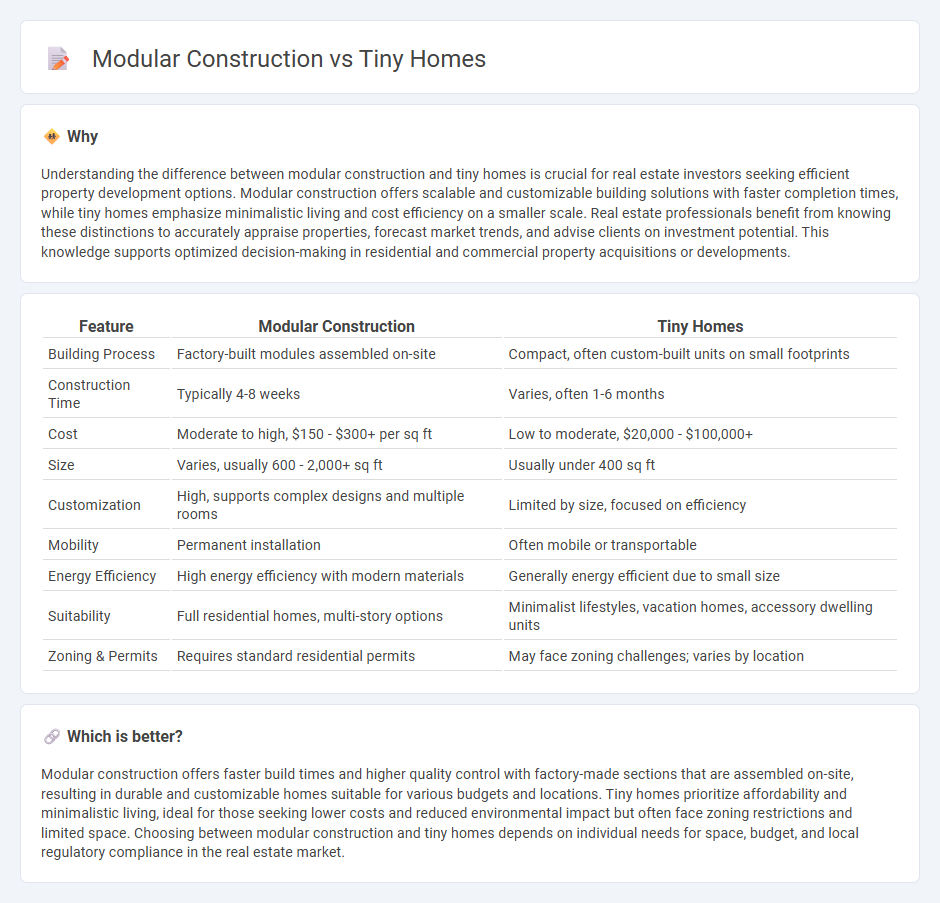
| Feature | Modular Construction | Tiny Homes |
|---|---|---|
| Building Process | Factory-built modules assembled on-site | Compact, often custom-built units on small footprints |
| Construction Time | Typically 4-8 weeks | Varies, often 1-6 months |
| Cost | Moderate to high, $150 - $300+ per sq ft | Low to moderate, $20,000 - $100,000+ |
| Size | Varies, usually 600 - 2,000+ sq ft | Usually under 400 sq ft |
| Customization | High, supports complex designs and multiple rooms | Limited by size, focused on efficiency |
| Mobility | Permanent installation | Often mobile or transportable |
| Energy Efficiency | High energy efficiency with modern materials | Generally energy efficient due to small size |
| Suitability | Full residential homes, multi-story options | Minimalist lifestyles, vacation homes, accessory dwelling units |
| Zoning & Permits | Requires standard residential permits | May face zoning challenges; varies by location |
Which is better?
Modular construction offers faster build times and higher quality control with factory-made sections that are assembled on-site, resulting in durable and customizable homes suitable for various budgets and locations. Tiny homes prioritize affordability and minimalistic living, ideal for those seeking lower costs and reduced environmental impact but often face zoning restrictions and limited space. Choosing between modular construction and tiny homes depends on individual needs for space, budget, and local regulatory compliance in the real estate market.
Connection
Modular construction and tiny homes are connected through their emphasis on efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability in real estate development. Modular construction uses prefabricated sections to streamline building processes, significantly reducing construction time and waste, which aligns perfectly with the compact, resource-efficient design of tiny homes. This synergy enables the rapid delivery of affordable, eco-friendly housing options, addressing urban space constraints and increasing market accessibility.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations significantly impact the feasibility of tiny homes and modular construction, with many municipalities imposing strict minimum size requirements that often exclude tiny homes. Modular construction benefits from traditional building codes and zoning laws more readily, allowing greater flexibility in residential development. Explore comprehensive zoning guidelines to understand how local policies shape the adoption of these housing alternatives.
Building Codes
Building codes for tiny homes often vary significantly by location, with many jurisdictions imposing restrictions on minimum square footage, foundation requirements, and utility connections. Modular construction typically adheres to stringent building codes similar to traditional homes, ensuring compliance with safety, structural integrity, and energy efficiency standards. Explore further to understand how building code differences impact the planning and approval process for tiny homes versus modular construction.
Permanence of Structure
Tiny homes typically offer limited permanence, often designed for mobility or temporary placement, with foundations that may not meet traditional building codes. Modular construction provides a more permanent structural solution, with factory-built modules assembled on-site, ensuring compliance with local regulations and greater durability. Explore how permanence impacts investment and lifestyle choices in both tiny homes and modular buildings.
Source and External Links
Father Builds Ultra-Affordable Tiny Home for Himself and His Daughter - Shane built a sustainable, off-grid tiny home for himself and his daughter using salvaged materials and DIY methods for just AUD$35,000, incorporating solar passive design and meaningful personal touches.
Clever Tiny Homes - High-end. Not high-cost - Clever Tiny Homes is a major North American manufacturer offering thoughtfully designed, high-quality tiny homes with modern amenities, available as mobile Tiny Homes on Wheels or modular ADUs on foundations, and shipping nationwide.
Our Modern Tiny Home & in a Tiny House Community - The Akinpelu family documents their transition into a minimalist 300 sq ft tiny home within a tiny house village, highlighting the sense of community, affordability, and the practicalities of downsized urban living.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com