Smart contracts utilize blockchain technology to automate real estate transactions, reducing the need for traditional legal intermediaries such as lawyers and escrow agents. These digital agreements enhance transparency, decrease transaction costs, and speed up property transfers by executing terms automatically when predefined conditions are met. Explore how smart contracts are transforming real estate processes and reshaping the role of legal professionals.
Why it is important
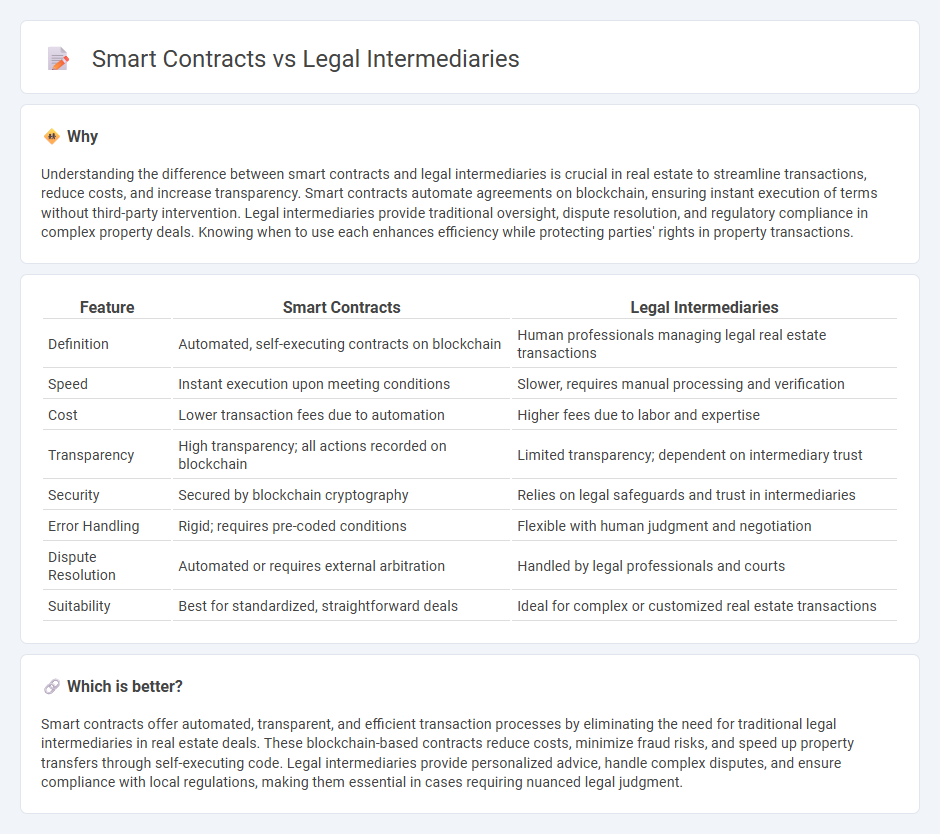
Understanding the difference between smart contracts and legal intermediaries is crucial in real estate to streamline transactions, reduce costs, and increase transparency. Smart contracts automate agreements on blockchain, ensuring instant execution of terms without third-party intervention. Legal intermediaries provide traditional oversight, dispute resolution, and regulatory compliance in complex property deals. Knowing when to use each enhances efficiency while protecting parties' rights in property transactions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Contracts | Legal Intermediaries |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated, self-executing contracts on blockchain | Human professionals managing legal real estate transactions |
| Speed | Instant execution upon meeting conditions | Slower, requires manual processing and verification |
| Cost | Lower transaction fees due to automation | Higher fees due to labor and expertise |
| Transparency | High transparency; all actions recorded on blockchain | Limited transparency; dependent on intermediary trust |
| Security | Secured by blockchain cryptography | Relies on legal safeguards and trust in intermediaries |
| Error Handling | Rigid; requires pre-coded conditions | Flexible with human judgment and negotiation |
| Dispute Resolution | Automated or requires external arbitration | Handled by legal professionals and courts |
| Suitability | Best for standardized, straightforward deals | Ideal for complex or customized real estate transactions |
Which is better?
Smart contracts offer automated, transparent, and efficient transaction processes by eliminating the need for traditional legal intermediaries in real estate deals. These blockchain-based contracts reduce costs, minimize fraud risks, and speed up property transfers through self-executing code. Legal intermediaries provide personalized advice, handle complex disputes, and ensure compliance with local regulations, making them essential in cases requiring nuanced legal judgment.
Connection
Smart contracts automate real estate transactions by securely executing agreements based on predefined conditions, reducing the need for traditional legal intermediaries. Legal intermediaries still play a crucial role in verifying contract validity, overseeing compliance, and resolving disputes to ensure enforceability within regulatory frameworks. Integrating smart contracts with legal oversight enhances transaction efficiency while maintaining legal integrity in real estate deals.
Key Terms
Escrow
Legal intermediaries in escrow services manage funds or assets between parties to ensure contract fulfillment, relying on trusted third parties like lawyers or financial institutions. Smart contracts automate escrow processes through blockchain technology, enabling secure, transparent transactions without intermediaries by executing predefined conditions. Explore how smart contracts revolutionize escrow by reducing costs and enhancing security.
Notary
Legal intermediaries such as notaries play a critical role in authenticating and certifying documents, ensuring compliance with jurisdictional laws and providing trust in transactions. Smart contracts automate contract execution using blockchain technology, offering efficiency, transparency, and immutability but often lack human judgment in nuanced legal contexts. Explore how the interplay between notarial services and smart contracts is reshaping legal frameworks and transactional security.
Blockchain
Legal intermediaries traditionally facilitate contract enforcement by verifying identities, managing trust, and resolving disputes, but they often incur higher costs and slower processes. Smart contracts on blockchain automate contract execution through self-executing code, offering transparency, immutability, and reduced reliance on third parties. Explore how blockchain technology is transforming contract law and reshaping the future of legal agreements.
Source and External Links
The Emergence of Lay Intermediaries Furnishing Legal Services - This article discusses the emergence of lay intermediaries in legal services, traditionally prohibited but now re-evaluated under First Amendment freedoms.
Intermediary - In law, intermediaries can facilitate communication between vulnerable parties and the court, while in other contexts, they act as brokers or agents.
Intermediaries | CFTC - This webpage details intermediaries in futures, swaps, or options trading, requiring registration and compliance with various financial regulations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com