Co-living spaces offer shared amenities and communal living designed to foster social interaction, appealing primarily to young professionals and students in urban areas. Multifamily housing consists of separate residential units within one building or complex, catering to families seeking privacy and long-term residence. Explore the key differences and benefits of co-living versus multifamily housing to determine the best fit for your lifestyle and investment goals.
Why it is important
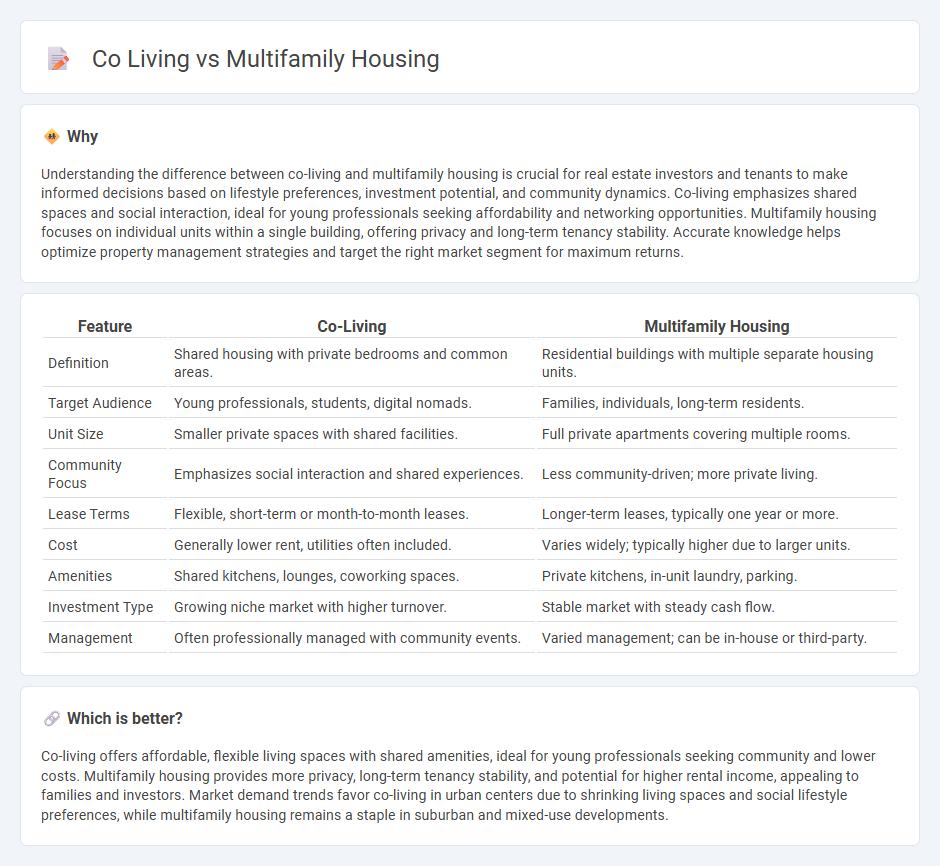
Understanding the difference between co-living and multifamily housing is crucial for real estate investors and tenants to make informed decisions based on lifestyle preferences, investment potential, and community dynamics. Co-living emphasizes shared spaces and social interaction, ideal for young professionals seeking affordability and networking opportunities. Multifamily housing focuses on individual units within a single building, offering privacy and long-term tenancy stability. Accurate knowledge helps optimize property management strategies and target the right market segment for maximum returns.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Co-Living | Multifamily Housing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared housing with private bedrooms and common areas. | Residential buildings with multiple separate housing units. |
| Target Audience | Young professionals, students, digital nomads. | Families, individuals, long-term residents. |
| Unit Size | Smaller private spaces with shared facilities. | Full private apartments covering multiple rooms. |
| Community Focus | Emphasizes social interaction and shared experiences. | Less community-driven; more private living. |
| Lease Terms | Flexible, short-term or month-to-month leases. | Longer-term leases, typically one year or more. |
| Cost | Generally lower rent, utilities often included. | Varies widely; typically higher due to larger units. |
| Amenities | Shared kitchens, lounges, coworking spaces. | Private kitchens, in-unit laundry, parking. |
| Investment Type | Growing niche market with higher turnover. | Stable market with steady cash flow. |
| Management | Often professionally managed with community events. | Varied management; can be in-house or third-party. |
Which is better?
Co-living offers affordable, flexible living spaces with shared amenities, ideal for young professionals seeking community and lower costs. Multifamily housing provides more privacy, long-term tenancy stability, and potential for higher rental income, appealing to families and investors. Market demand trends favor co-living in urban centers due to shrinking living spaces and social lifestyle preferences, while multifamily housing remains a staple in suburban and mixed-use developments.
Connection
Co-living and multifamily housing share a focus on maximizing residential density while offering communal living spaces that foster social interaction and cost efficiency. Both models leverage shared amenities and common areas to create affordable and flexible housing solutions, appealing to urban professionals and millennials seeking community-oriented environments. The integration of co-living within multifamily buildings enhances utilization rates and addresses growing demands for affordable urban housing options.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Multifamily housing typically involves individual ownership of separate units within a larger building, enabling residents to own their apartments and share common areas, while co-living arrangements often feature collective ownership or leasing with shared responsibilities and communal living spaces. Ownership structures in multifamily housing emphasize legal property rights and investment opportunities, contrasting with co-living's flexible, community-driven tenancy models prioritizing social interaction. Explore further to understand how ownership impacts lifestyle choices and financial commitments in these housing models.
Lease Agreements
Multifamily housing lease agreements typically involve long-term, individual contracts for separate units, offering tenants stability and defined responsibilities. In contrast, co-living lease agreements often feature flexible terms with shared living spaces and collective responsibilities, promoting community interaction. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which lease structure best suits your lifestyle and legal needs.
Shared Amenities
Multifamily housing typically offers private living spaces complemented by community amenities such as gyms, pools, and laundry facilities that enhance residents' convenience while maintaining personal privacy. Co-living spaces emphasize maximized shared amenities like communal kitchens, coworking areas, and social lounges designed to foster interaction and collaboration among residents. Explore how these differing approaches to shared amenities impact lifestyle and community dynamics.
Source and External Links
Multifamily residential - Wikipedia - Multifamily residential housing refers to buildings or complexes containing multiple separate housing units for different households, such as apartment buildings and condominiums, often stacked or side-by-side, with a history dating back to ancient urban centers like Rome.
Multifamily Homes: Types and Trends | NAHB - About 31.4% of U.S. residences are multifamily, including apartments, condominiums, and townhouses, with current trends focusing on smart, healthy, and environmentally conscious amenities.
What is multifamily housing and what are the benefits? - Multifamily housing comprises properties with multiple households living simultaneously and offers affordability and risk reduction benefits, making it popular among first-time buyers and investors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com