Accessory dwelling units (ADUs) offer homeowners a flexible way to increase property value and rental income by adding secondary living spaces on single-family lots. Fourplexes, consisting of four separate units in one building, provide higher rental yields and greater investment potential in multi-family housing markets. Explore the differences between ADUs and fourplexes to determine the best real estate strategy for your investment goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) and Fourplexes is crucial for real estate investors because ADUs are secondary housing units on single-family lots, typically enhancing property value and rental income with lower construction costs. Fourplexes are multi-family buildings with four separate units, offering higher rental yields and economies of scale but requiring greater investment and property management. Knowing these distinctions helps investors optimize zoning compliance, financing options, and target market strategies. Accurate knowledge ensures maximizing return on investment while adhering to local building regulations and community planning goals.
Comparison Table
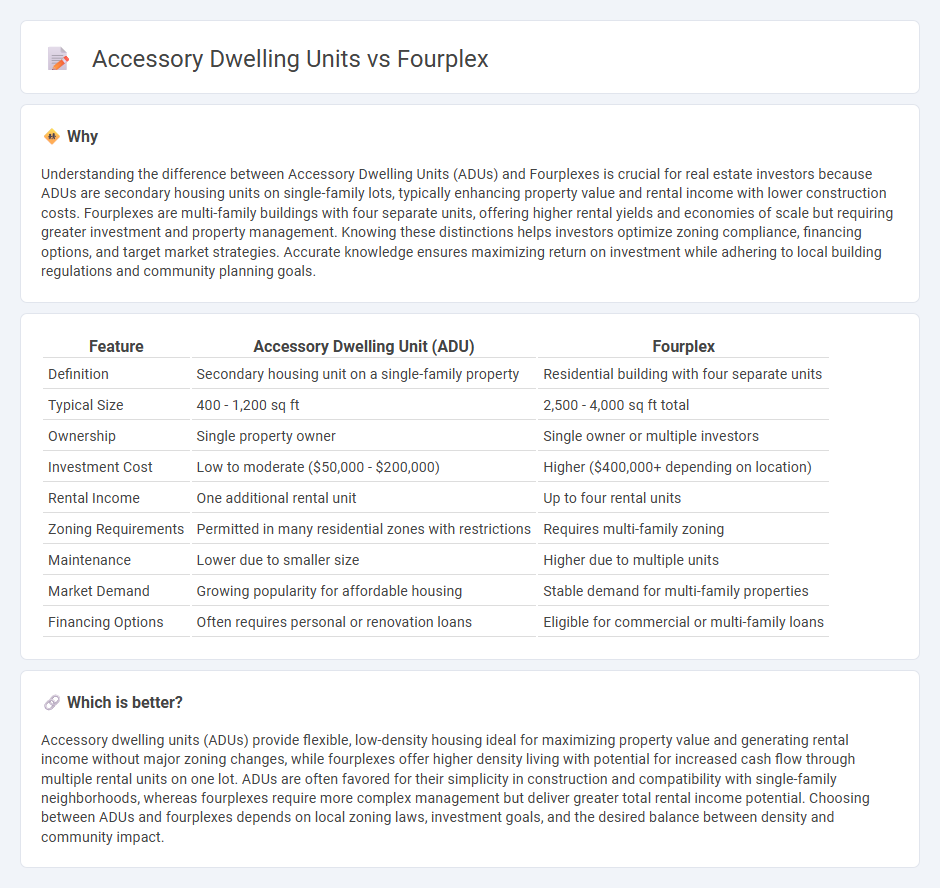
| Feature | Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU) | Fourplex |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Secondary housing unit on a single-family property | Residential building with four separate units |
| Typical Size | 400 - 1,200 sq ft | 2,500 - 4,000 sq ft total |
| Ownership | Single property owner | Single owner or multiple investors |
| Investment Cost | Low to moderate ($50,000 - $200,000) | Higher ($400,000+ depending on location) |
| Rental Income | One additional rental unit | Up to four rental units |
| Zoning Requirements | Permitted in many residential zones with restrictions | Requires multi-family zoning |
| Maintenance | Lower due to smaller size | Higher due to multiple units |
| Market Demand | Growing popularity for affordable housing | Stable demand for multi-family properties |
| Financing Options | Often requires personal or renovation loans | Eligible for commercial or multi-family loans |
Which is better?
Accessory dwelling units (ADUs) provide flexible, low-density housing ideal for maximizing property value and generating rental income without major zoning changes, while fourplexes offer higher density living with potential for increased cash flow through multiple rental units on one lot. ADUs are often favored for their simplicity in construction and compatibility with single-family neighborhoods, whereas fourplexes require more complex management but deliver greater total rental income potential. Choosing between ADUs and fourplexes depends on local zoning laws, investment goals, and the desired balance between density and community impact.
Connection
Accessory dwelling units (ADUs) and fourplexes both contribute to increasing urban housing density by maximizing the use of existing residential properties. ADUs provide affordable, compact living spaces on single-family lots, while fourplexes offer multiple distinct units within one structure, supporting diverse housing options in multifamily zoning areas. Both solutions address housing shortages and promote efficient land use in growing metropolitan regions.
Key Terms
Zoning regulations
Zoning regulations for fourplexes typically vary by municipality with many urban areas permitting higher density residential use, while accessory dwelling units (ADUs) often face more lenient zoning standards allowing them as secondary units on single-family lots. Fourplex zoning frequently requires multifamily residential designations, minimum lot sizes, and parking mandates, whereas ADUs benefit from relaxed setback rules and streamlined approval processes in many regions. Explore local zoning codes and ordinances to understand how these regulations impact development opportunities and maximize property value.
Property value
Fourplex properties typically generate higher overall rental income due to multiple separate units, significantly boosting property value through increased cash flow and investment appeal. Accessory dwelling units (ADUs), while offering less total rental income, enhance property value by providing flexible living spaces and making properties more attractive to a broader range of buyers seeking additional housing options. Explore detailed comparisons and market impact analysis to understand which property type maximizes your investment returns.
Rental income potential
Fourplex properties generate higher rental income by offering four separate units, maximizing occupancy and cash flow compared to accessory dwelling units (ADUs) that typically provide one additional rental space. ADUs are advantageous in markets with stringent zoning laws or where single-family homes dominate, offering flexible, smaller-scale rental income opportunities. Explore our detailed analysis to understand which property type aligns best with your investment goals and rental income potential.
Source and External Links
Fourplex House Plans - This webpage provides information on fourplex house plans and how they can be used to maximize rental income.
What Is a Fourplex? Pros and Cons Explained - This article discusses the features and benefits of living in a fourplex, including affordability and community aspects.
Guide to Fourplexes: The Pros and Cons of Owning a Fourplex - This guide outlines the advantages and disadvantages of owning a fourplex, focusing on cash flow potential and financing options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com