Upzoning increases allowable building density, enabling taller structures and more units, which can boost housing supply in urban areas. Form-based codes focus on regulating building form and design to create predictable streetscapes and maintain neighborhood character, rather than solely controlling land use. Explore how these zoning strategies impact urban development and community growth.
Why it is important
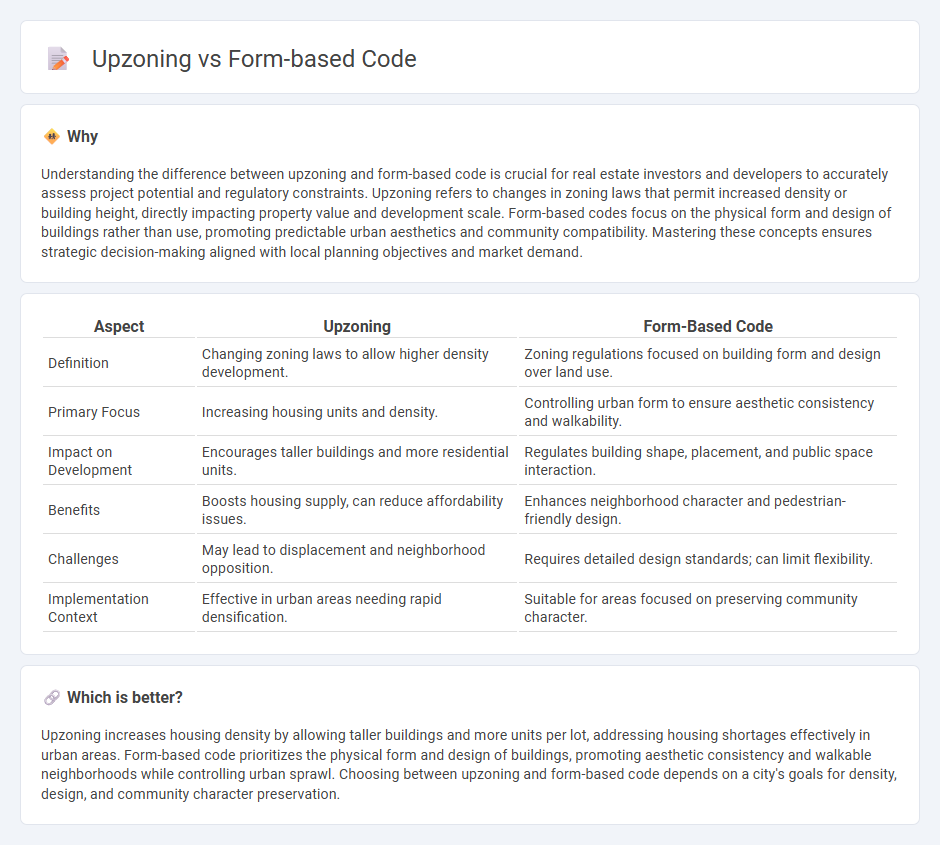
Understanding the difference between upzoning and form-based code is crucial for real estate investors and developers to accurately assess project potential and regulatory constraints. Upzoning refers to changes in zoning laws that permit increased density or building height, directly impacting property value and development scale. Form-based codes focus on the physical form and design of buildings rather than use, promoting predictable urban aesthetics and community compatibility. Mastering these concepts ensures strategic decision-making aligned with local planning objectives and market demand.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Upzoning | Form-Based Code |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Changing zoning laws to allow higher density development. | Zoning regulations focused on building form and design over land use. |
| Primary Focus | Increasing housing units and density. | Controlling urban form to ensure aesthetic consistency and walkability. |
| Impact on Development | Encourages taller buildings and more residential units. | Regulates building shape, placement, and public space interaction. |
| Benefits | Boosts housing supply, can reduce affordability issues. | Enhances neighborhood character and pedestrian-friendly design. |
| Challenges | May lead to displacement and neighborhood opposition. | Requires detailed design standards; can limit flexibility. |
| Implementation Context | Effective in urban areas needing rapid densification. | Suitable for areas focused on preserving community character. |
Which is better?
Upzoning increases housing density by allowing taller buildings and more units per lot, addressing housing shortages effectively in urban areas. Form-based code prioritizes the physical form and design of buildings, promoting aesthetic consistency and walkable neighborhoods while controlling urban sprawl. Choosing between upzoning and form-based code depends on a city's goals for density, design, and community character preservation.
Connection
Upzoning increases allowable building density and height, directly influencing the implementation of form-based codes that regulate architectural form, placement, and community design. Form-based codes provide clear, visually-oriented standards that guide developments within upzoned areas to create cohesive urban environments. This connection enhances land use efficiency while preserving neighborhood character and promoting walkability in real estate projects.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Form-based codes regulate urban design by specifying building form, placement, and appearance to create predictable streetscapes, emphasizing physical character over land use. Upzoning increases allowable density and building height, promoting higher population capacity and mixed-use development but often with less control over aesthetic outcomes. Explore how these zoning regulations impact community development and urban planning strategies in more detail.
Land Use
Form-based code regulates land use by emphasizing physical form and design standards, ensuring predictable urban character and mixed-use development. Upzoning increases allowable building density and land use intensity, often promoting higher residential or commercial capacity without detailed design guidelines. Explore more to understand their impacts on sustainable urban growth and zoning strategies.
Density
Form-based code emphasizes physical building form and streetscape design to achieve predictable urban density, controlling height, bulk, and placement rather than just allowable uses. Upzoning increases density primarily by permitting higher building heights or floor area ratios (FAR), often leading to taller structures with greater dwelling or commercial units on the same lot. Explore more to understand how these zoning strategies impact urban density and community character.
Source and External Links
6 Reasons Your City Needs a Form-Based Code - This article discusses the benefits of form-based codes for cities, focusing on their ability to create a high-quality public realm and foster a mix of activities in neighborhoods.
Form-Based Code - A form-based code is a type of land development regulation that emphasizes physical form over the separation of uses, aiming to create cohesive and walkable neighborhoods.
Form-Based Code Development - This page outlines Arlington's approach to form-based code development, focusing on creating vibrant destinations with mixed uses and preserving urban character.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com