Adaptive reuse properties transform existing buildings into new functional spaces, maximizing resource efficiency and preserving architectural heritage. Brownfield redevelopment focuses on cleaning and repurposing previously contaminated industrial or commercial sites, mitigating environmental risks while revitalizing urban areas. Explore more to understand which strategy best suits your real estate investment goals.
Why it is important
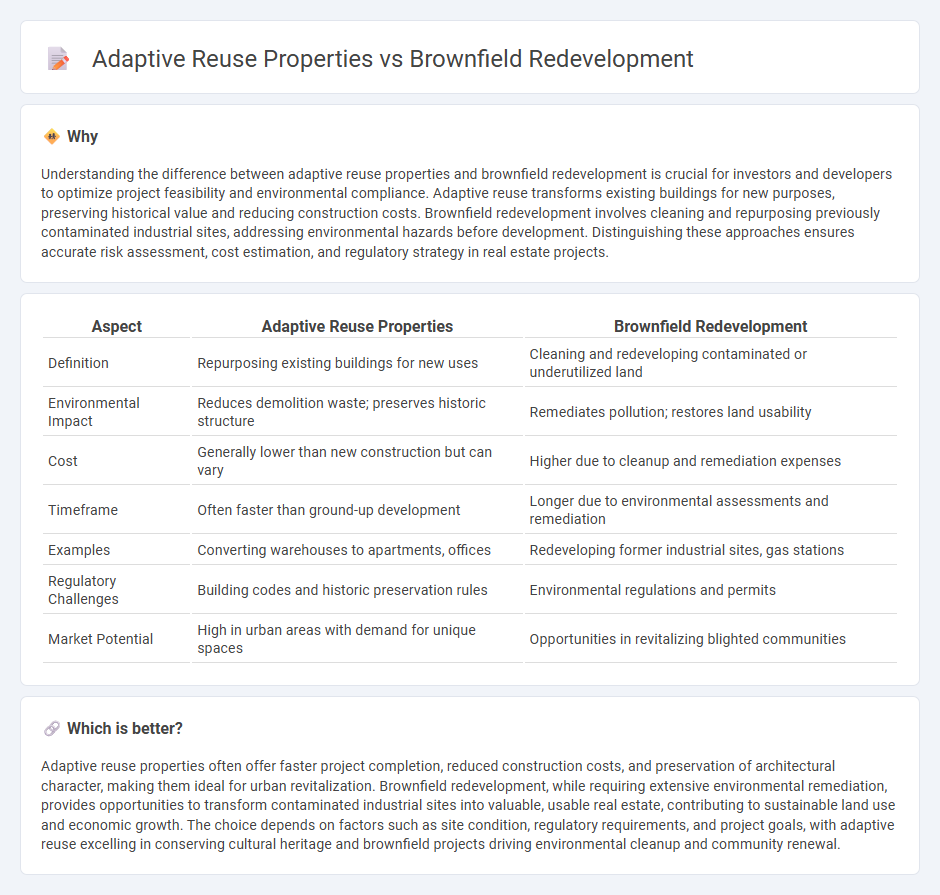
Understanding the difference between adaptive reuse properties and brownfield redevelopment is crucial for investors and developers to optimize project feasibility and environmental compliance. Adaptive reuse transforms existing buildings for new purposes, preserving historical value and reducing construction costs. Brownfield redevelopment involves cleaning and repurposing previously contaminated industrial sites, addressing environmental hazards before development. Distinguishing these approaches ensures accurate risk assessment, cost estimation, and regulatory strategy in real estate projects.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Adaptive Reuse Properties | Brownfield Redevelopment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repurposing existing buildings for new uses | Cleaning and redeveloping contaminated or underutilized land |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces demolition waste; preserves historic structure | Remediates pollution; restores land usability |
| Cost | Generally lower than new construction but can vary | Higher due to cleanup and remediation expenses |
| Timeframe | Often faster than ground-up development | Longer due to environmental assessments and remediation |
| Examples | Converting warehouses to apartments, offices | Redeveloping former industrial sites, gas stations |
| Regulatory Challenges | Building codes and historic preservation rules | Environmental regulations and permits |
| Market Potential | High in urban areas with demand for unique spaces | Opportunities in revitalizing blighted communities |
Which is better?
Adaptive reuse properties often offer faster project completion, reduced construction costs, and preservation of architectural character, making them ideal for urban revitalization. Brownfield redevelopment, while requiring extensive environmental remediation, provides opportunities to transform contaminated industrial sites into valuable, usable real estate, contributing to sustainable land use and economic growth. The choice depends on factors such as site condition, regulatory requirements, and project goals, with adaptive reuse excelling in conserving cultural heritage and brownfield projects driving environmental cleanup and community renewal.
Connection
Adaptive reuse properties and brownfield redevelopment are interconnected through their shared focus on revitalizing underutilized or contaminated urban sites into functional real estate assets. Brownfield redevelopment transforms previously industrial or polluted land into safe, economically viable properties, which adaptive reuse further enhances by repurposing existing structures to meet modern needs. This synergy promotes sustainable urban development, reduces environmental impact, and preserves historical and architectural value in real estate markets.
Key Terms
Environmental Remediation
Brownfield redevelopment involves the cleanup and repurposing of previously contaminated industrial or commercial sites, requiring extensive environmental remediation to remove pollutants and ensure site safety. Adaptive reuse focuses on transforming existing structures for new purposes while addressing environmental concerns such as asbestos removal, lead paint abatement, and energy efficiency upgrades. Explore the differences in environmental remediation strategies to understand how each approach supports sustainable urban development.
Historic Preservation
Brownfield redevelopment involves the cleanup and repurposing of contaminated or underutilized industrial sites, often requiring environmental remediation to preserve historical elements while meeting modern safety standards. Adaptive reuse properties focus on transforming existing historic buildings for new purposes, maintaining architectural integrity and cultural heritage without major demolition. Explore more about how historic preservation shapes sustainable urban development through these revitalization techniques.
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations significantly impact brownfield redevelopment by often requiring environmental assessments and specific land use changes to address contamination and ensure safe reuse. Adaptive reuse projects must navigate zoning categories that may restrict alterations in building use or limit structural modifications, necessitating variances or rezoning applications. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how zoning nuances shape redevelopment opportunities for these property types.
Source and External Links
What is Brownfield Redevelopment? A Guide for Developers - This guide outlines the process and benefits of transforming abandoned or contaminated properties into productive spaces, including economic revitalization and community growth.
Smart Growth and Infill Brownfields Redevelopment | US EPA - This webpage discusses how brownfields can be redeveloped using smart growth strategies to create sustainable community assets and reduce development pressure on green spaces.
Brownfields | US EPA - The EPA provides grants and assistance for assessing, cleaning up, and reusing contaminated properties, aiming to revitalize communities through brownfield redevelopment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com