Sale leaseback and 1031 exchange are strategic real estate investment tools that maximize asset value and tax efficiency. Sale leaseback allows property owners to sell their asset while remaining tenants, freeing up capital and maintaining operational control. Explore these methods to optimize your real estate portfolio and understand which strategy aligns best with your financial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sale-leaseback and 1031 exchange is crucial for real estate investors to optimize tax benefits and improve cash flow strategies. Sale-leaseback allows property owners to sell their asset and simultaneously lease it back, freeing capital while maintaining operational control. A 1031 exchange enables deferral of capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds from a sold property into a like-kind property. Knowing these distinctions maximizes investment returns and aligns real estate decisions with financial goals.
Comparison Table
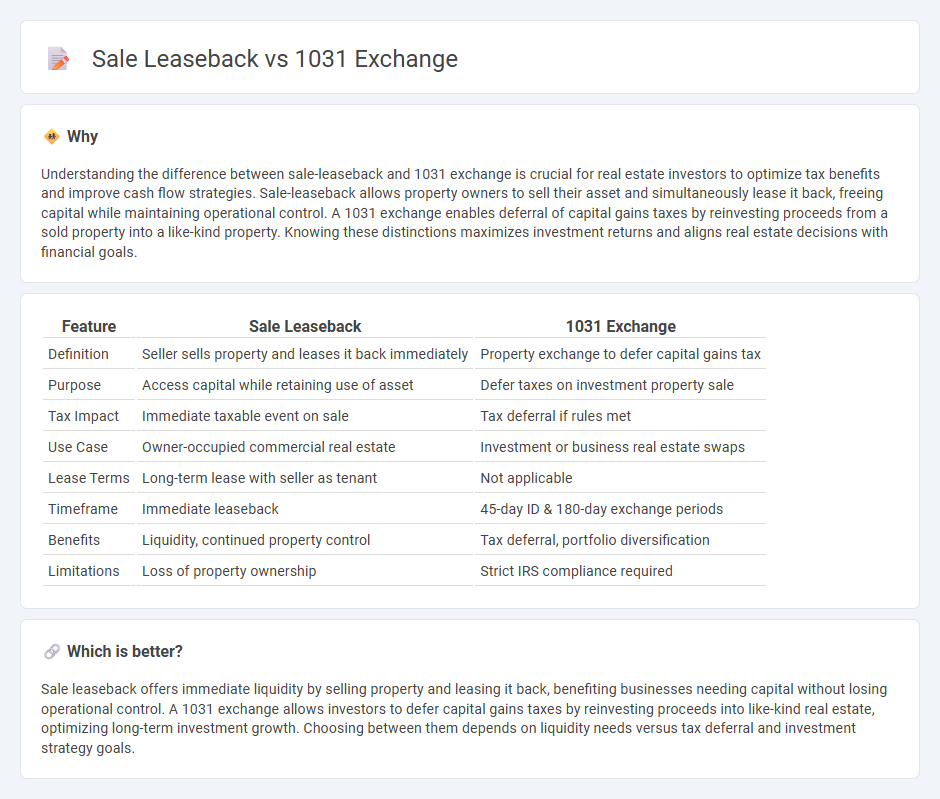
| Feature | Sale Leaseback | 1031 Exchange |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seller sells property and leases it back immediately | Property exchange to defer capital gains tax |
| Purpose | Access capital while retaining use of asset | Defer taxes on investment property sale |
| Tax Impact | Immediate taxable event on sale | Tax deferral if rules met |
| Use Case | Owner-occupied commercial real estate | Investment or business real estate swaps |
| Lease Terms | Long-term lease with seller as tenant | Not applicable |
| Timeframe | Immediate leaseback | 45-day ID & 180-day exchange periods |
| Benefits | Liquidity, continued property control | Tax deferral, portfolio diversification |
| Limitations | Loss of property ownership | Strict IRS compliance required |
Which is better?
Sale leaseback offers immediate liquidity by selling property and leasing it back, benefiting businesses needing capital without losing operational control. A 1031 exchange allows investors to defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds into like-kind real estate, optimizing long-term investment growth. Choosing between them depends on liquidity needs versus tax deferral and investment strategy goals.
Connection
Sale leaseback transactions and 1031 exchanges are connected through their use in real estate investment strategies to defer capital gains taxes. Both mechanisms enable property owners to optimize cash flow and reinvest proceeds without immediate tax liabilities, where sale leasebacks convert owned real estate into leased assets for operational liquidity. 1031 exchanges facilitate the exchange of like-kind properties to defer taxes while maintaining or increasing investment portfolios, enhancing flexibility in property management and capital allocation.
Key Terms
Capital Gains Tax
A 1031 exchange allows investors to defer Capital Gains Tax by reinvesting the proceeds from a property sale into a like-kind property, preserving investment capital and promoting portfolio growth. In contrast, a sale-leaseback transaction triggers immediate Capital Gains Tax liability, as the property is sold outright and leased back, offering liquidity but incurring tax consequences. Explore detailed strategies to optimize tax outcomes in real estate transactions.
Like-Kind Property
A 1031 exchange allows investors to defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds from the sale of like-kind property into a similar asset, ensuring the preservation of investment capital. In contrast, a sale-leaseback involves selling an asset and leasing it back, converting ownership into operational expense while retaining property use, but does not provide tax deferral on like-kind property. Explore detailed benefits and strategies to optimize your commercial real estate holdings with these transaction types.
Triple Net Lease
A 1031 exchange allows real estate investors to defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds from a property sale into a like-kind property, often involving triple net (NNN) lease assets known for stable, long-term income streams. Sale leaseback transactions convert owned properties into leased assets, providing immediate liquidity while maintaining triple net lease agreements that place property expenses like taxes, insurance, and maintenance on the tenant. Explore more to understand how these strategies leverage triple net leases for tax efficiency and cash flow optimization.
Source and External Links
1031 exchange | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - A 1031 exchange allows real estate investors to defer capital gains tax by reinvesting proceeds from the sale of a property into a new, like-kind property, provided identification and purchase are completed within strict deadlines.
1031 Exchange: How it Works - TurboTax Tax Tips & Videos - Intuit - The key benefit of a 1031 exchange is the deferral of all capital gains taxes when the sale proceeds are fully reinvested into a property of equal or greater value, with several types of exchanges available, each requiring adherence to specific rules.
What is a 1031 exchange and how does it work? - Fidelity Investments - To qualify for a 1031 exchange, both properties must be held for investment or business use (like-kind), the replacement property must be of equal or greater value, and a qualified intermediary must hold the funds during the exchange--proceeds cannot be accessed directly by the seller.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com