Nature inclusive design integrates natural elements like green roofs, native plants, and sustainable materials to enhance urban living while promoting environmental resilience. Affordable housing focuses on providing cost-effective, accessible residences for low to moderate-income individuals, addressing social equity and community stability. Explore how these approaches intersect to create sustainable, inclusive communities that balance ecological health with economic affordability.
Why it is important
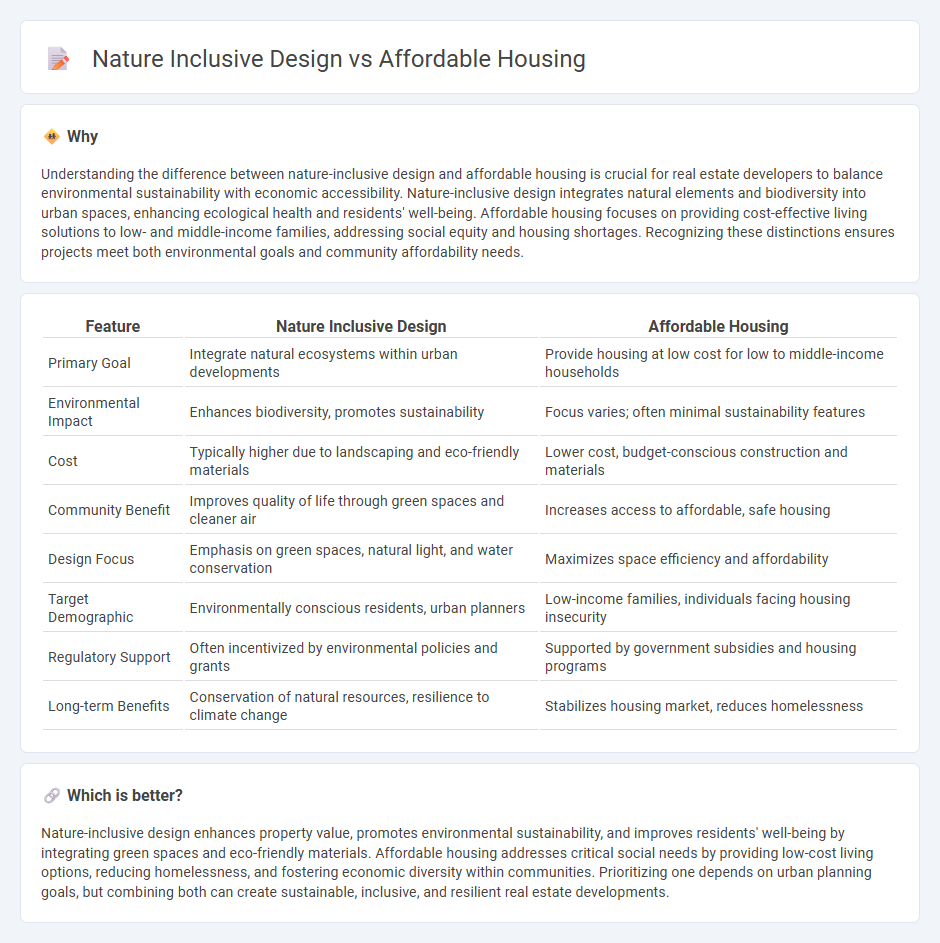
Understanding the difference between nature-inclusive design and affordable housing is crucial for real estate developers to balance environmental sustainability with economic accessibility. Nature-inclusive design integrates natural elements and biodiversity into urban spaces, enhancing ecological health and residents' well-being. Affordable housing focuses on providing cost-effective living solutions to low- and middle-income families, addressing social equity and housing shortages. Recognizing these distinctions ensures projects meet both environmental goals and community affordability needs.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Nature Inclusive Design | Affordable Housing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Integrate natural ecosystems within urban developments | Provide housing at low cost for low to middle-income households |
| Environmental Impact | Enhances biodiversity, promotes sustainability | Focus varies; often minimal sustainability features |
| Cost | Typically higher due to landscaping and eco-friendly materials | Lower cost, budget-conscious construction and materials |
| Community Benefit | Improves quality of life through green spaces and cleaner air | Increases access to affordable, safe housing |
| Design Focus | Emphasis on green spaces, natural light, and water conservation | Maximizes space efficiency and affordability |
| Target Demographic | Environmentally conscious residents, urban planners | Low-income families, individuals facing housing insecurity |
| Regulatory Support | Often incentivized by environmental policies and grants | Supported by government subsidies and housing programs |
| Long-term Benefits | Conservation of natural resources, resilience to climate change | Stabilizes housing market, reduces homelessness |
Which is better?
Nature-inclusive design enhances property value, promotes environmental sustainability, and improves residents' well-being by integrating green spaces and eco-friendly materials. Affordable housing addresses critical social needs by providing low-cost living options, reducing homelessness, and fostering economic diversity within communities. Prioritizing one depends on urban planning goals, but combining both can create sustainable, inclusive, and resilient real estate developments.
Connection
Nature-inclusive design integrates green spaces and sustainable materials into affordable housing projects, enhancing residents' well-being and reducing environmental impact. Incorporating biophilic elements like community gardens, green roofs, and natural ventilation improves air quality and energy efficiency, lowering utility costs for low-income families. This synergy supports social equity by providing healthier living environments while promoting ecological sustainability in real estate development.
Key Terms
Housing Affordability
Housing affordability remains a critical global challenge, with millions seeking cost-effective solutions that do not compromise environmental integrity. Nature-inclusive design integrates natural elements into housing projects, promoting sustainability but often perceived as increasing upfront costs. Explore innovative strategies that balance both affordability and ecological harmony to address the dual demand effectively.
Green Infrastructure
Affordable housing developments that integrate Green Infrastructure, such as permeable pavements and urban green spaces, demonstrate improved stormwater management and enhanced biodiversity. Nature inclusive design promotes energy efficiency and climate resilience while addressing social equity by providing healthier living environments for low-income communities. Explore how balancing affordable housing with Green Infrastructure harnesses ecological benefits and fosters sustainable urban growth.
Urban Biodiversity
Affordable housing projects integrating nature-inclusive design promote urban biodiversity by incorporating green roofs, community gardens, and native plant landscaping. These features enhance ecosystem services, support pollinators, and improve residents' well-being while addressing housing affordability challenges. Discover how urban planning balances housing needs with biodiversity preservation for sustainable city living.
Source and External Links
What is Affordable Housing? - Local Housing Solutions - Affordable housing means housing costs that consume no more than 30% of a household's income, leaving enough for other necessities like food, transportation, and health care, addressing the broader impact of high housing costs on communities and individuals.
Affordable Rentals - San Diego Housing Commission (SDHC) - SDHC offers affordable rental housing options and partners with developers to create and manage thousands of affordable units for households with lower incomes in San Diego, including an online searchable housing dashboard.
Rental assistance | USAGov - The U.S. government provides affordable rental housing programs such as Section 8 vouchers, subsidized housing, and public housing aimed at low-income households, veterans, seniors, and people with disabilities, detailing eligibility and application processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com