Agrihoods integrate sustainable agriculture with residential living, offering green spaces and fresh produce to foster community wellness and environmental stewardship. Affordable housing complexes focus on providing cost-effective, accessible residences to support low- and moderate-income families in urban and suburban areas. Explore the benefits and distinct characteristics of these housing models to determine the best fit for your community goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between agrihoods and affordable housing complexes is crucial for real estate investors and developers to target the right market and optimize property value. Agrihoods integrate agriculture with residential living, appealing to eco-conscious buyers seeking sustainable communities. Affordable housing complexes focus on providing low-cost residences to address housing affordability and social equity. Recognizing these distinctions helps in strategic planning, marketing, and meeting regulatory requirements effectively.
Comparison Table
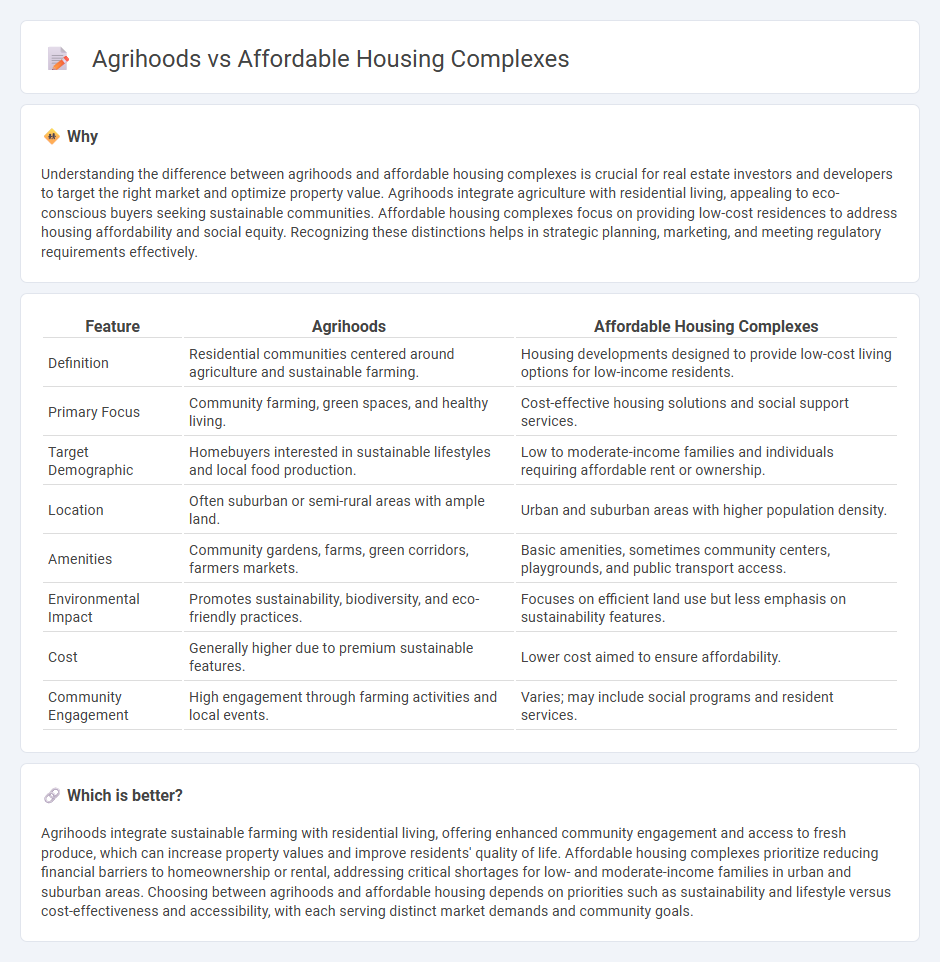
| Feature | Agrihoods | Affordable Housing Complexes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Residential communities centered around agriculture and sustainable farming. | Housing developments designed to provide low-cost living options for low-income residents. |
| Primary Focus | Community farming, green spaces, and healthy living. | Cost-effective housing solutions and social support services. |
| Target Demographic | Homebuyers interested in sustainable lifestyles and local food production. | Low to moderate-income families and individuals requiring affordable rent or ownership. |
| Location | Often suburban or semi-rural areas with ample land. | Urban and suburban areas with higher population density. |
| Amenities | Community gardens, farms, green corridors, farmers markets. | Basic amenities, sometimes community centers, playgrounds, and public transport access. |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainability, biodiversity, and eco-friendly practices. | Focuses on efficient land use but less emphasis on sustainability features. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to premium sustainable features. | Lower cost aimed to ensure affordability. |
| Community Engagement | High engagement through farming activities and local events. | Varies; may include social programs and resident services. |
Which is better?
Agrihoods integrate sustainable farming with residential living, offering enhanced community engagement and access to fresh produce, which can increase property values and improve residents' quality of life. Affordable housing complexes prioritize reducing financial barriers to homeownership or rental, addressing critical shortages for low- and moderate-income families in urban and suburban areas. Choosing between agrihoods and affordable housing depends on priorities such as sustainability and lifestyle versus cost-effectiveness and accessibility, with each serving distinct market demands and community goals.
Connection
Agrihoods integrate sustainable agriculture within residential communities, creating opportunities for affordable housing complexes to provide access to fresh food and green spaces. These developments enhance community well-being by promoting food security, reducing living costs, and fostering social interaction in affordable housing settings. Combining agrihoods with affordable housing addresses urban food deserts while supporting environmentally conscious living.
Key Terms
**Affordable Housing Complexes:**
Affordable housing complexes provide cost-effective residential options designed to support low- to moderate-income families by offering subsidized rents and government-backed financial assistance. These complexes typically emphasize accessibility to essential urban amenities, public transportation, and social services to promote community stability and economic inclusion. Explore how affordable housing complexes contribute to sustainable urban development and social equity by learning more about their design and impact.
Income Restriction
Income-restricted affordable housing complexes primarily target low- to moderate-income households, ensuring accessibility through stringent eligibility criteria based on area median income (AMI) levels. Agrihoods, while sometimes offering mixed-income housing, typically lack formal income restrictions, emphasizing a lifestyle integrated with sustainable farming rather than affordability mandates. Explore the nuances of income eligibility in different housing models to better understand their social impact.
Subsidized Rent
Affordable housing complexes typically offer subsidized rent programs funded by government agencies to provide low-income families with financial relief, ensuring rent is often capped at 30% of household income. Agrihoods, while promoting sustainable living through integrated farming and community spaces, rarely include subsidized rent options, making them less accessible for lower-income residents. Explore how these housing models impact community affordability and sustainability to understand their benefits better.
Source and External Links
Affordable Housing | Cherry Hill Township, NJ - This webpage provides information on affordable housing programs in Cherry Hill, including the Plaza Grande and The Grand communities.
Affordable Rentals - SDHC - The San Diego Housing Commission offers various affordable rental housing options through partnerships with developers across the city.
Affordable Housing Communities | Santa Rosa, CA - This resource provides an online map and information about affordable housing properties in Santa Rosa, including multifamily and senior citizen rentals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com