Agrihood communities integrate sustainable agriculture and residential living, offering residents access to fresh, locally grown produce within a shared farm environment. Cohousing focuses on intentional neighborhood design with private homes clustered around shared spaces to foster strong social connections and collaborative living. Explore more about these innovative real estate models shaping community lifestyles.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between agrihood communities and cohousing is crucial for real estate investors to align their investments with target demographics and lifestyle preferences. Agrihoods focus on integrating agriculture and sustainability, appealing to buyers interested in farm-to-table living and community farming. Cohousing emphasizes shared spaces and collaborative living, attracting buyers seeking strong social connections and shared resources. Identifying these distinctions ensures accurate marketing strategies and enhances property value by matching buyer expectations.
Comparison Table
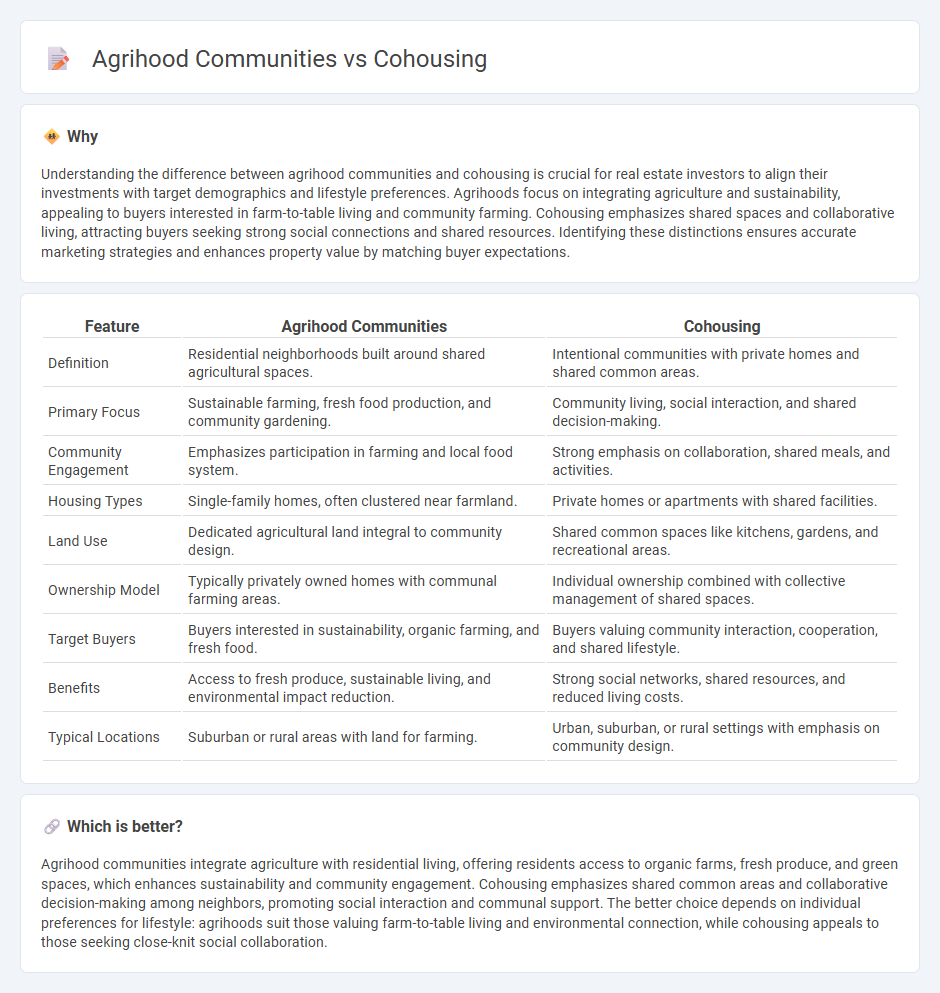
| Feature | Agrihood Communities | Cohousing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Residential neighborhoods built around shared agricultural spaces. | Intentional communities with private homes and shared common areas. |
| Primary Focus | Sustainable farming, fresh food production, and community gardening. | Community living, social interaction, and shared decision-making. |
| Community Engagement | Emphasizes participation in farming and local food system. | Strong emphasis on collaboration, shared meals, and activities. |
| Housing Types | Single-family homes, often clustered near farmland. | Private homes or apartments with shared facilities. |
| Land Use | Dedicated agricultural land integral to community design. | Shared common spaces like kitchens, gardens, and recreational areas. |
| Ownership Model | Typically privately owned homes with communal farming areas. | Individual ownership combined with collective management of shared spaces. |
| Target Buyers | Buyers interested in sustainability, organic farming, and fresh food. | Buyers valuing community interaction, cooperation, and shared lifestyle. |
| Benefits | Access to fresh produce, sustainable living, and environmental impact reduction. | Strong social networks, shared resources, and reduced living costs. |
| Typical Locations | Suburban or rural areas with land for farming. | Urban, suburban, or rural settings with emphasis on community design. |
Which is better?
Agrihood communities integrate agriculture with residential living, offering residents access to organic farms, fresh produce, and green spaces, which enhances sustainability and community engagement. Cohousing emphasizes shared common areas and collaborative decision-making among neighbors, promoting social interaction and communal support. The better choice depends on individual preferences for lifestyle: agrihoods suit those valuing farm-to-table living and environmental connection, while cohousing appeals to those seeking close-knit social collaboration.
Connection
Agrihood communities and cohousing share a focus on sustainable, communal living by integrating shared agricultural spaces where residents collaboratively grow food, fostering strong social bonds and reducing environmental impact. Both models emphasize cooperative decision-making and shared amenities, promoting a lifestyle centered around community engagement and resource efficiency. This connection enhances real estate value by attracting buyers seeking eco-friendly, socially connected neighborhoods.
Key Terms
Shared Amenities
Cohousing communities emphasize shared amenities such as common kitchens, communal dining areas, and multipurpose rooms designed to foster social interaction and collaboration among neighbors. Agrihood communities prioritize shared agricultural spaces like community gardens, orchards, and farm-to-table facilities that promote sustainable living and local food production. Explore the unique benefits of these community models to determine which shared amenities best suit your lifestyle preferences.
Community Governance
Cohousing communities emphasize collective decision-making through consensus or democratic voting, fostering equal participation among residents in community governance. Agrihoods integrate agricultural production with residential areas, often guided by a management team or homeowners' association that balances farming operations with community engagement. Explore deeper insights into how governance models shape social dynamics and sustainability in both community types.
Sustainable Land Use
Cohousing communities emphasize shared living spaces and communal decision-making to enhance social sustainability while minimizing land footprint through clustered housing designs. Agrihoods integrate residential living with agricultural landscapes, promoting sustainable land use by preserving green spaces and supporting local food production. Explore how these innovative community models contribute to sustainable land use practices and environmental resilience.
Source and External Links
Cohousing - Wikipedia - Cohousing is an intentional, self-governing, cooperative community where residents live in private homes clustered around shared spaces, collaboratively planning activities and resources while maintaining individual privacy and independence.
THE COHOUSING COMPANY - Cohousing communities are collaboratively developed neighborhoods with private homes arranged around shared common areas, emphasizing equal decision-making, resident self-management, and a balance between community interaction and personal retreat.
The Cohousing Association of America - Cohousing combines private homes with shared indoor and outdoor spaces designed to foster supportive neighbor relationships, resource sharing, and intergenerational connection, though affordability and access remain challenges for some prospective residents.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com