Reverse logistics focuses on the process of returning products from consumers back to manufacturers for reuse, refurbishing, or recycling, optimizing supply chain efficiency and sustainability. Waste management logistics deals with the collection, transportation, and disposal of waste materials, ensuring regulatory compliance and environmental protection. Explore deeper insights into how these two logistics approaches enhance operational performance and sustainability goals.
Why it is important
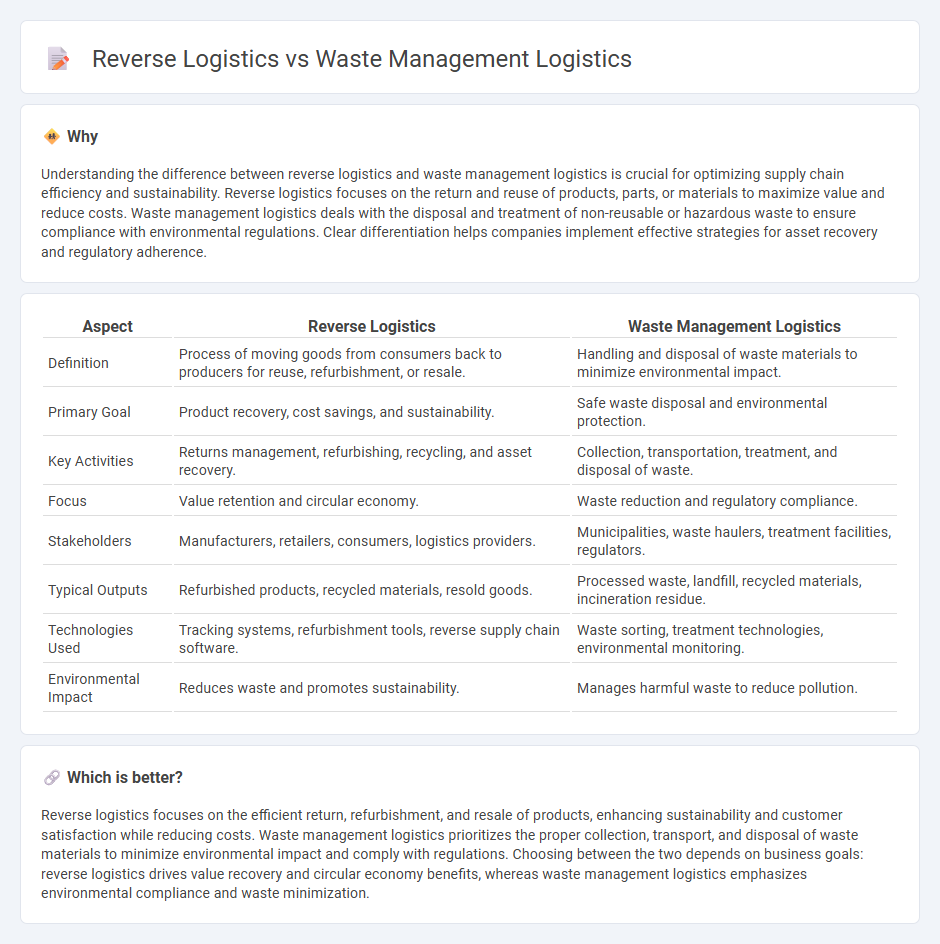
Understanding the difference between reverse logistics and waste management logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and sustainability. Reverse logistics focuses on the return and reuse of products, parts, or materials to maximize value and reduce costs. Waste management logistics deals with the disposal and treatment of non-reusable or hazardous waste to ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Clear differentiation helps companies implement effective strategies for asset recovery and regulatory adherence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reverse Logistics | Waste Management Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of moving goods from consumers back to producers for reuse, refurbishment, or resale. | Handling and disposal of waste materials to minimize environmental impact. |
| Primary Goal | Product recovery, cost savings, and sustainability. | Safe waste disposal and environmental protection. |
| Key Activities | Returns management, refurbishing, recycling, and asset recovery. | Collection, transportation, treatment, and disposal of waste. |
| Focus | Value retention and circular economy. | Waste reduction and regulatory compliance. |
| Stakeholders | Manufacturers, retailers, consumers, logistics providers. | Municipalities, waste haulers, treatment facilities, regulators. |
| Typical Outputs | Refurbished products, recycled materials, resold goods. | Processed waste, landfill, recycled materials, incineration residue. |
| Technologies Used | Tracking systems, refurbishment tools, reverse supply chain software. | Waste sorting, treatment technologies, environmental monitoring. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and promotes sustainability. | Manages harmful waste to reduce pollution. |
Which is better?
Reverse logistics focuses on the efficient return, refurbishment, and resale of products, enhancing sustainability and customer satisfaction while reducing costs. Waste management logistics prioritizes the proper collection, transport, and disposal of waste materials to minimize environmental impact and comply with regulations. Choosing between the two depends on business goals: reverse logistics drives value recovery and circular economy benefits, whereas waste management logistics emphasizes environmental compliance and waste minimization.
Connection
Reverse logistics and waste management logistics are interconnected processes focused on the efficient handling of returned products and materials to minimize environmental impact and reduce costs. Reverse logistics involves the return, refurbishment, and redistribution of goods, while waste management logistics ensures proper collection, transportation, and disposal or recycling of unusable materials. Integrating these logistics streams enhances sustainability by promoting resource recovery and reducing landfill dependency.
Key Terms
**Waste Management Logistics:**
Waste management logistics involves the systematic collection, transportation, processing, and disposal of waste materials to ensure environmental compliance and operational efficiency. It prioritizes the handling of municipal solid waste, hazardous waste, and recyclables using specialized vehicles, route optimization, and facility coordination to minimize costs and emissions. Explore how advanced waste management logistics can transform sustainability efforts and reduce environmental impact.
Collection
Waste management logistics involves the structured collection and transportation of waste materials from various sources to disposal or recycling facilities, emphasizing efficiency and regulatory compliance. Reverse logistics specifically targets the retrieval of used or discarded products from consumers for reuse, refurbishment, or recycling, optimizing the return flow and minimizing environmental impact. Explore more to understand how collection strategies differ and integrate within these logistics frameworks.
Treatment
Waste management logistics involves the collection, transportation, and treatment of waste to minimize environmental impact, emphasizing processes like incineration, recycling, and landfill management. Reverse logistics focuses on the return flow of products for refurbishment, recycling, or proper disposal, often integrating advanced tracking systems to ensure efficient treatment and recovery. Explore the nuances and advancements in treatment strategies for both waste management and reverse logistics to enhance sustainability efforts.
Source and External Links
Logistics Waste Management | Use Cases - Real-time tracking, route optimization, and geofencing enable efficient waste collection, regulatory compliance, and data-driven improvements in logistics waste management.
Waste Management Logistics Definition and Meaning - Waste management logistics organizes the collection, transportation, and disposal of waste materials to minimize environmental impact, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with regulations.
Revolutionizing Waste Management Logistics: The Role of Advanced Technologies - Smart bins, route optimization software, and asset tracking technologies streamline operations, cut emissions, and enhance sustainability in waste management logistics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com