Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines logistics by automating repetitive tasks such as order processing and inventory management, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology improves real-time tracking and asset visibility through wireless data capture, reducing errors in supply chain operations. Explore how integrating RPA and RFID can revolutionize your logistics workflows for maximum productivity.
Why it is important
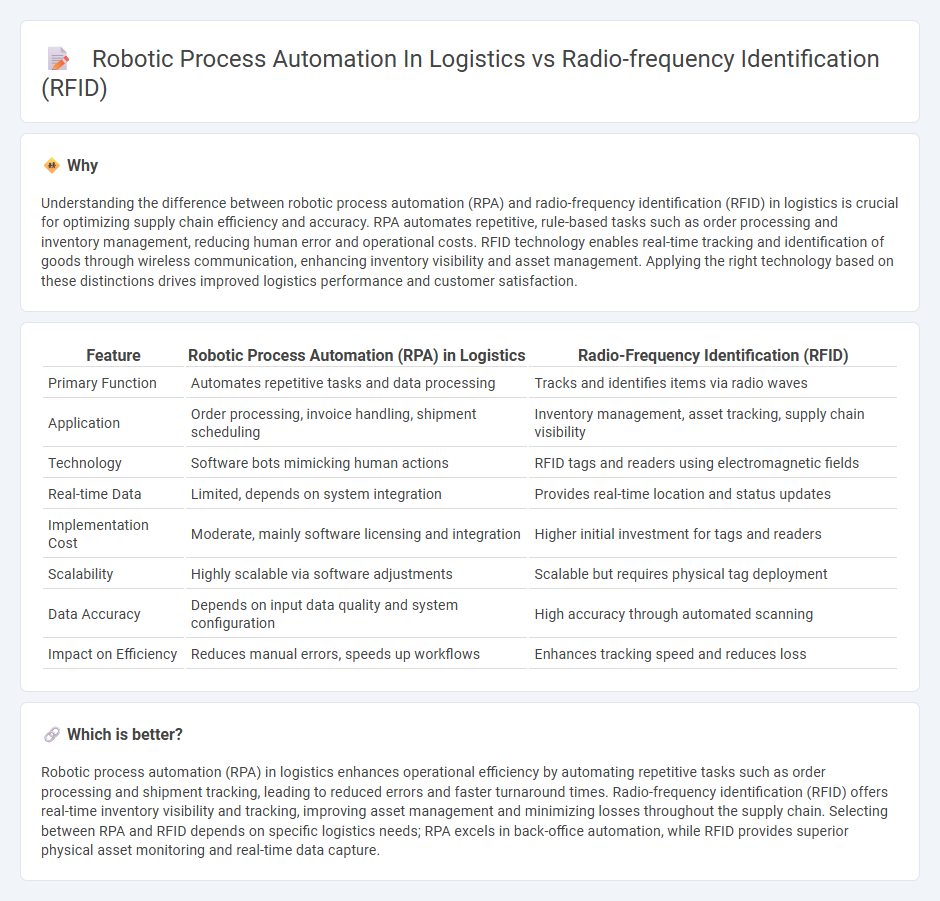
Understanding the difference between robotic process automation (RPA) and radio-frequency identification (RFID) in logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and accuracy. RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks such as order processing and inventory management, reducing human error and operational costs. RFID technology enables real-time tracking and identification of goods through wireless communication, enhancing inventory visibility and asset management. Applying the right technology based on these distinctions drives improved logistics performance and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Logistics | Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Automates repetitive tasks and data processing | Tracks and identifies items via radio waves |
| Application | Order processing, invoice handling, shipment scheduling | Inventory management, asset tracking, supply chain visibility |
| Technology | Software bots mimicking human actions | RFID tags and readers using electromagnetic fields |
| Real-time Data | Limited, depends on system integration | Provides real-time location and status updates |
| Implementation Cost | Moderate, mainly software licensing and integration | Higher initial investment for tags and readers |
| Scalability | Highly scalable via software adjustments | Scalable but requires physical tag deployment |
| Data Accuracy | Depends on input data quality and system configuration | High accuracy through automated scanning |
| Impact on Efficiency | Reduces manual errors, speeds up workflows | Enhances tracking speed and reduces loss |
Which is better?
Robotic process automation (RPA) in logistics enhances operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks such as order processing and shipment tracking, leading to reduced errors and faster turnaround times. Radio-frequency identification (RFID) offers real-time inventory visibility and tracking, improving asset management and minimizing losses throughout the supply chain. Selecting between RPA and RFID depends on specific logistics needs; RPA excels in back-office automation, while RFID provides superior physical asset monitoring and real-time data capture.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics enhances efficiency by automating repetitive tasks such as inventory management, order processing, and shipment tracking, utilizing data captured through Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) systems. RFID technology provides real-time visibility of goods movement and asset tracking, enabling RPA to make data-driven decisions and reduce human errors in supply chain operations. Integration of RPA with RFID accelerates operational workflows, reduces costs, and improves accuracy in logistics management.
Key Terms
Asset Tracking (RFID)
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) enhances asset tracking in logistics by providing real-time visibility and automated data capture through wireless tags, significantly reducing manual errors and improving inventory accuracy. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) complements asset management by streamlining workflow automation, processing data from RFID systems faster, and enabling seamless integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. Explore how combining RFID with RPA drives transformative efficiency in logistics asset tracking.
Workflow Automation (RPA)
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) enhances asset tracking and inventory management by providing real-time data capture through wireless tags, significantly improving supply chain visibility. Robotic process automation (RPA) streamlines workflow automation by mimicking human interactions with software systems, enabling faster order processing, billing, and demand forecasting without physical hardware changes. Explore how integrating RFID with RPA can optimize logistics operations for improved efficiency and accuracy.
Inventory Management
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) enhances inventory accuracy by enabling real-time tracking of goods through wireless communication, significantly reducing manual scanning errors and improving stock visibility. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) optimizes inventory management by automating data entry, order processing, and inventory reconciliation, streamlining backend workflows without physical interaction with inventory items. Explore the distinct advantages of RFID and RPA technologies in logistics to transform your inventory management strategies.
Source and External Links
Introduction of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) - GeeksforGeeks - RFID is a wireless technology using electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, functioning without direct line-of-sight and frequently used in inventory management and asset tracking.
Radio-frequency identification - Wikipedia - RFID systems include tags and readers; tags transmit digital data when triggered by reader signals and can be passive (powered by the reader's radio waves) or active (battery-powered), with wide applications but privacy concerns arising from their ability to identify objects and people without line-of-sight.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) | Technology, History ... - Britannica - RFID uses electromagnetic waves to track and identify tags attached to objects or living beings from several meters away, and it is commonly applied in various industries for tracking items and components along supply chains.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com