Dynamic rerouting in logistics leverages real-time data and GPS technology to adjust delivery routes instantly, enhancing efficiency and reducing delays. Geofencing creates virtual boundaries using GPS or RFID, triggering specific actions when vehicles enter or exit designated zones to improve security and operational control. Explore the benefits and applications of dynamic rerouting and geofencing to optimize your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
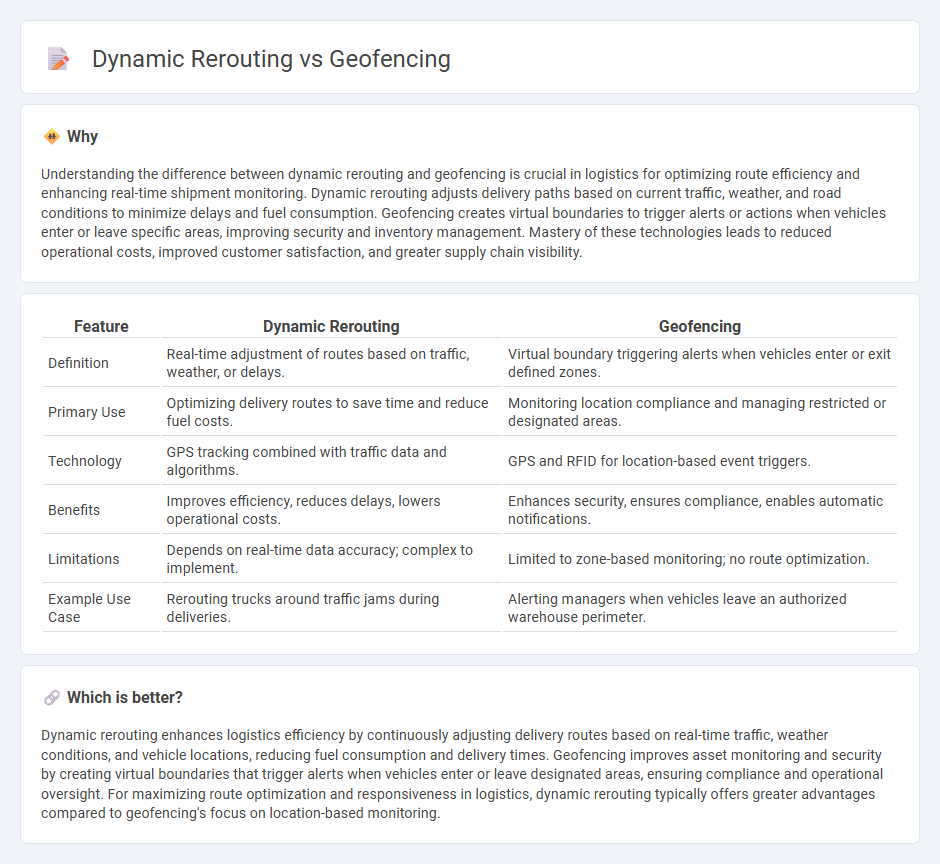
Understanding the difference between dynamic rerouting and geofencing is crucial in logistics for optimizing route efficiency and enhancing real-time shipment monitoring. Dynamic rerouting adjusts delivery paths based on current traffic, weather, and road conditions to minimize delays and fuel consumption. Geofencing creates virtual boundaries to trigger alerts or actions when vehicles enter or leave specific areas, improving security and inventory management. Mastery of these technologies leads to reduced operational costs, improved customer satisfaction, and greater supply chain visibility.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dynamic Rerouting | Geofencing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time adjustment of routes based on traffic, weather, or delays. | Virtual boundary triggering alerts when vehicles enter or exit defined zones. |
| Primary Use | Optimizing delivery routes to save time and reduce fuel costs. | Monitoring location compliance and managing restricted or designated areas. |
| Technology | GPS tracking combined with traffic data and algorithms. | GPS and RFID for location-based event triggers. |
| Benefits | Improves efficiency, reduces delays, lowers operational costs. | Enhances security, ensures compliance, enables automatic notifications. |
| Limitations | Depends on real-time data accuracy; complex to implement. | Limited to zone-based monitoring; no route optimization. |
| Example Use Case | Rerouting trucks around traffic jams during deliveries. | Alerting managers when vehicles leave an authorized warehouse perimeter. |
Which is better?
Dynamic rerouting enhances logistics efficiency by continuously adjusting delivery routes based on real-time traffic, weather conditions, and vehicle locations, reducing fuel consumption and delivery times. Geofencing improves asset monitoring and security by creating virtual boundaries that trigger alerts when vehicles enter or leave designated areas, ensuring compliance and operational oversight. For maximizing route optimization and responsiveness in logistics, dynamic rerouting typically offers greater advantages compared to geofencing's focus on location-based monitoring.
Connection
Dynamic rerouting in logistics leverages real-time data to adjust delivery routes based on current traffic conditions, weather, and other factors, enhancing efficiency and reducing delays. Geofencing creates virtual boundaries that trigger specific actions when a vehicle enters or exits these zones, providing precise monitoring and control over fleet movements. Integrating geofencing with dynamic rerouting enables logistics companies to optimize routes while maintaining strict compliance with operational zones and delivery schedules.
Key Terms
**Geofencing:**
Geofencing establishes virtual boundaries using GPS or RFID technology to trigger alerts or actions when a device enters or exits a predefined area, enhancing location-based management and security. This technology is widely used in fleet management, retail marketing, and asset tracking, providing real-time monitoring and precise geospatial control. Discover how geofencing optimizes business operations and customer engagement by exploring advanced use cases and integration strategies.
Virtual boundaries
Geofencing creates virtual boundaries by defining specific geographic areas using GPS or RFID technology, triggering alerts or actions when devices enter or exit these zones. Dynamic rerouting uses real-time data to adjust routes based on traffic conditions, but does not inherently establish virtual perimeters around locations. Explore the differences between geofencing and dynamic rerouting to optimize location-based services effectively.
Location-based alerts
Geofencing technology triggers location-based alerts by creating virtual perimeters around predefined geographic areas, enabling real-time notifications when a device enters or exits these zones. Dynamic rerouting enhances navigation efficiency by continuously analyzing traffic conditions and adjusting routes to optimize travel time without predefined boundaries. Explore the detailed mechanisms and applications of these technologies to understand their impact on location-aware services.
Source and External Links
What is geofencing and how is it used? - TechTarget - Geofencing is a location-based marketing technology that uses GPS, RFID, Wi-Fi, or cellular data to create a virtual boundary around a physical location, triggering preprogrammed actions when a device enters or exits this area.
What is Geofencing? Geofencing definition, history, applications ... - Radar - Geofencing employs GPS and other location technologies to create a virtual perimeter that triggers targeted actions or notifications when a user's device crosses this boundary, enabling personalized and contextually relevant interactions for businesses and users.
What is Geofencing? - Verizon Connect - A geofence is a virtual perimeter created with mapping software around a physical location that can detect and notify when a GPS-enabled device enters or leaves this area, useful for applications such as asset tracking, security, and monitoring.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com