Micro-fulfillment centers optimize last-mile delivery by using advanced automation to store and pick small product quantities rapidly, enhancing urban supply chain efficiency. Traditional warehouses handle larger inventories and prioritize bulk storage and long-term inventory management, often located in suburban areas. Explore how these contrasting logistics models impact delivery speed and operational costs.
Why it is important
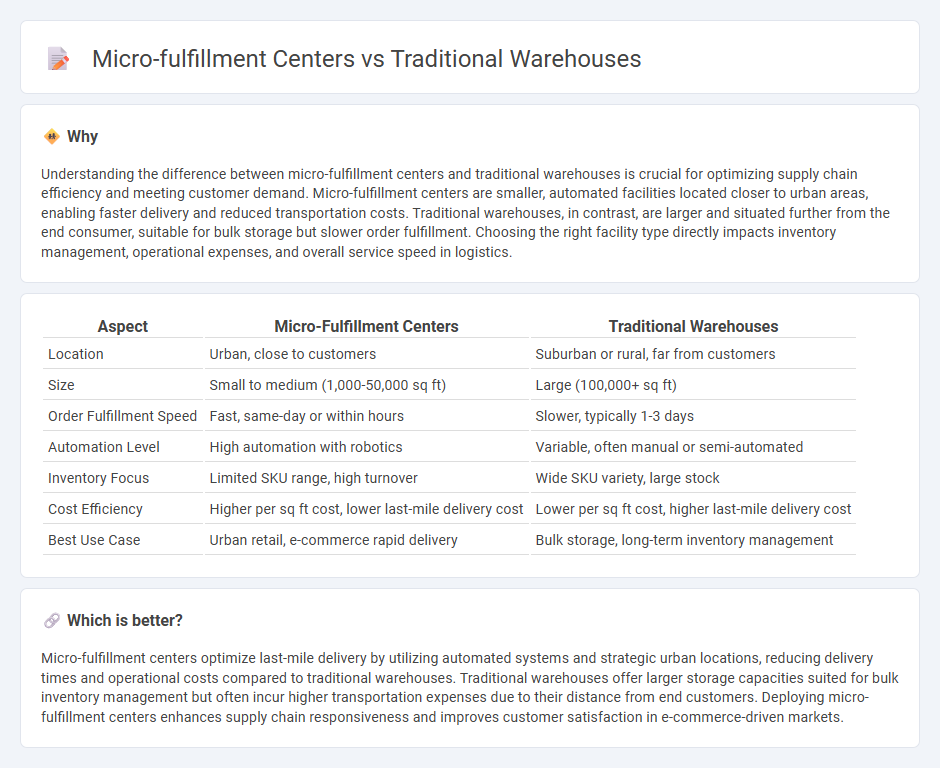
Understanding the difference between micro-fulfillment centers and traditional warehouses is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and meeting customer demand. Micro-fulfillment centers are smaller, automated facilities located closer to urban areas, enabling faster delivery and reduced transportation costs. Traditional warehouses, in contrast, are larger and situated further from the end consumer, suitable for bulk storage but slower order fulfillment. Choosing the right facility type directly impacts inventory management, operational expenses, and overall service speed in logistics.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Micro-Fulfillment Centers | Traditional Warehouses |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Urban, close to customers | Suburban or rural, far from customers |
| Size | Small to medium (1,000-50,000 sq ft) | Large (100,000+ sq ft) |
| Order Fulfillment Speed | Fast, same-day or within hours | Slower, typically 1-3 days |
| Automation Level | High automation with robotics | Variable, often manual or semi-automated |
| Inventory Focus | Limited SKU range, high turnover | Wide SKU variety, large stock |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher per sq ft cost, lower last-mile delivery cost | Lower per sq ft cost, higher last-mile delivery cost |
| Best Use Case | Urban retail, e-commerce rapid delivery | Bulk storage, long-term inventory management |
Which is better?
Micro-fulfillment centers optimize last-mile delivery by utilizing automated systems and strategic urban locations, reducing delivery times and operational costs compared to traditional warehouses. Traditional warehouses offer larger storage capacities suited for bulk inventory management but often incur higher transportation expenses due to their distance from end customers. Deploying micro-fulfillment centers enhances supply chain responsiveness and improves customer satisfaction in e-commerce-driven markets.
Connection
Micro-fulfillment centers and traditional warehouses form an interconnected logistics network that enhances inventory management and order fulfillment speed. Traditional warehouses store bulk inventory while micro-fulfillment centers, located closer to urban areas, enable rapid last-mile delivery through automated systems. This synergy optimizes supply chain efficiency by balancing storage capacity and quick response to consumer demand.
Key Terms
Storage Density
Traditional warehouses typically offer lower storage density due to expansive layouts designed for bulk storage and large inventory volumes. Micro-fulfillment centers optimize storage density by utilizing vertical space and automated systems, significantly increasing inventory per square foot. Discover how businesses can enhance operational efficiency through higher storage density in micro-fulfillment centers.
Order Processing Speed
Traditional warehouses typically process orders in bulk, resulting in longer fulfillment times due to centralized locations and manual handling. Micro-fulfillment centers use automation and are strategically located closer to customers, significantly reducing order processing speed and enabling rapid delivery. Explore how these innovations can transform your supply chain efficiency.
Proximity to End Customer
Traditional warehouses are typically located on the outskirts of urban areas, prioritizing large storage capacity and cost efficiency but often resulting in longer delivery times. Micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) are strategically placed closer to densely populated city centers, enabling faster order processing and reduced last-mile delivery costs. Explore more about how proximity impacts operational efficiency and customer satisfaction in modern supply chains.
Source and External Links
What Is Traditional Warehousing- Concept, Benefits & Operation - Traditional warehouses are permanent buildings designed for long-term storage of large quantities of goods, using systematic processes like palletized storage and manual inventory tracking, providing businesses control over inventory and logistics operations.
Cross-Docking vs. Traditional Warehousing: Which Is Better? - Traditional warehousing relies largely on manual labor for stock management, order picking, and shipping, with little to no automation, focusing on storing goods to prepare them for sale or distribution.
Smart Warehouse vs. Traditional Warehouse - Portable Intelligence - Traditional warehouses have rigid infrastructure and manual operations that can lead to inefficiencies such as errors in inventory management, slower order fulfillment, and limited real-time stock visibility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com