Last mile delivery focuses on the efficient transportation of goods from distribution centers directly to customers, aiming to minimize delivery time and costs while enhancing customer satisfaction. Reverse logistics manages the return flow of products, handling returns, recycling, and disposal processes to optimize resource recovery and reduce environmental impact. Explore the critical differences and strategies behind last mile delivery and reverse logistics to improve your supply chain performance.
Why it is important
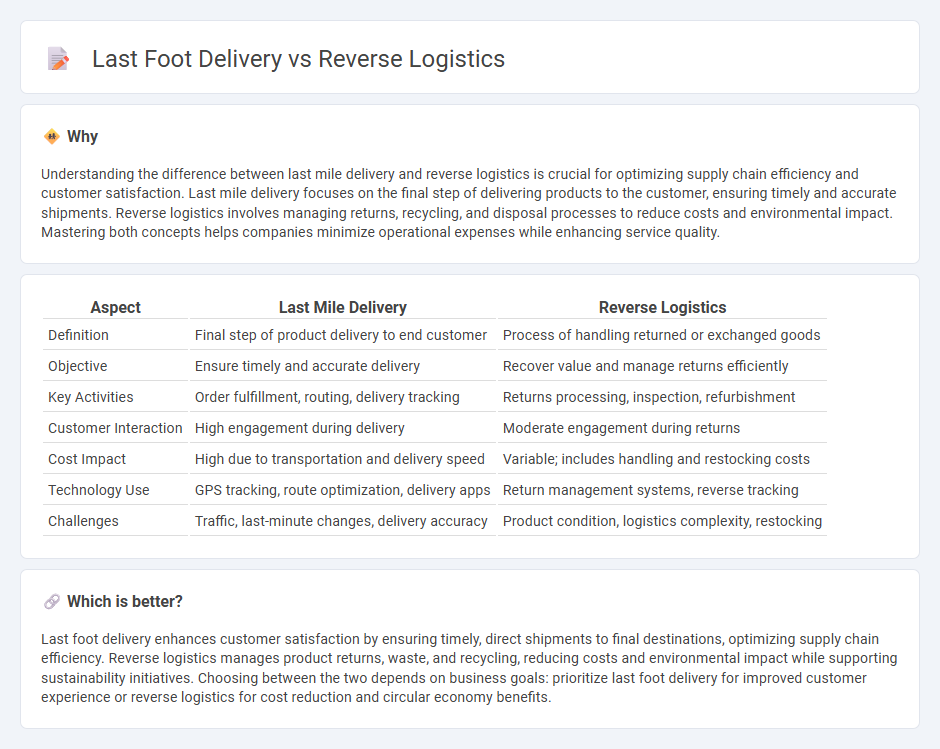
Understanding the difference between last mile delivery and reverse logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Last mile delivery focuses on the final step of delivering products to the customer, ensuring timely and accurate shipments. Reverse logistics involves managing returns, recycling, and disposal processes to reduce costs and environmental impact. Mastering both concepts helps companies minimize operational expenses while enhancing service quality.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Last Mile Delivery | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Final step of product delivery to end customer | Process of handling returned or exchanged goods |
| Objective | Ensure timely and accurate delivery | Recover value and manage returns efficiently |
| Key Activities | Order fulfillment, routing, delivery tracking | Returns processing, inspection, refurbishment |
| Customer Interaction | High engagement during delivery | Moderate engagement during returns |
| Cost Impact | High due to transportation and delivery speed | Variable; includes handling and restocking costs |
| Technology Use | GPS tracking, route optimization, delivery apps | Return management systems, reverse tracking |
| Challenges | Traffic, last-minute changes, delivery accuracy | Product condition, logistics complexity, restocking |
Which is better?
Last foot delivery enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring timely, direct shipments to final destinations, optimizing supply chain efficiency. Reverse logistics manages product returns, waste, and recycling, reducing costs and environmental impact while supporting sustainability initiatives. Choosing between the two depends on business goals: prioritize last foot delivery for improved customer experience or reverse logistics for cost reduction and circular economy benefits.
Connection
Last foot delivery and reverse logistics are interconnected processes in the supply chain, focusing on the final stages of product movement. Last foot delivery ensures timely distribution to the end consumer's location, while reverse logistics manages the efficient return, recycling, or disposal of products after use. Optimizing both enhances customer satisfaction, reduces operational costs, and supports sustainable practices.
Key Terms
**Reverse Logistics:**
Reverse logistics involves the process of moving goods from the end consumer back to the retailer or manufacturer for returns, repairs, recycling, or disposal, ensuring efficient handling of returned products and waste management. This system reduces environmental impact and recovers value by refurbishing or reselling returned items, thus optimizing supply chain sustainability. Discover how mastering reverse logistics can boost your business efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Returns Management
Reverse logistics streamlines the process of returning products from customers back to warehouses, emphasizing efficient handling, inspection, and restocking. Last foot delivery focuses on the final stage of product transportation, ensuring timely and accurate deliveries to the customer's doorstep. Explore in-depth strategies to enhance returns management and optimize both reverse logistics and last foot delivery operations.
Refurbishment
Reverse logistics involves the process of returning products from customers back to manufacturers or warehouses for refurbishment, recycling, or disposal, emphasizing sustainability and cost efficiency. Last foot delivery refers to the final step of product delivery to the customer's doorstep, prioritizing speed and convenience but sometimes impacting refurbishment potential. Explore how integrating reverse logistics with last foot delivery can optimize refurbishment outcomes and enhance circular economy practices.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - c3controls - Reverse logistics is the process of moving goods from the customer back to the manufacturer or distributor for return, repair, remanufacture, or recycling, aimed at cost-effective flow and sustainability in the supply chain.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and Strategies - Reverse logistics manages returns, surplus goods, leases, and refurbishments, varying by industry with processes such as return authorization and scheduling return shipments.
Reverse logistics - Wikipedia - Reverse logistics encompasses operations related to the backward flow of products for value recovery or proper disposal, including remanufacturing and refurbishing, with a growing market worth nearly $1 trillion globally in 2023.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com