Quick commerce focuses on ultra-fast delivery of goods, often within minutes, catering to immediate consumer needs through localized micro fulfillment centers. Omnichannel retail integrates multiple sales channels, including physical stores and online platforms, to provide a seamless and consistent shopping experience. Explore more to understand how these strategies reshape customer expectations and supply chain dynamics.
Why it is important
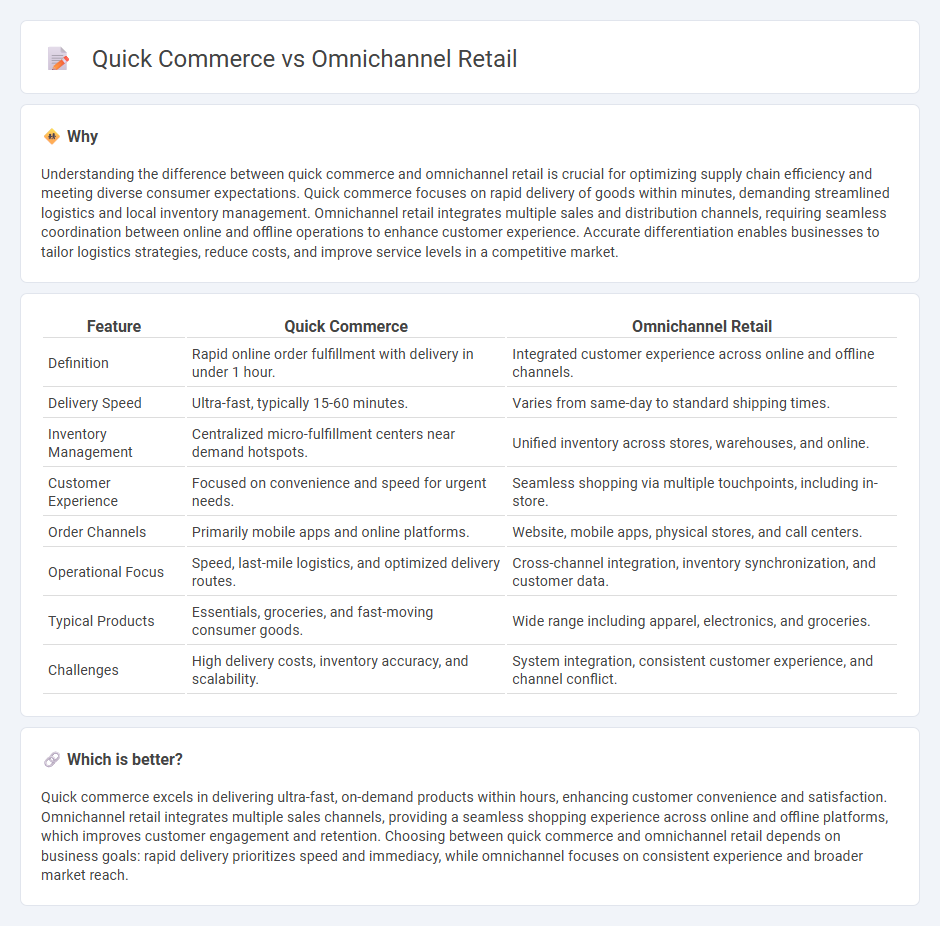
Understanding the difference between quick commerce and omnichannel retail is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and meeting diverse consumer expectations. Quick commerce focuses on rapid delivery of goods within minutes, demanding streamlined logistics and local inventory management. Omnichannel retail integrates multiple sales and distribution channels, requiring seamless coordination between online and offline operations to enhance customer experience. Accurate differentiation enables businesses to tailor logistics strategies, reduce costs, and improve service levels in a competitive market.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Quick Commerce | Omnichannel Retail |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid online order fulfillment with delivery in under 1 hour. | Integrated customer experience across online and offline channels. |
| Delivery Speed | Ultra-fast, typically 15-60 minutes. | Varies from same-day to standard shipping times. |
| Inventory Management | Centralized micro-fulfillment centers near demand hotspots. | Unified inventory across stores, warehouses, and online. |
| Customer Experience | Focused on convenience and speed for urgent needs. | Seamless shopping via multiple touchpoints, including in-store. |
| Order Channels | Primarily mobile apps and online platforms. | Website, mobile apps, physical stores, and call centers. |
| Operational Focus | Speed, last-mile logistics, and optimized delivery routes. | Cross-channel integration, inventory synchronization, and customer data. |
| Typical Products | Essentials, groceries, and fast-moving consumer goods. | Wide range including apparel, electronics, and groceries. |
| Challenges | High delivery costs, inventory accuracy, and scalability. | System integration, consistent customer experience, and channel conflict. |
Which is better?
Quick commerce excels in delivering ultra-fast, on-demand products within hours, enhancing customer convenience and satisfaction. Omnichannel retail integrates multiple sales channels, providing a seamless shopping experience across online and offline platforms, which improves customer engagement and retention. Choosing between quick commerce and omnichannel retail depends on business goals: rapid delivery prioritizes speed and immediacy, while omnichannel focuses on consistent experience and broader market reach.
Connection
Quick commerce leverages omnichannel retail strategies by integrating online and offline channels to ensure rapid order fulfillment and delivery. Omnichannel retail enhances customer experience through seamless inventory visibility and flexible fulfillment options, enabling quick commerce businesses to meet high-speed delivery demands. This synergy drives efficiency, reduces delivery times, and supports consumer expectations for instant gratification.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Omnichannel retail integrates inventory management across multiple sales channels, providing real-time stock visibility and synchronized order fulfillment to enhance customer experience. Quick commerce prioritizes rapid inventory turnover and localized fulfillment centers to enable ultra-fast delivery, often within minutes, optimizing stock allocation for immediate demand. Discover how advanced inventory strategies drive efficiency and customer satisfaction in both retail models.
Order Fulfillment
Omnichannel retail integrates multiple sales channels, including physical stores, online platforms, and mobile apps, to enhance customer experience and streamline order fulfillment through centralized inventory management and flexible delivery options. Quick commerce prioritizes ultra-fast delivery, often within minutes or hours, leveraging localized micro-fulfillment centers and real-time inventory tracking to meet immediate consumer demand. Explore our in-depth analysis to understand how optimizing order fulfillment strategies in both models drives operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Last-Mile Delivery
Omnichannel retail integrates multiple shopping channels, optimizing last-mile delivery through coordinated inventory and flexible fulfillment options like buy-online-pickup-in-store (BOPIS) and curbside pickup. Quick commerce, or q-commerce, emphasizes ultra-fast delivery, leveraging localized micro-fulfillment centers and agile logistics to meet customer expectations for delivery within minutes or hours. Explore the latest strategies and technologies transforming last-mile delivery in omnichannel and q-commerce models.
Source and External Links
What is Omni-Channel Retail? | Salesforce US - Omni-channel retailing is a model where shoppers interact seamlessly with multiple physical and digital sales channels, retaining their information and enabling them to resume transactions across devices and platforms, creating a unified shopping experience unlike siloed multichannel retailing.
What is Omnichannel Retailing? Basics Explained - Magestore - Omnichannel retail integrates all physical and online sales channels with centralized data management like an omnichannel POS, enabling customers to start buying in one channel and finish in another, thus offering a seamless and personalized shopping experience.
What Is Omnichannel Retail? How it Works and Examples (2024) - Omnichannel retail is a fully integrated commerce approach that blends all shopping touchpoints--including physical stores, mobile devices, social media, and online marketplaces--into one unified customer experience, improving personalization, convenience, and sales.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com