Milk run logistics optimize delivery by consolidating multiple shipments into a single route, reducing transportation costs and improving supply chain efficiency. Direct shipment sends goods straight from supplier to customer, minimizing handling time and ensuring faster delivery for urgent or perishable items. Discover how choosing between milk run and direct shipment can streamline your logistics operations and boost productivity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between milk run and direct shipment is crucial in logistics because milk run optimizes transportation by consolidating multiple deliveries into a single route, reducing costs and environmental impact. Direct shipment enables faster delivery by sending goods directly from supplier to customer, crucial for time-sensitive products. Choosing the right method improves supply chain efficiency, inventory management, and customer satisfaction. This knowledge ultimately drives better decision-making in logistics and supply chain operations.
Comparison Table
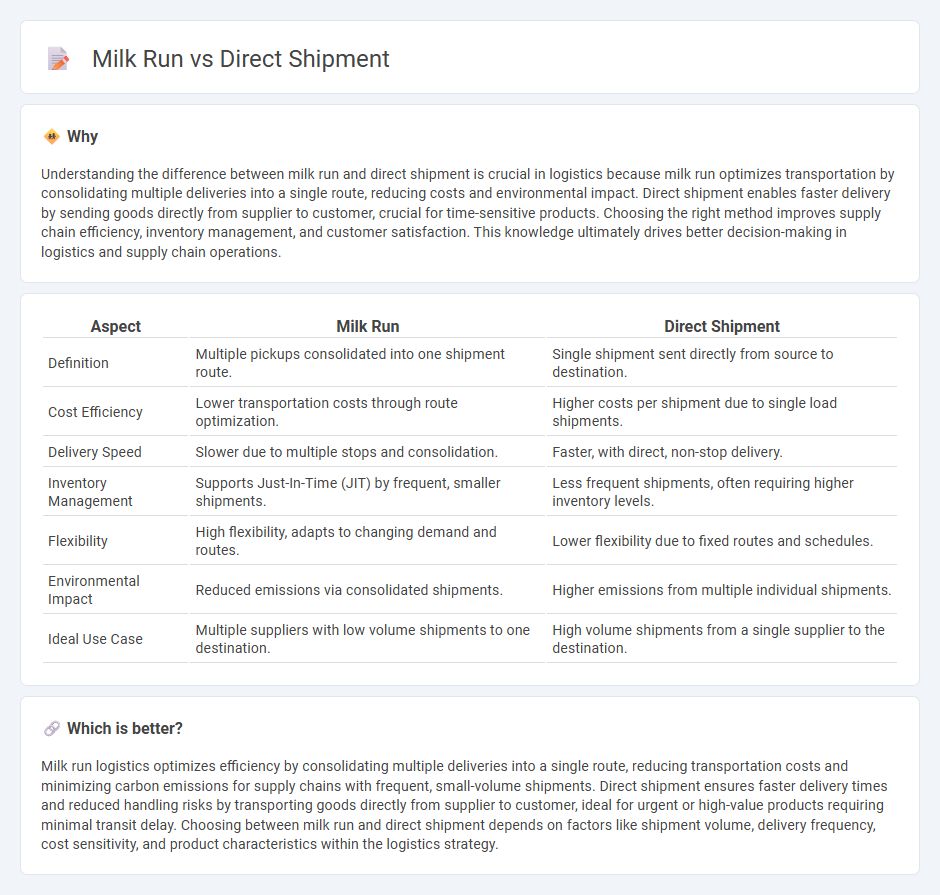
| Aspect | Milk Run | Direct Shipment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple pickups consolidated into one shipment route. | Single shipment sent directly from source to destination. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower transportation costs through route optimization. | Higher costs per shipment due to single load shipments. |
| Delivery Speed | Slower due to multiple stops and consolidation. | Faster, with direct, non-stop delivery. |
| Inventory Management | Supports Just-In-Time (JIT) by frequent, smaller shipments. | Less frequent shipments, often requiring higher inventory levels. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, adapts to changing demand and routes. | Lower flexibility due to fixed routes and schedules. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced emissions via consolidated shipments. | Higher emissions from multiple individual shipments. |
| Ideal Use Case | Multiple suppliers with low volume shipments to one destination. | High volume shipments from a single supplier to the destination. |
Which is better?
Milk run logistics optimizes efficiency by consolidating multiple deliveries into a single route, reducing transportation costs and minimizing carbon emissions for supply chains with frequent, small-volume shipments. Direct shipment ensures faster delivery times and reduced handling risks by transporting goods directly from supplier to customer, ideal for urgent or high-value products requiring minimal transit delay. Choosing between milk run and direct shipment depends on factors like shipment volume, delivery frequency, cost sensitivity, and product characteristics within the logistics strategy.
Connection
Milk run and direct shipment both play critical roles in optimizing supply chain logistics by improving transportation efficiency and reducing costs. Milk run consolidates multiple deliveries into a single route, minimizing empty trips and enhancing load optimization, while direct shipment focuses on sending goods straight from the supplier to the customer, reducing handling time and inventory levels. Combining these methods enables companies to balance speed and cost-effectiveness in their distribution strategies.
Key Terms
Transportation Cost
Direct shipment often leads to higher transportation costs due to dedicated truckloads and longer routes, increasing fuel consumption and freight charges. Milk run logistics optimize transportation costs by consolidating multiple deliveries into a single route, reducing empty miles and improving vehicle utilization. Explore more to understand how these methods impact your supply chain budget effectively.
Routing Efficiency
Direct shipment minimizes transit time by sending goods straight from origin to destination, reducing handling and potential delays. Milk run consolidates multiple deliveries into one route, optimizing load capacity and reducing transportation costs through efficient stops. Explore more to understand which routing strategy best suits your supply chain needs.
Delivery Frequency
Direct shipment typically involves less frequent deliveries, often scheduled for larger volume shipments to minimize transportation costs and handling time. Milk run logistics prioritize frequent, consolidated deliveries from multiple suppliers, optimizing route efficiency and inventory turnover for just-in-time production. Discover how adjusting delivery frequency between direct shipments and milk run strategies can enhance your supply chain responsiveness and cost-efficiency.
Source and External Links
Direct Shipping: Definition, Advantages, Disadvantages - Direct shipping is a method where goods are shipped directly from the supplier to the customer without stopping at warehouses or seller facilities, saving logistics costs but risking quality control and seller reputation.
What Is Direct Shipping? Pros and Cons of Direct Shipping - Direct shipping is an in-house order fulfillment method where the seller ships products directly to customers, bypassing intermediaries, allowing full control over inventory and customer experience.
Direct Shipping: A Comprehensive Guide - Direct shipping involves suppliers shipping products straight to customers on behalf of retailers, eliminating warehousing and offering greater branding control compared to dropshipping.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com