Grey market shipping involves the unauthorized distribution of goods through unofficial channels, often bypassing manufacturer warranties and standard supply chains. Third-party logistics (3PL) providers offer authorized, comprehensive supply chain services including warehousing, transportation, and fulfillment, ensuring reliability and compliance. Explore more to understand the key differences and impact on your business logistics strategy.
Why it is important
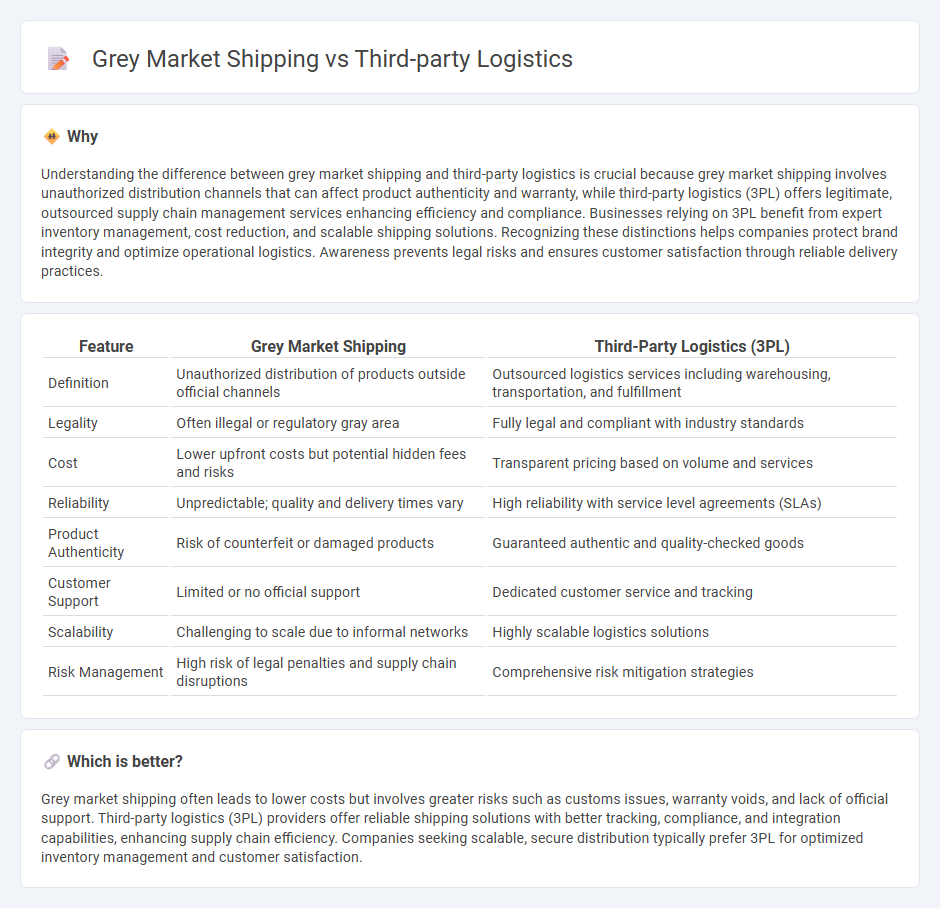
Understanding the difference between grey market shipping and third-party logistics is crucial because grey market shipping involves unauthorized distribution channels that can affect product authenticity and warranty, while third-party logistics (3PL) offers legitimate, outsourced supply chain management services enhancing efficiency and compliance. Businesses relying on 3PL benefit from expert inventory management, cost reduction, and scalable shipping solutions. Recognizing these distinctions helps companies protect brand integrity and optimize operational logistics. Awareness prevents legal risks and ensures customer satisfaction through reliable delivery practices.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Grey Market Shipping | Third-Party Logistics (3PL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unauthorized distribution of products outside official channels | Outsourced logistics services including warehousing, transportation, and fulfillment |
| Legality | Often illegal or regulatory gray area | Fully legal and compliant with industry standards |
| Cost | Lower upfront costs but potential hidden fees and risks | Transparent pricing based on volume and services |
| Reliability | Unpredictable; quality and delivery times vary | High reliability with service level agreements (SLAs) |
| Product Authenticity | Risk of counterfeit or damaged products | Guaranteed authentic and quality-checked goods |
| Customer Support | Limited or no official support | Dedicated customer service and tracking |
| Scalability | Challenging to scale due to informal networks | Highly scalable logistics solutions |
| Risk Management | High risk of legal penalties and supply chain disruptions | Comprehensive risk mitigation strategies |
Which is better?
Grey market shipping often leads to lower costs but involves greater risks such as customs issues, warranty voids, and lack of official support. Third-party logistics (3PL) providers offer reliable shipping solutions with better tracking, compliance, and integration capabilities, enhancing supply chain efficiency. Companies seeking scalable, secure distribution typically prefer 3PL for optimized inventory management and customer satisfaction.
Connection
Grey market shipping often relies on third-party logistics providers to manage the distribution of unauthorized or counterfeit goods across borders. Third-party logistics companies facilitate complex supply chain activities such as storage, transportation, and delivery that enable grey market products to reach consumers without official authorization. This interconnection challenges brand control and regulatory compliance within global logistics networks.
Key Terms
Outsourcing
Outsourcing third-party logistics (3PL) involves partnering with specialized providers to manage warehousing, transportation, and fulfillment services, ensuring streamlined supply chain operations and compliance with regulations. In contrast, grey market shipping bypasses authorized distribution channels, posing risks such as counterfeit products, voided warranties, and legal complications. Explore more to understand how strategic outsourcing in logistics can enhance efficiency and protect your brand integrity.
Parallel Importation
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers manage supply chain operations, warehousing, and distribution for businesses, ensuring efficient product flow within authorized channels. Grey market shipping involves unauthorized importation of genuine products sold outside official distribution systems, which often impacts brand control and warranty validity. Explore detailed insights into how parallel importation shapes global trade and supply chain strategies.
Supply Chain Integrity
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers enhance supply chain integrity by ensuring authorized sourcing, real-time tracking, and compliance with industry standards, minimizing risks of counterfeit products and unauthorized channel diversion. In contrast, grey market shipping often bypasses official distribution channels, leading to challenges such as lack of warranty, product authenticity issues, and potential regulatory violations that compromise supply chain transparency and reliability. Explore further to understand how strategic logistics choices safeguard your supply chain integrity and business reputation.
Source and External Links
What is a 3PL? Third-party logistics definition, process, and resources - A 3PL (third-party logistics) provider manages functions like warehousing, picking, packing, and shipping products on behalf of businesses to optimize supply chain and improve cost efficiency in fulfillment.
What is 3PL (third-party logistics)? | Definition from TechTarget - 3PL providers offer outsourced logistics services such as storage, transportation, and fulfillment, allowing businesses to focus on core activities while controlling shipping and distribution costs.
Understanding 3PL: Benefits and Purpose of Third-Party Logistics - Partnering with 3PL companies enables businesses to enhance supply chain management with scalable services including transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and order fulfillment to reduce costs and boost flexibility.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com