Container pooling streamlines supply chains by sharing reusable containers among multiple companies, reducing costs and environmental impact. Closed loop systems focus on maintaining containers within a specific network, ensuring controlled and efficient reuse. Explore the differences between container pooling and closed loop systems to optimize your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
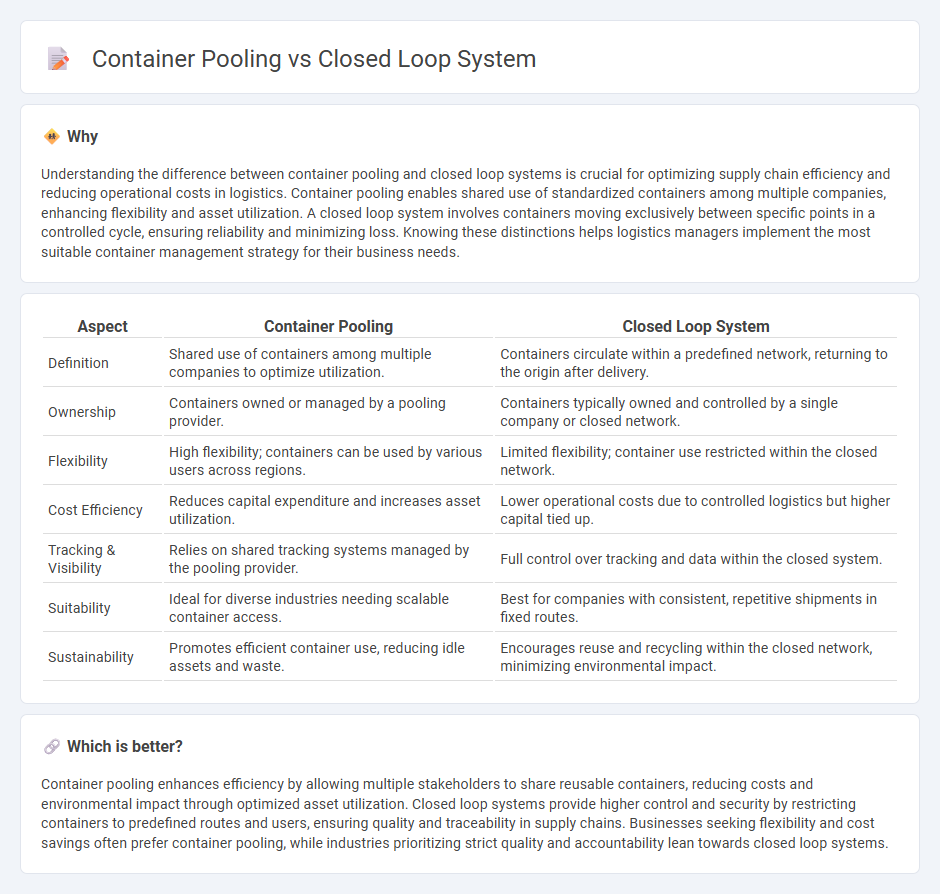
Understanding the difference between container pooling and closed loop systems is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing operational costs in logistics. Container pooling enables shared use of standardized containers among multiple companies, enhancing flexibility and asset utilization. A closed loop system involves containers moving exclusively between specific points in a controlled cycle, ensuring reliability and minimizing loss. Knowing these distinctions helps logistics managers implement the most suitable container management strategy for their business needs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Container Pooling | Closed Loop System |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared use of containers among multiple companies to optimize utilization. | Containers circulate within a predefined network, returning to the origin after delivery. |
| Ownership | Containers owned or managed by a pooling provider. | Containers typically owned and controlled by a single company or closed network. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; containers can be used by various users across regions. | Limited flexibility; container use restricted within the closed network. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces capital expenditure and increases asset utilization. | Lower operational costs due to controlled logistics but higher capital tied up. |
| Tracking & Visibility | Relies on shared tracking systems managed by the pooling provider. | Full control over tracking and data within the closed system. |
| Suitability | Ideal for diverse industries needing scalable container access. | Best for companies with consistent, repetitive shipments in fixed routes. |
| Sustainability | Promotes efficient container use, reducing idle assets and waste. | Encourages reuse and recycling within the closed network, minimizing environmental impact. |
Which is better?
Container pooling enhances efficiency by allowing multiple stakeholders to share reusable containers, reducing costs and environmental impact through optimized asset utilization. Closed loop systems provide higher control and security by restricting containers to predefined routes and users, ensuring quality and traceability in supply chains. Businesses seeking flexibility and cost savings often prefer container pooling, while industries prioritizing strict quality and accountability lean towards closed loop systems.
Connection
Container pooling enhances logistics efficiency by enabling shared use of standardized containers among multiple stakeholders, reducing idle time and costs. Closed loop systems complement container pooling by ensuring containers are consistently tracked, maintained, and returned within the supply chain, minimizing waste and environmental impact. Together, they streamline asset utilization, promote sustainability, and improve supply chain transparency.
Key Terms
**Closed Loop System:**
Closed loop systems optimize resource utilization by continuously recycling containers within a defined supply chain, ensuring reduced waste and lower environmental impact compared to single-use packaging. These systems rely on tracking technologies like RFID or QR codes to monitor container lifecycle, enhancing efficiency and accountability throughout the process. Discover how closed loop systems transform sustainability and cost-efficiency in packaging solutions.
Reverse Logistics
Closed loop systems in reverse logistics emphasize the continuous flow of products from consumption back to production, ensuring efficient reuse, remanufacturing, or recycling. Container pooling optimizes the management and circulation of reusable containers, reducing waste and operational costs by sharing containers across multiple users within the supply chain. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how these strategies improve sustainability and cost-efficiency in reverse logistics.
Asset Tracking
Closed loop systems ensure accurate asset tracking by using RFID or barcode technology to monitor assets from deployment to return, minimizing loss and improving utilization rates. Container pooling enhances asset management by sharing standardized containers across multiple users, enabling real-time tracking and streamlined logistics through IoT-enabled sensors. Explore how combining closed loop systems and container pooling can optimize asset tracking efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Source and External Links
Closed-loop Systems - Electronics Tutorials - A closed-loop system uses feedback from the output to the input to automatically reduce errors and maintain the desired output, such as a dryer adjusting heat based on moisture sensed in clothes.
Open-Loop vs Closed-Loop Control Systems: Features, Examples ... - A closed loop control system continuously monitors its output and adjusts its input to maintain a desired condition, for example, a thermostat regulating room temperature by feedback.
What is a closed loop control system? - TechTarget - Closed loop control systems automatically regulate a process via feedback without human intervention, such as heating systems using temperature sensors to maintain set points accurately.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com