Grey market shipping involves the import and distribution of genuine products through unauthorized channels, often bypassing official customs regulations and warranty protections. Bonded warehouses are secure storage facilities authorized by customs to hold imported goods without immediate duty payment, ensuring compliance and streamlined clearance upon release. Explore more about how these logistics strategies impact supply chain efficiency and risk management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between grey market shipping and bonded warehouses is crucial for managing supply chain risks and ensuring regulatory compliance. Grey market shipping involves the unauthorized importation of genuine goods, potentially leading to legal issues and warranty invalidation. Bonded warehouses securely store imported goods under customs control, deferring duties until products enter the local market, enhancing cost efficiency. Proper knowledge prevents financial losses and protects brand integrity in global logistics operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Grey Market Shipping | Bonded Warehouses |
|---|---|---|
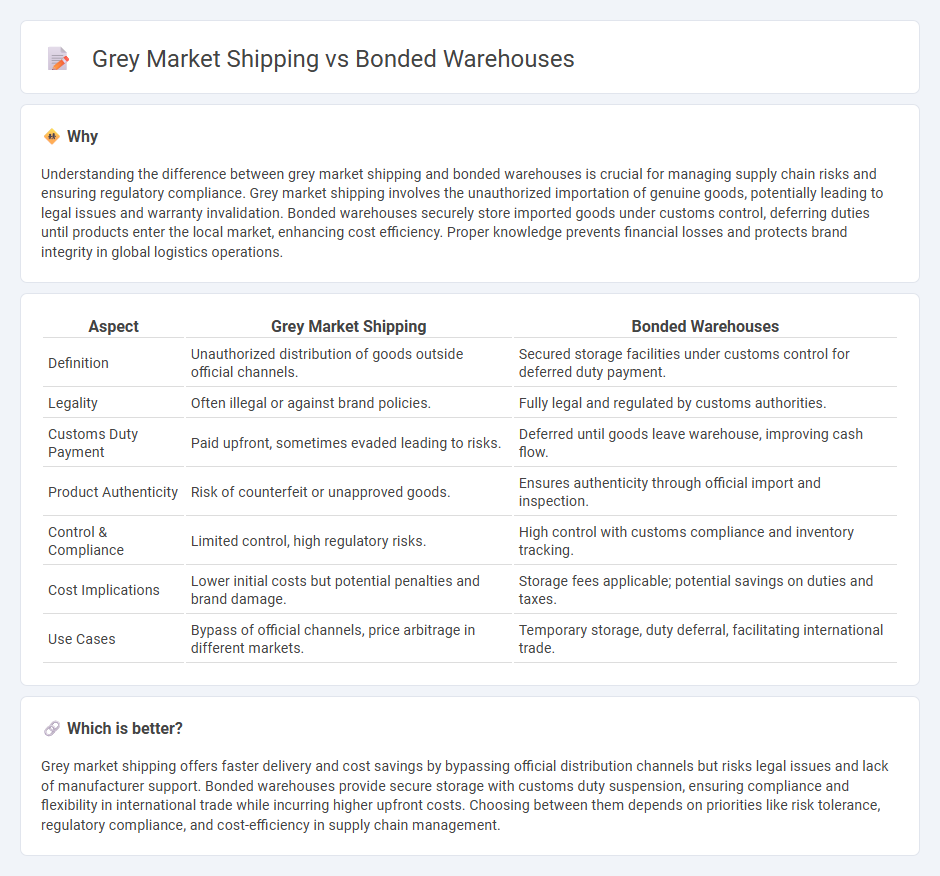
| Definition | Unauthorized distribution of goods outside official channels. | Secured storage facilities under customs control for deferred duty payment. |
| Legality | Often illegal or against brand policies. | Fully legal and regulated by customs authorities. |
| Customs Duty Payment | Paid upfront, sometimes evaded leading to risks. | Deferred until goods leave warehouse, improving cash flow. |
| Product Authenticity | Risk of counterfeit or unapproved goods. | Ensures authenticity through official import and inspection. |
| Control & Compliance | Limited control, high regulatory risks. | High control with customs compliance and inventory tracking. |
| Cost Implications | Lower initial costs but potential penalties and brand damage. | Storage fees applicable; potential savings on duties and taxes. |
| Use Cases | Bypass of official channels, price arbitrage in different markets. | Temporary storage, duty deferral, facilitating international trade. |
Which is better?
Grey market shipping offers faster delivery and cost savings by bypassing official distribution channels but risks legal issues and lack of manufacturer support. Bonded warehouses provide secure storage with customs duty suspension, ensuring compliance and flexibility in international trade while incurring higher upfront costs. Choosing between them depends on priorities like risk tolerance, regulatory compliance, and cost-efficiency in supply chain management.
Connection
Grey market shipping leverages bonded warehouses to store imported goods without immediate customs duties, facilitating the distribution of products outside official supply chains. Bonded warehouses act as secure locations where companies hold inventory under customs control, delaying duty payments until the goods enter the local market or are re-exported. This connection enables grey market operators to minimize costs and navigate regulatory complexities while moving products internationally.
Key Terms
Customs Clearance
Bonded warehouses offer secure storage for imported goods under Customs supervision, allowing deferred payment of duties and taxes until clearance, ensuring legal compliance and reduced risk of penalties. Grey market shipping bypasses authorized channels, often resulting in complications with Customs clearance due to non-compliance with import regulations and potential seizure of goods. Explore detailed differences in Customs clearance procedures to optimize your international shipping strategy.
Duty Payment
Bonded warehouses allow importers to store goods without paying duties immediately, deferring tax payments until the products enter the domestic market, thereby optimizing cash flow and compliance with customs regulations. Grey market shipping circumvents authorized distribution channels, often resulting in improper or unpaid duties, risking penalties and legal consequences. Explore more about how duty payment processes impact international trade strategies and compliance.
Parallel Importation
Bonded warehouses enable companies to store imported goods without immediate customs duty, facilitating parallel importation by allowing products to be efficiently redistributed across different markets. Grey market shipping involves the unauthorized import and sale of genuine goods outside the official distribution channels, often bypassing local regulations and warranty protections. Explore the nuances of these methods to understand their impact on global trade and consumer rights.
Source and External Links
Bonded warehouse - Wikipedia - A bonded warehouse is a secured area where imported dutiable goods can be stored, manipulated, or undergo limited manufacturing operations under customs supervision without paying duty until the goods are exported or withdrawn for consumption, with goods often stored up to five years in the U.S.
Using Bonded Warehouses to Manage Tariff Costs for U.S. E-commerce Businesses - Bonded warehouses allow importers to store goods duty-free for extended periods (often up to five years), improving cash flow and permitting some repackaging or assembly under customs approval before duties are paid upon withdrawal for sale or use.
Bonded warehouse - Logistics of Things - DHL - Bonded warehouses are secure facilities, government- or privately-owned, that store goods before customs duties and taxes are paid, helping businesses better manage inventory and cash flow with legal limits on storage time and restrictions on goods like perishables or explosives.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com