Dynamic route optimization leverages real-time data and advanced algorithms to continuously adjust delivery paths, reducing fuel consumption and improving delivery speed. Static route planning relies on predetermined routes that do not change based on current conditions, often leading to inefficiencies during unexpected delays or traffic changes. Discover how dynamic routing can transform logistics operations and increase overall efficiency.
Why it is important
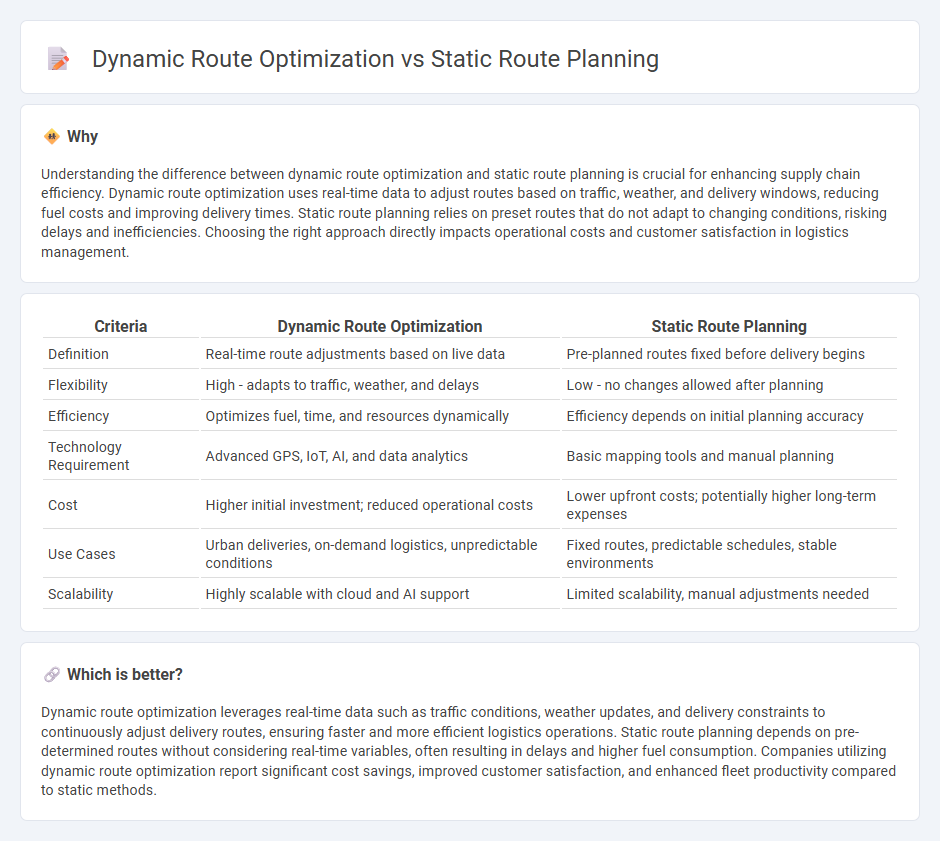
Understanding the difference between dynamic route optimization and static route planning is crucial for enhancing supply chain efficiency. Dynamic route optimization uses real-time data to adjust routes based on traffic, weather, and delivery windows, reducing fuel costs and improving delivery times. Static route planning relies on preset routes that do not adapt to changing conditions, risking delays and inefficiencies. Choosing the right approach directly impacts operational costs and customer satisfaction in logistics management.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Dynamic Route Optimization | Static Route Planning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time route adjustments based on live data | Pre-planned routes fixed before delivery begins |
| Flexibility | High - adapts to traffic, weather, and delays | Low - no changes allowed after planning |
| Efficiency | Optimizes fuel, time, and resources dynamically | Efficiency depends on initial planning accuracy |
| Technology Requirement | Advanced GPS, IoT, AI, and data analytics | Basic mapping tools and manual planning |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; reduced operational costs | Lower upfront costs; potentially higher long-term expenses |
| Use Cases | Urban deliveries, on-demand logistics, unpredictable conditions | Fixed routes, predictable schedules, stable environments |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with cloud and AI support | Limited scalability, manual adjustments needed |
Which is better?
Dynamic route optimization leverages real-time data such as traffic conditions, weather updates, and delivery constraints to continuously adjust delivery routes, ensuring faster and more efficient logistics operations. Static route planning depends on pre-determined routes without considering real-time variables, often resulting in delays and higher fuel consumption. Companies utilizing dynamic route optimization report significant cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced fleet productivity compared to static methods.
Connection
Dynamic route optimization enhances static route planning by continuously adjusting pre-set routes based on real-time traffic, weather, and delivery data. Static route planning establishes efficient baseline routes using historical data and fixed schedules, while dynamic optimization refines these routes to reduce fuel consumption, delivery times, and operational costs. Integrating both approaches improves overall logistics efficiency and responsiveness, ensuring timely deliveries and optimized resource allocation.
Key Terms
Fixed Paths
Static route planning relies on predefined, fixed paths established before travel, ensuring consistent navigation but lacking adaptability to real-time changes. Dynamic route optimization adjusts routes on the fly based on current traffic conditions, road closures, or other unexpected events, improving efficiency and reducing delays. Explore more about how fixed path strategies impact logistics and fleet management efficiency.
Real-Time Data
Static route planning relies on predetermined paths without considering real-time traffic, weather, or road conditions, making it less adaptable to unexpected delays. Dynamic route optimization uses real-time data from GPS, traffic sensors, and historical patterns to continuously adjust routes for improved delivery efficiency and reduced fuel consumption. Explore how leveraging dynamic route optimization can transform logistics by enhancing accuracy and responsiveness.
Adaptive Routing
Static route planning uses predetermined paths based on fixed criteria such as distance or time, lacking real-time adaptability to changing conditions. Dynamic route optimization, particularly with Adaptive Routing, leverages real-time traffic data, weather, and road conditions to continuously update routes for improved efficiency and reduced delays. Explore how Adaptive Routing transforms logistics by enhancing flexibility, reducing costs, and improving delivery reliability.
Source and External Links
What is Static Routing? - CBT Nuggets - Static routing involves manually configuring fixed routes on routers, sending traffic along predetermined paths without using dynamic routing protocols, making it simpler and more predictable but less scalable and flexible than dynamic routing.
Static routing - Wikipedia - Static routing is a routing method where fixed routes are manually set and remain unchanged unless manually edited, with routes defined by destination and gateway, often combined with dynamic routes in the routing table.
Configuring Static Routing - Cisco - Static routes typically have a low administrative distance (default 1) so routers prefer them over dynamic routes, and static routing includes types such as directly connected, fully specified, and floating static routes for backup purposes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com