Collaborative logistics involves multiple organizations sharing resources, information, and transportation to optimize supply chain efficiency and reduce costs. Reverse logistics focuses on the process of returning goods from customers back to sellers or manufacturers for return, repair, recycling, or disposal, emphasizing sustainability and cost recovery. Explore how these distinct logistics strategies can enhance operational performance and environmental responsibility.
Why it is important
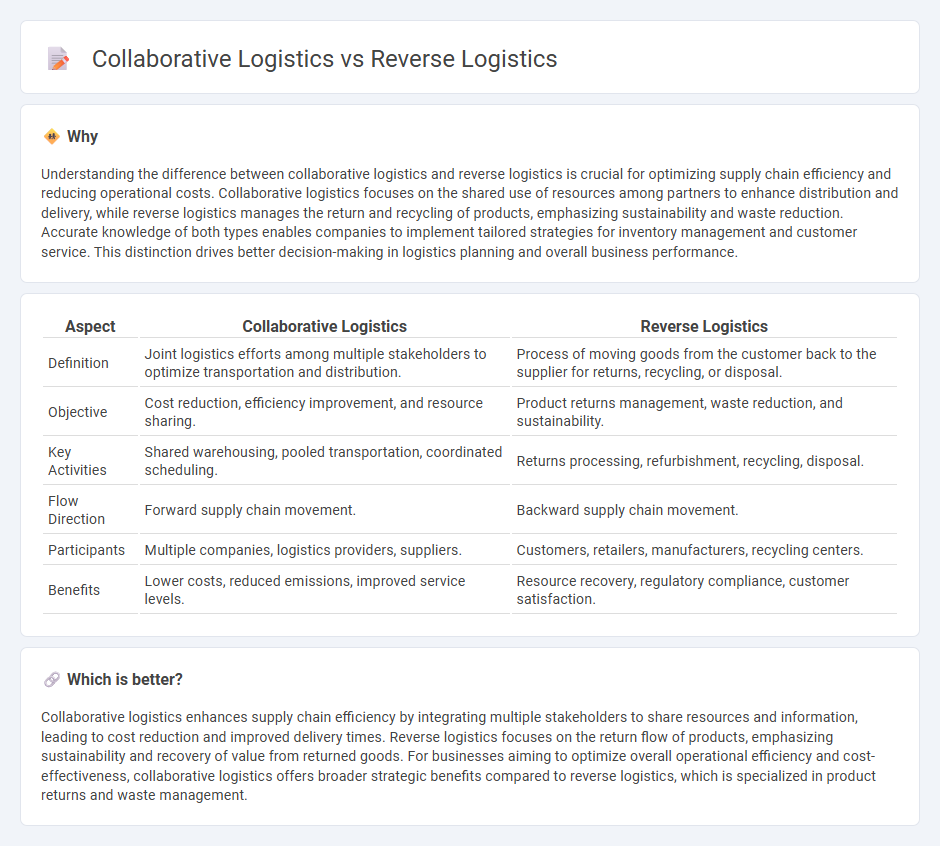
Understanding the difference between collaborative logistics and reverse logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing operational costs. Collaborative logistics focuses on the shared use of resources among partners to enhance distribution and delivery, while reverse logistics manages the return and recycling of products, emphasizing sustainability and waste reduction. Accurate knowledge of both types enables companies to implement tailored strategies for inventory management and customer service. This distinction drives better decision-making in logistics planning and overall business performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Collaborative Logistics | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Joint logistics efforts among multiple stakeholders to optimize transportation and distribution. | Process of moving goods from the customer back to the supplier for returns, recycling, or disposal. |
| Objective | Cost reduction, efficiency improvement, and resource sharing. | Product returns management, waste reduction, and sustainability. |
| Key Activities | Shared warehousing, pooled transportation, coordinated scheduling. | Returns processing, refurbishment, recycling, disposal. |
| Flow Direction | Forward supply chain movement. | Backward supply chain movement. |
| Participants | Multiple companies, logistics providers, suppliers. | Customers, retailers, manufacturers, recycling centers. |
| Benefits | Lower costs, reduced emissions, improved service levels. | Resource recovery, regulatory compliance, customer satisfaction. |
Which is better?
Collaborative logistics enhances supply chain efficiency by integrating multiple stakeholders to share resources and information, leading to cost reduction and improved delivery times. Reverse logistics focuses on the return flow of products, emphasizing sustainability and recovery of value from returned goods. For businesses aiming to optimize overall operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness, collaborative logistics offers broader strategic benefits compared to reverse logistics, which is specialized in product returns and waste management.
Connection
Collaborative logistics and reverse logistics intersect through shared resources and data exchange to enhance supply chain efficiency and sustainability. Collaborative logistics leverages partnerships among multiple stakeholders to optimize transportation, warehousing, and inventory management, which supports the effective collection and processing of returned goods in reverse logistics. Integration of these approaches reduces operational costs, minimizes environmental impact, and improves customer satisfaction by streamlining return flows and asset recovery.
Key Terms
**Reverse Logistics:**
Reverse logistics centers on managing returns, recycling, refurbishment, and disposal of products to optimize sustainability and reduce waste in the supply chain. It involves the efficient handling of returned goods, minimizing costs, and recovering value through processes such as remanufacturing or resale. Explore how reverse logistics can enhance your supply chain's environmental and economic performance.
Returns Management
Reverse logistics centers on the efficient handling of product returns, refurbishments, recycling, and disposal processes, aiming to recover value and reduce waste. Collaborative logistics enhances returns management by integrating multiple stakeholders--suppliers, retailers, and logistics providers--to share data, resources, and strategies for streamlined returns processing and cost reduction. Explore further to understand how these logistics approaches optimize returns management and improve supply chain sustainability.
Remanufacturing
Reverse logistics handles the return and refurbishment of products, emphasizing the efficient recovery of materials for remanufacturing processes. Collaborative logistics integrates multiple stakeholders to optimize supply chain efficiency, enabling shared resources and information flow to enhance remanufacturing outcomes. Explore how these logistics strategies drive sustainable remanufacturing and circular economy initiatives.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - This webpage explains reverse logistics as the process of moving goods from customers back to manufacturers for return, repair, remanufacture, recycling, or disposal.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and... - This guide provides an overview of reverse logistics, including its types, processes, and economic incentives across various industries.
What Is Reverse Logistics in Supply Chain Management? - This article discusses the importance of reverse logistics in managing customer returns, reducing waste, and maximizing product value through processes like remanufacturing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com