Hyper-local delivery focuses on fulfilling customer orders within a small geographic area, often within the same city or neighborhood, enabling faster delivery times and increased customer satisfaction. Direct-to-store delivery bypasses central warehouses by shipping products straight from manufacturers or local suppliers to retail locations, reducing inventory holding costs and improving stock freshness. Explore the advantages, operational strategies, and challenges of both delivery models to optimize your logistics network.
Why it is important
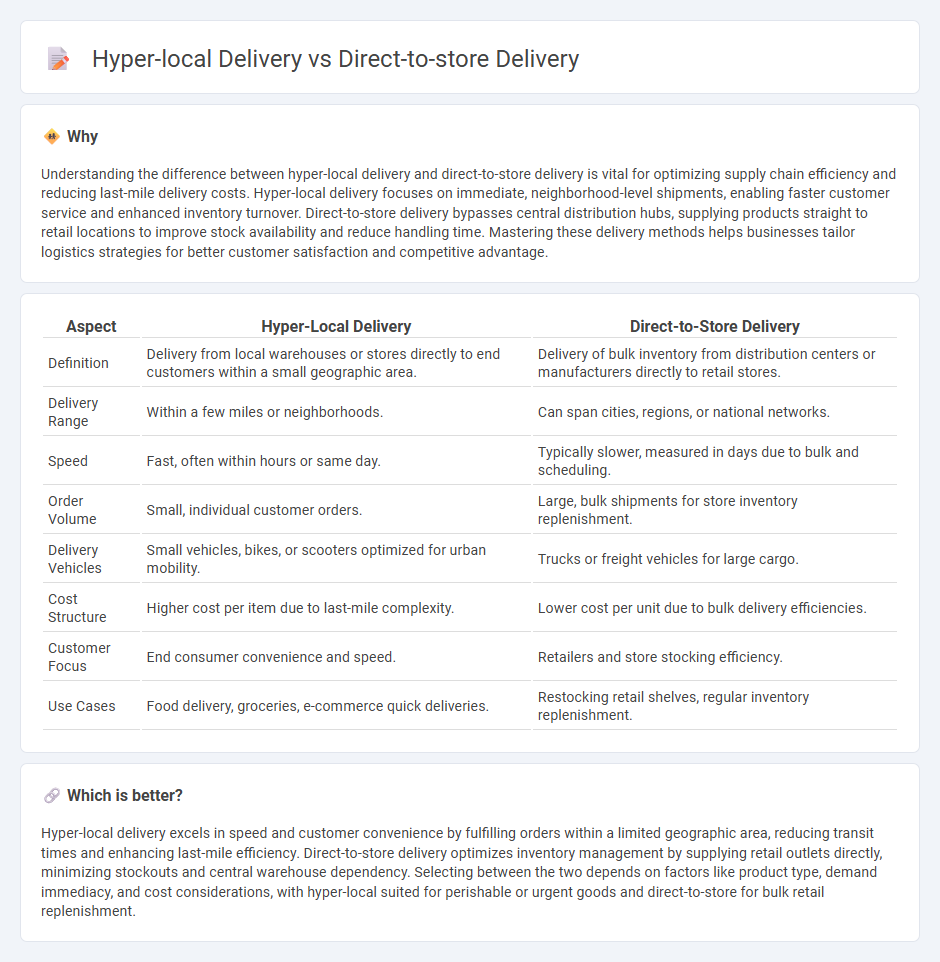
Understanding the difference between hyper-local delivery and direct-to-store delivery is vital for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing last-mile delivery costs. Hyper-local delivery focuses on immediate, neighborhood-level shipments, enabling faster customer service and enhanced inventory turnover. Direct-to-store delivery bypasses central distribution hubs, supplying products straight to retail locations to improve stock availability and reduce handling time. Mastering these delivery methods helps businesses tailor logistics strategies for better customer satisfaction and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Hyper-Local Delivery | Direct-to-Store Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delivery from local warehouses or stores directly to end customers within a small geographic area. | Delivery of bulk inventory from distribution centers or manufacturers directly to retail stores. |
| Delivery Range | Within a few miles or neighborhoods. | Can span cities, regions, or national networks. |
| Speed | Fast, often within hours or same day. | Typically slower, measured in days due to bulk and scheduling. |
| Order Volume | Small, individual customer orders. | Large, bulk shipments for store inventory replenishment. |
| Delivery Vehicles | Small vehicles, bikes, or scooters optimized for urban mobility. | Trucks or freight vehicles for large cargo. |
| Cost Structure | Higher cost per item due to last-mile complexity. | Lower cost per unit due to bulk delivery efficiencies. |
| Customer Focus | End consumer convenience and speed. | Retailers and store stocking efficiency. |
| Use Cases | Food delivery, groceries, e-commerce quick deliveries. | Restocking retail shelves, regular inventory replenishment. |
Which is better?
Hyper-local delivery excels in speed and customer convenience by fulfilling orders within a limited geographic area, reducing transit times and enhancing last-mile efficiency. Direct-to-store delivery optimizes inventory management by supplying retail outlets directly, minimizing stockouts and central warehouse dependency. Selecting between the two depends on factors like product type, demand immediacy, and cost considerations, with hyper-local suited for perishable or urgent goods and direct-to-store for bulk retail replenishment.
Connection
Hyper-local delivery and direct-to-store delivery both optimize supply chain efficiency by reducing last-mile transit times and lowering transportation costs. Hyper-local delivery leverages localized inventory hubs to fulfill orders rapidly within a limited geographic area, while direct-to-store delivery bypasses central warehouses by sending goods directly from suppliers to retail locations. This connection enhances inventory management, ensures fresher product availability, and improves customer satisfaction through faster replenishment cycles.
Key Terms
**Direct-to-Store Delivery:**
Direct-to-Store Delivery (DSD) streamlines inventory management by shipping products directly from manufacturers or distributors to retail stores, bypassing central warehouses. This method enhances product availability and reduces lead times for fast-moving consumer goods, ensuring retailers can quickly restock high-demand items. Explore how DSD can optimize your supply chain efficiency and boost retail performance.
Distribution Center
Direct-to-store delivery (DSD) bypasses Distribution Centers (DCs) by shipping products straight from manufacturers to retail outlets, enhancing speed and reducing handling costs. Hyper-local delivery often relies on DCs as fulfillment hubs to aggregate inventory before rapid last-mile distribution within a confined geographic area, optimizing delivery efficiency and inventory management. Explore how integrating DC strategies can elevate your supply chain performance and customer satisfaction.
Route Optimization
Direct-to-store delivery streamlines supply chains by shipping inventory directly from warehouses to retail outlets, reducing handling and improving inventory turnover rates. Hyper-local delivery emphasizes last-mile efficiency within small geographic areas, leveraging route optimization to ensure rapid fulfillment and reduced transportation costs. Explore how advanced route optimization technologies are transforming both delivery models for maximum operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
What Is Direct-Store Delivery (DSD)? What Are Its Benefits? - FarEye - Direct-Store Delivery (DSD) is a retail distribution model where manufacturers or suppliers deliver products directly to retail stores, bypassing traditional distribution centers, enhancing product freshness, supply chain efficiency, and customer satisfaction through direct order processing, delivery, and in-store merchandising.
The Benefits of Direct-to-Store Delivery - SupplierWiki - DSD is a process used especially for fast-moving or perishable goods like food and beverages, enabling suppliers to deliver directly to stores without going through distribution centers, ensuring speed and synchronicity, particularly important during peak seasons.
What Is Direct Store Delivery? - Bernick's - DSD delivers products straight from suppliers to stores while bypassing retailer distribution centers, often including merchandising services and frequent deliveries, which enhances shelf management, sales control, and retailer-supplier relationships.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com