Cold chain logistics ensures the precise temperature-controlled transportation of perishable goods like pharmaceuticals and food, maintaining product integrity from origin to destination. Freight forwarding involves managing the shipment of goods across multiple modes of transport, optimizing routes, and handling customs to ensure timely delivery. Discover how these critical logistics solutions transform supply chain efficiency and reliability.
Why it is important
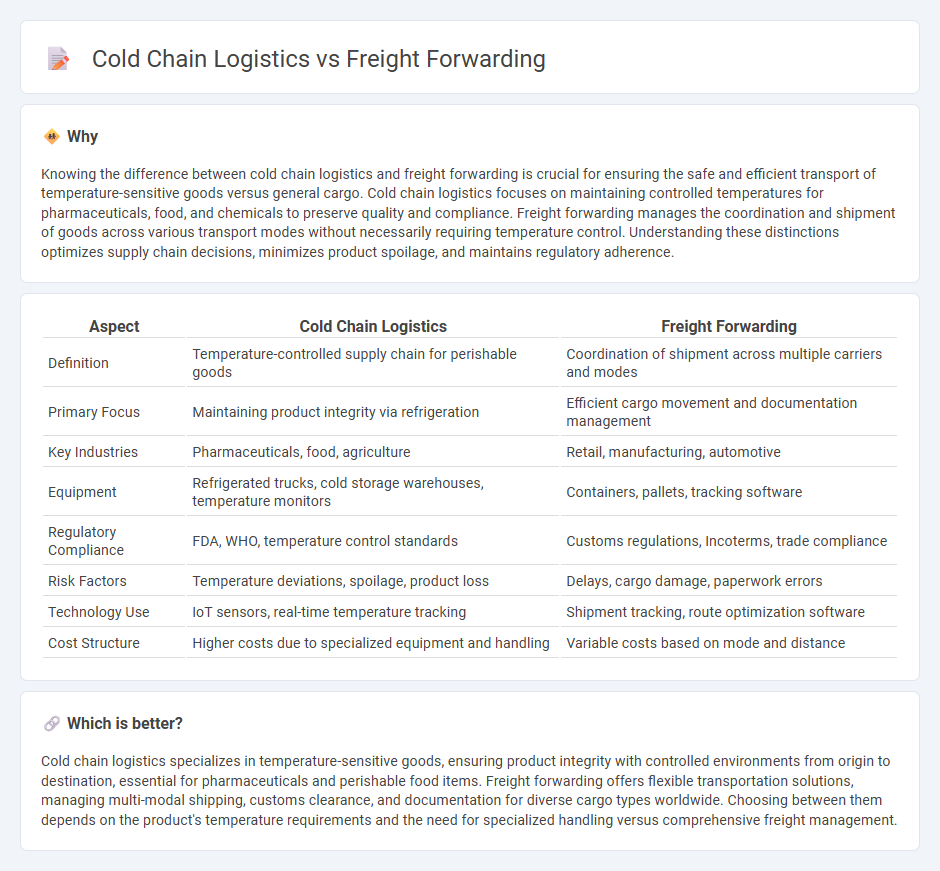
Knowing the difference between cold chain logistics and freight forwarding is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient transport of temperature-sensitive goods versus general cargo. Cold chain logistics focuses on maintaining controlled temperatures for pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals to preserve quality and compliance. Freight forwarding manages the coordination and shipment of goods across various transport modes without necessarily requiring temperature control. Understanding these distinctions optimizes supply chain decisions, minimizes product spoilage, and maintains regulatory adherence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain Logistics | Freight Forwarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods | Coordination of shipment across multiple carriers and modes |
| Primary Focus | Maintaining product integrity via refrigeration | Efficient cargo movement and documentation management |
| Key Industries | Pharmaceuticals, food, agriculture | Retail, manufacturing, automotive |
| Equipment | Refrigerated trucks, cold storage warehouses, temperature monitors | Containers, pallets, tracking software |
| Regulatory Compliance | FDA, WHO, temperature control standards | Customs regulations, Incoterms, trade compliance |
| Risk Factors | Temperature deviations, spoilage, product loss | Delays, cargo damage, paperwork errors |
| Technology Use | IoT sensors, real-time temperature tracking | Shipment tracking, route optimization software |
| Cost Structure | Higher costs due to specialized equipment and handling | Variable costs based on mode and distance |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics specializes in temperature-sensitive goods, ensuring product integrity with controlled environments from origin to destination, essential for pharmaceuticals and perishable food items. Freight forwarding offers flexible transportation solutions, managing multi-modal shipping, customs clearance, and documentation for diverse cargo types worldwide. Choosing between them depends on the product's temperature requirements and the need for specialized handling versus comprehensive freight management.
Connection
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive goods are maintained within optimal conditions during transit, critical for pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals. Freight forwarding coordinates the movement of these temperature-controlled shipments across multiple transport modes and geographies, ensuring timely and compliant delivery. Integration of cold chain logistics with freight forwarding enhances supply chain efficiency, reduces spoilage risks, and meets regulatory standards.
Key Terms
**Freight Forwarding:**
Freight forwarding involves coordinating the shipment of goods across multiple carriers, countries, and transportation modes, ensuring efficient customs clearance and timely delivery. Key aspects include route optimization, documentation management, and cargo consolidation, which help minimize costs and transit times. Explore more to understand how freight forwarding streamlines global supply chain operations.
Documentation
Freight forwarding documentation focuses on bills of lading, commercial invoices, and customs declarations to ensure smooth international shipping processes. Cold chain logistics documentation requires detailed temperature logs, handling instructions, and regulatory compliance forms to maintain product integrity throughout transit. Explore the specific documentation needs of each to optimize your supply chain efficiency.
Carrier Selection
Carrier selection in freight forwarding emphasizes cost-efficiency and transit speed, focusing on optimizing routes and consolidating shipments for diverse cargo types. Cold chain logistics prioritizes carriers with specialized temperature-controlled transport, ensuring product integrity through advanced monitoring systems and compliance with stringent regulatory standards. Explore in-depth strategies to choose the right carrier for your specific shipping needs.
Source and External Links
What is freight forwarding? | Clarksons - Freight forwarding is the strategic planning and coordination of the international movement of goods via air, sea, rail and/or highway transportation, where freight forwarders act as intermediaries managing logistics and customs processes to ensure timely, safe delivery of cargo.
What Is Freight Forwarding? Definition, Benefits and Key Stages - Freight forwarding involves several key stages including export haulage, export customs clearance, and origin handling, whereby the freight forwarder coordinates transport, ensures legal compliance, and inspects shipments for damage or restrictions on behalf of clients.
About Freight Forwarding - FIATA - Freight forwarding encompasses services related to transportation, consolidation, storage, handling, and customs, aiming to facilitate international trade by ensuring goods move efficiently from origin to destination at the right place, time, condition, and cost.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com