Green corridors streamline transportation routes to minimize environmental impact by reducing emissions through optimized pathways and sustainable practices. Reverse logistics focuses on efficiently managing the return, recycling, or disposal of products to support circular economy principles and decrease waste. Explore how these approaches revolutionize supply chain sustainability and operational efficiency.
Why it is important
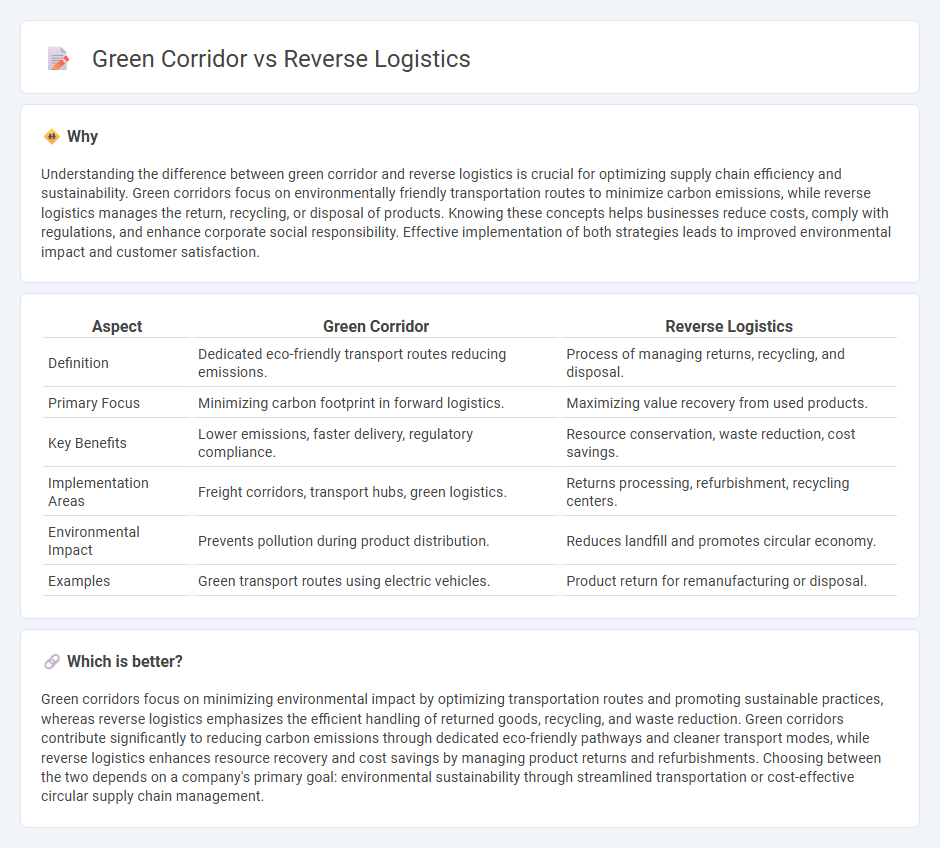
Understanding the difference between green corridor and reverse logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and sustainability. Green corridors focus on environmentally friendly transportation routes to minimize carbon emissions, while reverse logistics manages the return, recycling, or disposal of products. Knowing these concepts helps businesses reduce costs, comply with regulations, and enhance corporate social responsibility. Effective implementation of both strategies leads to improved environmental impact and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Corridor | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dedicated eco-friendly transport routes reducing emissions. | Process of managing returns, recycling, and disposal. |
| Primary Focus | Minimizing carbon footprint in forward logistics. | Maximizing value recovery from used products. |
| Key Benefits | Lower emissions, faster delivery, regulatory compliance. | Resource conservation, waste reduction, cost savings. |
| Implementation Areas | Freight corridors, transport hubs, green logistics. | Returns processing, refurbishment, recycling centers. |
| Environmental Impact | Prevents pollution during product distribution. | Reduces landfill and promotes circular economy. |
| Examples | Green transport routes using electric vehicles. | Product return for remanufacturing or disposal. |
Which is better?
Green corridors focus on minimizing environmental impact by optimizing transportation routes and promoting sustainable practices, whereas reverse logistics emphasizes the efficient handling of returned goods, recycling, and waste reduction. Green corridors contribute significantly to reducing carbon emissions through dedicated eco-friendly pathways and cleaner transport modes, while reverse logistics enhances resource recovery and cost savings by managing product returns and refurbishments. Choosing between the two depends on a company's primary goal: environmental sustainability through streamlined transportation or cost-effective circular supply chain management.
Connection
Green corridors enhance sustainability by streamlining reverse logistics processes to efficiently manage product returns, waste recycling, and resource recovery. Reverse logistics reduces environmental impact through optimized transportation routes and lowered carbon emissions within green corridor frameworks. Integrating both concepts improves supply chain circularity and promotes eco-friendly logistics operations.
Key Terms
Reverse Logistics:
Reverse logistics involves the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer for returns, repairs, recycling, or disposal, optimizing resource use and minimizing waste. It plays a crucial role in sustainability by reducing landfill impact and promoting circular economy principles through efficient recovery and reuse of materials. Discover more about how reverse logistics transforms supply chain sustainability and operational efficiency.
Returns Management
Reverse logistics optimizes the process of returns management by efficiently handling product returns, refurbishments, and recycling to reduce waste and costs. Green corridors emphasize sustainable transportation routes, minimizing carbon emissions and environmental impact during the return journey. Explore how integrating these strategies can enhance returns management and sustainability goals.
Remanufacturing
Reverse logistics involves the process of returning and recycling used products, while green corridors emphasize sustainable transportation routes minimizing environmental impact. In remanufacturing, reverse logistics ensures the efficient collection and handling of returned items, whereas green corridors optimize the supply chain's carbon footprint by promoting eco-friendly transit solutions. Discover how integrating reverse logistics with green corridors can enhance remanufacturing efficiency and sustainability.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - c3controls - Reverse logistics is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the cost-effective flow of goods from the point of consumption back to the origin for return, repair, refurbishment, recycling, or proper disposal, aiming to recapture value and enhance supply chain efficiency by integrating lean principles.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and Strategies - Reverse logistics involves managing returns, refurbishments, or recycling across different industries and typically follows a process including return authorization, scheduling shipments, and handling refunds or replacements to maximize value recapture and sustainability.
Reverse logistics - Wikipedia - Reverse logistics refers to all operations related to the upstream movement of goods from customers back to the manufacturer or distributor to capture value or dispose of them properly, encompassing remanufacturing, refurbishing, and recycling, with significant growth in relevance due to environmental concerns and green supply chain management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com