Dynamic routing optimizes delivery paths in real-time by analyzing current traffic conditions, road closures, and vehicle locations to minimize travel time and costs. Eco-routing focuses on reducing fuel consumption and carbon emissions by selecting routes that promote fuel efficiency, even if they are longer in distance. Discover how integrating these advanced routing strategies can enhance sustainable logistics operations.
Why it is important
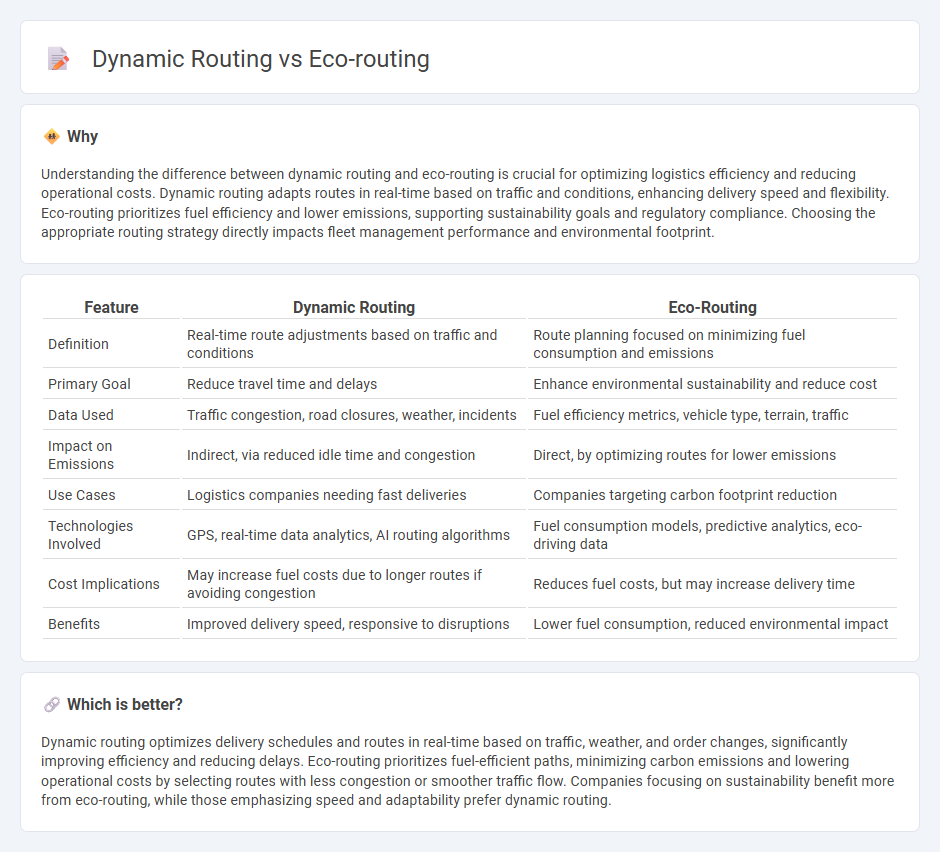
Understanding the difference between dynamic routing and eco-routing is crucial for optimizing logistics efficiency and reducing operational costs. Dynamic routing adapts routes in real-time based on traffic and conditions, enhancing delivery speed and flexibility. Eco-routing prioritizes fuel efficiency and lower emissions, supporting sustainability goals and regulatory compliance. Choosing the appropriate routing strategy directly impacts fleet management performance and environmental footprint.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dynamic Routing | Eco-Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time route adjustments based on traffic and conditions | Route planning focused on minimizing fuel consumption and emissions |
| Primary Goal | Reduce travel time and delays | Enhance environmental sustainability and reduce cost |
| Data Used | Traffic congestion, road closures, weather, incidents | Fuel efficiency metrics, vehicle type, terrain, traffic |
| Impact on Emissions | Indirect, via reduced idle time and congestion | Direct, by optimizing routes for lower emissions |
| Use Cases | Logistics companies needing fast deliveries | Companies targeting carbon footprint reduction |
| Technologies Involved | GPS, real-time data analytics, AI routing algorithms | Fuel consumption models, predictive analytics, eco-driving data |
| Cost Implications | May increase fuel costs due to longer routes if avoiding congestion | Reduces fuel costs, but may increase delivery time |
| Benefits | Improved delivery speed, responsive to disruptions | Lower fuel consumption, reduced environmental impact |
Which is better?
Dynamic routing optimizes delivery schedules and routes in real-time based on traffic, weather, and order changes, significantly improving efficiency and reducing delays. Eco-routing prioritizes fuel-efficient paths, minimizing carbon emissions and lowering operational costs by selecting routes with less congestion or smoother traffic flow. Companies focusing on sustainability benefit more from eco-routing, while those emphasizing speed and adaptability prefer dynamic routing.
Connection
Dynamic routing leverages real-time data such as traffic conditions and delivery schedules to optimize transportation routes, reducing delays and fuel consumption. Eco-routing integrates environmental factors by prioritizing routes that minimize carbon emissions and energy use, often aligning with dynamic routing algorithms for efficient and sustainable logistics. Together, they enhance fleet management by balancing operational efficiency with ecological impact reduction.
Key Terms
**Eco-routing:**
Eco-routing optimizes navigation routes to reduce fuel consumption and minimize environmental impact by choosing paths with less traffic congestion, lower elevation changes, and smoother driving conditions. Unlike traditional dynamic routing, which prioritizes the fastest or shortest paths, eco-routing incorporates real-time data on vehicle emissions, fuel efficiency, and traffic patterns to enhance eco-friendly travel. Explore how eco-routing technology can revolutionize sustainable transportation and cut carbon emissions.
Fuel Efficiency
Eco-routing prioritizes fuel efficiency by selecting routes that minimize fuel consumption through factors like reduced idling, smoother traffic flow, and shorter distances. Dynamic routing adapts routes based on real-time traffic conditions but may not always prioritize fuel savings as its primary goal. Explore further to understand how integrating eco-routing with dynamic data can maximize fuel economy.
Emissions Reduction
Eco-routing optimizes vehicle paths to minimize fuel consumption and reduce greenhouse gas emissions by considering factors like traffic conditions, road grades, and speed limits. Dynamic routing adapts routes in real-time based on current traffic data to improve travel efficiency but does not specifically prioritize emission reduction. Explore how combining eco-routing with dynamic data can further enhance emissions reduction strategies.
Source and External Links
Navigate more sustainably and optimize for fuel savings with eco-friendly routing - Eco-routing is a feature in Google's Routes API that provides routes optimized for fuel or energy efficiency based on vehicle engine type, traffic, road conditions, and factors such as hill steepness and stop-and-go traffic to reduce fuel consumption and CO2 emissions.
Get an eco-friendly route | Routes API - Google for Developers - The Routes API returns both default and eco-friendly routes, optimizing for lower overall fuel consumption and uses data from regional vehicle averages and traffic conditions to estimate fuel savings and emissions reductions, especially effective for hybrid and electric vehicles in urban or hilly settings.
Eco-Routing Algorithm for Energy Savings in Connected Vehicles Using Commercial Navigation Information - An advanced eco-routing algorithm leveraging Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication and commercial APIs identifies the most energy-efficient routes between origins and destinations, achieving up to 10-15% energy savings in real-world tests over baseline routes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com