Cold chain logistics involves temperature-controlled storage and transportation essential for preserving perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals, ensuring quality and safety throughout the supply chain. Warehousing encompasses broader storage solutions that handle a variety of goods, focusing on inventory management, space optimization, and efficient distribution. Explore the key differences and strategic advantages of cold chain versus traditional warehousing to optimize your supply chain operations.
Why it is important
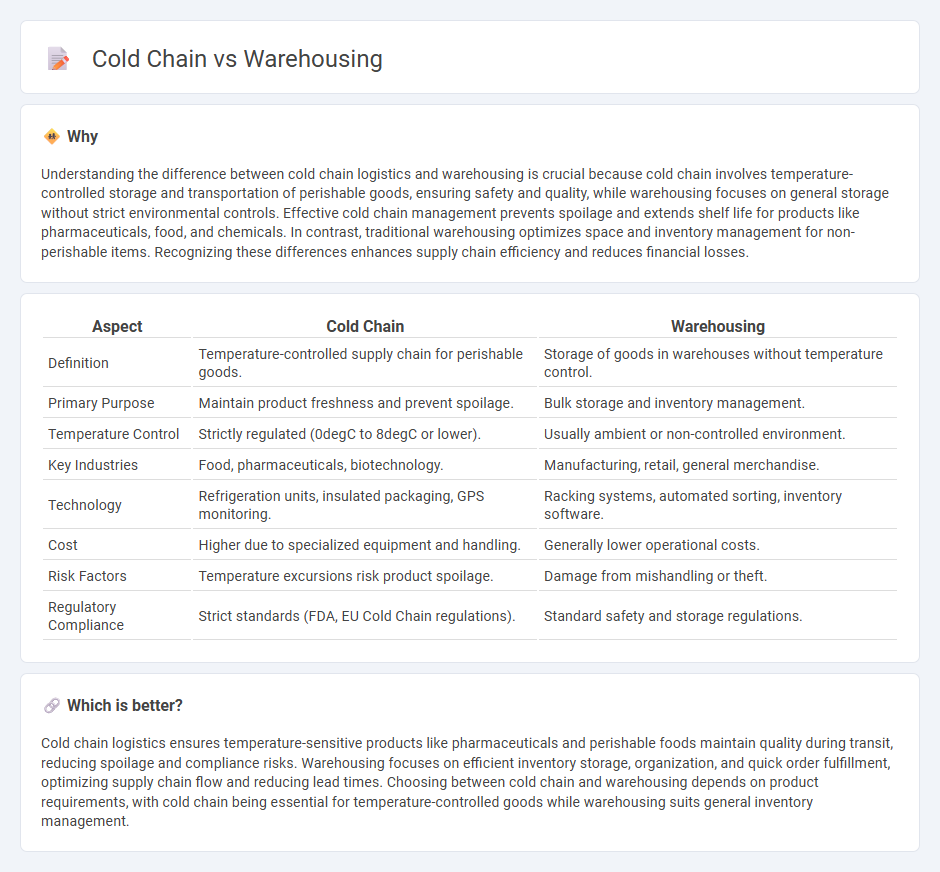
Understanding the difference between cold chain logistics and warehousing is crucial because cold chain involves temperature-controlled storage and transportation of perishable goods, ensuring safety and quality, while warehousing focuses on general storage without strict environmental controls. Effective cold chain management prevents spoilage and extends shelf life for products like pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals. In contrast, traditional warehousing optimizes space and inventory management for non-perishable items. Recognizing these differences enhances supply chain efficiency and reduces financial losses.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain | Warehousing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods. | Storage of goods in warehouses without temperature control. |
| Primary Purpose | Maintain product freshness and prevent spoilage. | Bulk storage and inventory management. |
| Temperature Control | Strictly regulated (0degC to 8degC or lower). | Usually ambient or non-controlled environment. |
| Key Industries | Food, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology. | Manufacturing, retail, general merchandise. |
| Technology | Refrigeration units, insulated packaging, GPS monitoring. | Racking systems, automated sorting, inventory software. |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized equipment and handling. | Generally lower operational costs. |
| Risk Factors | Temperature excursions risk product spoilage. | Damage from mishandling or theft. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strict standards (FDA, EU Cold Chain regulations). | Standard safety and storage regulations. |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals and perishable foods maintain quality during transit, reducing spoilage and compliance risks. Warehousing focuses on efficient inventory storage, organization, and quick order fulfillment, optimizing supply chain flow and reducing lead times. Choosing between cold chain and warehousing depends on product requirements, with cold chain being essential for temperature-controlled goods while warehousing suits general inventory management.
Connection
Cold chain logistics play a crucial role in warehousing by maintaining temperature-controlled environments that ensure the integrity of perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals. Specialized refrigerated warehouses equipped with climate control systems enable safe storage and transit, reducing spoilage and extending product shelf life. Integrating cold chain processes within warehousing optimizes supply chain efficiency and compliance with regulatory standards for temperature-sensitive products.
Key Terms
**Warehousing:**
Warehousing involves the storage, handling, and management of goods in a controlled environment to ensure inventory accuracy and timely distribution. Key elements include inventory management systems, optimized space utilization, and adherence to safety standards to maintain product integrity. Discover how advanced warehousing solutions enhance supply chain efficiency and operational resilience.
Storage
Warehousing primarily involves the storage of non-perishable goods in controlled environments, ensuring inventory management and easy accessibility. Cold chain storage, a specialized segment of warehousing, maintains temperature-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals at specific low temperatures to prevent spoilage. Explore further to understand the crucial role of temperature control in supply chain logistics.
Inventory Management
Warehousing primarily involves storage of non-perishable goods with an emphasis on space optimization, inventory accuracy, and order fulfillment efficiency. Cold chain management requires strict temperature control and monitoring to maintain the integrity of perishable products, such as pharmaceuticals and fresh food, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Explore more about how innovative inventory management solutions enhance both warehousing and cold chain operations.
Source and External Links
What Is Warehousing? Definition, Types, and Key Features - Warehousing is the process of storing goods until ready for transport, involving planning space, managing inventory, and providing climate control to optimize supply chain efficiency.
Warehouse - Wikipedia - A warehouse is a large building for storing goods used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, and wholesalers, equipped with loading docks and material handling equipment, often managed by Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) to increase efficiency.
What Is Warehousing? Definition, Functions and Advantages - Indeed - Warehousing involves storing goods before distribution and includes various types such as private, public, co-op warehouses, and distribution centers, each serving different business needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com