Cold chain logistics involves the transportation and storage of temperature-sensitive products, such as pharmaceuticals and perishable foods, within controlled environments to maintain product integrity. Ambient logistics handles goods that do not require temperature regulation, focusing on efficient movement and storage under normal conditions. Explore the critical differences and best practices to optimize your supply chain management.
Why it is important
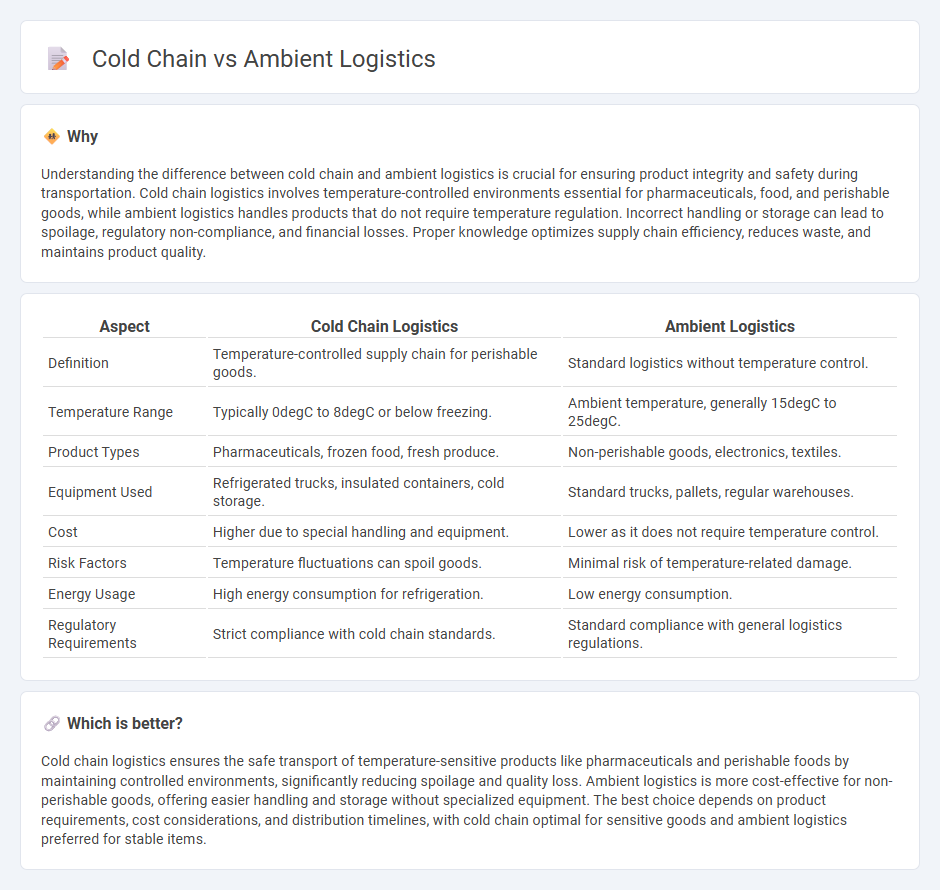
Understanding the difference between cold chain and ambient logistics is crucial for ensuring product integrity and safety during transportation. Cold chain logistics involves temperature-controlled environments essential for pharmaceuticals, food, and perishable goods, while ambient logistics handles products that do not require temperature regulation. Incorrect handling or storage can lead to spoilage, regulatory non-compliance, and financial losses. Proper knowledge optimizes supply chain efficiency, reduces waste, and maintains product quality.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain Logistics | Ambient Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods. | Standard logistics without temperature control. |
| Temperature Range | Typically 0degC to 8degC or below freezing. | Ambient temperature, generally 15degC to 25degC. |
| Product Types | Pharmaceuticals, frozen food, fresh produce. | Non-perishable goods, electronics, textiles. |
| Equipment Used | Refrigerated trucks, insulated containers, cold storage. | Standard trucks, pallets, regular warehouses. |
| Cost | Higher due to special handling and equipment. | Lower as it does not require temperature control. |
| Risk Factors | Temperature fluctuations can spoil goods. | Minimal risk of temperature-related damage. |
| Energy Usage | High energy consumption for refrigeration. | Low energy consumption. |
| Regulatory Requirements | Strict compliance with cold chain standards. | Standard compliance with general logistics regulations. |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics ensures the safe transport of temperature-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals and perishable foods by maintaining controlled environments, significantly reducing spoilage and quality loss. Ambient logistics is more cost-effective for non-perishable goods, offering easier handling and storage without specialized equipment. The best choice depends on product requirements, cost considerations, and distribution timelines, with cold chain optimal for sensitive goods and ambient logistics preferred for stable items.
Connection
Cold chain logistics ensures the temperature-controlled storage and transportation of perishable goods, preserving product quality from origin to destination. Ambient logistics handles non-temperature-sensitive items, but both systems often integrate to optimize supply chain efficiency and reduce overall costs. Combining cold chain and ambient logistics enables comprehensive management of diverse product categories within a single streamlined network.
Key Terms
Temperature Control
Ambient logistics manages goods at stable, non-refrigerated temperatures, ideal for products that do not require strict thermal regulation. Cold chain logistics ensures precise temperature control from storage to transportation, crucial for perishable items like pharmaceuticals and fresh food to maintain quality and safety. Explore the intricacies of temperature-controlled supply chains to optimize your logistics strategy.
Storage Requirements
Ambient logistics involves the storage and transportation of goods under normal temperature conditions, typically ranging from 15degC to 25degC, suitable for non-perishable items like electronics and clothing. Cold chain logistics requires specialized temperature-controlled environments, usually between -18degC and 8degC, to preserve perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals, frozen foods, and fresh produce. Explore the key differences in storage requirements to optimize supply chain efficiency and product integrity.
Product Shelf Life
Ambient logistics manage goods at controlled room temperature, typically between 15degC and 25degC, which suits non-perishable items with longer shelf lives such as canned foods and dry goods. Cold chain logistics maintain products at refrigerated or frozen temperatures, critical for perishable goods like pharmaceuticals, fresh produce, and dairy, significantly extending their product shelf life by slowing microbial growth and enzymatic activity. Explore the detailed differences in how these logistics systems impact product shelf life to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Source and External Links
Ambient Logistics Solutions - Ambient logistics involves high-quality, integrated logistics services primarily for food and drink companies, focusing on efficient storage, transportation, and distribution, including handling vehicles and general cargo with a strong reputation for reliability and professionalism.
Temp-controlled vs. Ambient Warehouses & Types of Products - Ambient logistics refers to managing goods in warehouses where temperature control is moderate to maintain dryness and prevent moisture damage, often used for high-value or perishable goods, combined with optimized transportation to keep products stable throughout the supply chain.
Ambient Logistics LLC | EROAD USA - Ambient Logistics LLC is a logistics company providing end-to-end solutions including consultation, installation, training, and compliance services, focusing on transit and safety management with technologies like ELD and GPS.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com