Shadow fleets operate outside traditional regulatory frameworks, utilizing older or unregistered vessels to reduce costs and bypass restrictions, contrasting with regular fleets that comply fully with international shipping laws and standards. This differentiation impacts global supply chain transparency, risk management, and environmental compliance, with shadow fleets often linked to increased operational risks. Explore further to understand how these fleet types influence global logistics strategies and maritime security.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between shadow fleet and regular fleet is vital for optimizing logistics efficiency and ensuring regulatory compliance. Shadow fleets, often unregistered or unofficial vessels, pose risks such as safety violations, insurance gaps, and tracking challenges, impacting supply chain reliability. Recognizing these distinctions allows companies to mitigate operational risks and enhance transparency in global shipping. This knowledge ultimately supports better resource allocation and strategic planning in logistics management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shadow Fleet | Regular Fleet |
|---|---|---|
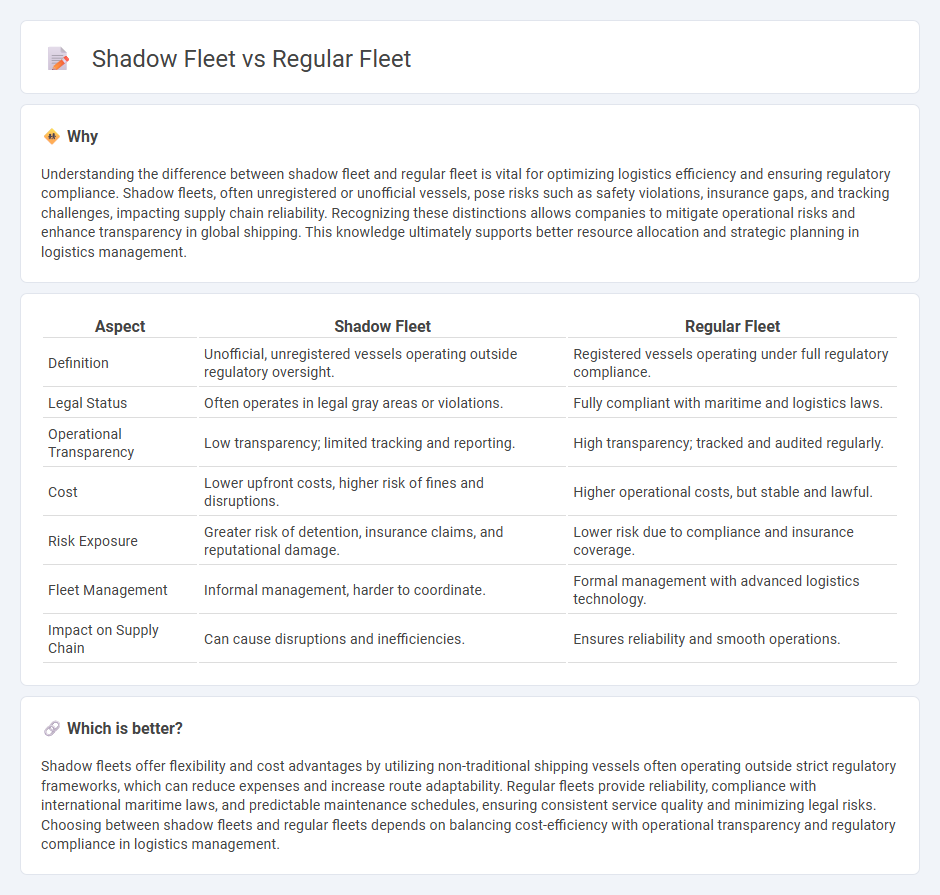
| Definition | Unofficial, unregistered vessels operating outside regulatory oversight. | Registered vessels operating under full regulatory compliance. |
| Legal Status | Often operates in legal gray areas or violations. | Fully compliant with maritime and logistics laws. |
| Operational Transparency | Low transparency; limited tracking and reporting. | High transparency; tracked and audited regularly. |
| Cost | Lower upfront costs, higher risk of fines and disruptions. | Higher operational costs, but stable and lawful. |
| Risk Exposure | Greater risk of detention, insurance claims, and reputational damage. | Lower risk due to compliance and insurance coverage. |
| Fleet Management | Informal management, harder to coordinate. | Formal management with advanced logistics technology. |
| Impact on Supply Chain | Can cause disruptions and inefficiencies. | Ensures reliability and smooth operations. |
Which is better?
Shadow fleets offer flexibility and cost advantages by utilizing non-traditional shipping vessels often operating outside strict regulatory frameworks, which can reduce expenses and increase route adaptability. Regular fleets provide reliability, compliance with international maritime laws, and predictable maintenance schedules, ensuring consistent service quality and minimizing legal risks. Choosing between shadow fleets and regular fleets depends on balancing cost-efficiency with operational transparency and regulatory compliance in logistics management.
Connection
Shadow fleets complement regular fleets by providing additional shipping capacity that helps mitigate risks from port congestion and geopolitical disruptions. These unofficial vessels often operate outside regulatory visibility, creating challenges in supply chain transparency but enhancing flexibility in global logistics operations. Integrating data from both fleets enables better predictive analytics and optimized routing strategies for efficient cargo delivery.
Key Terms
Asset Ownership
Regular fleets typically involve direct asset ownership where companies purchase and maintain vehicles, ensuring control over quality and operational efficiency. Shadow fleets consist of third-party owned vehicles, often leased or subcontracted, offering flexibility but with less control over maintenance and compliance. Explore deeper insights into asset ownership models and their impact on fleet management strategies.
Compliance
Regular fleets operate under strict regulatory compliance, adhering to international maritime laws, safety standards, and environmental regulations to ensure transparent and accountable shipping practices. Shadow fleets, often unregistered or operating under flags of convenience, face significant compliance challenges, increasing risks of legal penalties, environmental harm, and cargo mismanagement. Explore detailed insights on fleet compliance differences and risk mitigation strategies to safeguard your maritime operations.
Tracking Visibility
Regular fleets maintain consistent tracking visibility through standardized GPS systems and centralized monitoring platforms, ensuring real-time data accuracy and route optimization. Shadow fleets, operating unofficially or off-record, lack integrated tracking, resulting in limited visibility, heightened risk of cargo loss, and challenges in accountability. Explore comprehensive strategies to enhance tracking visibility and fleet management efficiency.
Source and External Links
Regular fleet Definition | Law Insider - Regular fleet refers to a group of five or more vehicles registered under the same owner(s) and assigned the same fleet identifier code.
Vehicle fleets | Washington State Department of Licensing - A regular fleet consists of 5 to 49 vehicles operating solely within Washington state, with yearly individual renewals for each vehicle.
Fleet Programs - NYC.gov/Finance - The Regular Fleet Program is designed for businesses with at least one vehicle in their fleet to manage parking violations and related administration easily.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com