Cold chain logistics focuses on the temperature-controlled transportation of perishable goods, ensuring product integrity through refrigeration and monitoring systems. Intermodal logistics integrates multiple transportation modes, such as rail, road, and sea, to optimize efficiency and reduce costs across long-distance supply chains. Explore the key differences and benefits of cold chain and intermodal logistics to enhance your supply chain strategy.
Why it is important
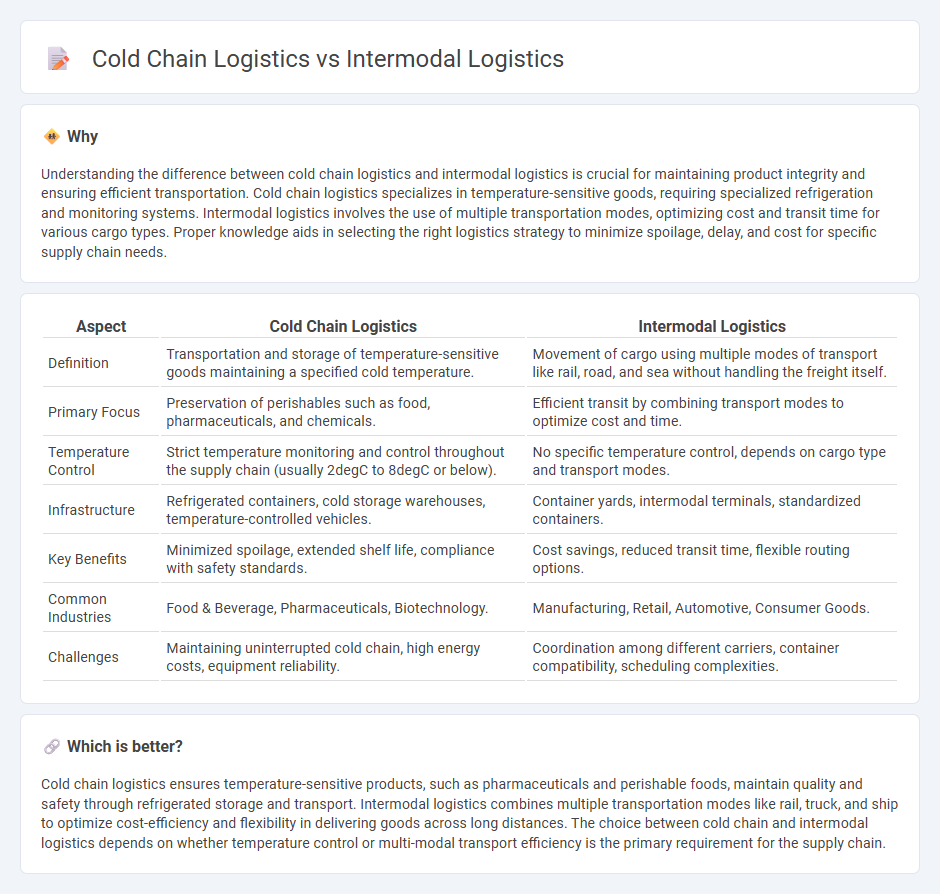
Understanding the difference between cold chain logistics and intermodal logistics is crucial for maintaining product integrity and ensuring efficient transportation. Cold chain logistics specializes in temperature-sensitive goods, requiring specialized refrigeration and monitoring systems. Intermodal logistics involves the use of multiple transportation modes, optimizing cost and transit time for various cargo types. Proper knowledge aids in selecting the right logistics strategy to minimize spoilage, delay, and cost for specific supply chain needs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain Logistics | Intermodal Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transportation and storage of temperature-sensitive goods maintaining a specified cold temperature. | Movement of cargo using multiple modes of transport like rail, road, and sea without handling the freight itself. |
| Primary Focus | Preservation of perishables such as food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. | Efficient transit by combining transport modes to optimize cost and time. |
| Temperature Control | Strict temperature monitoring and control throughout the supply chain (usually 2degC to 8degC or below). | No specific temperature control, depends on cargo type and transport modes. |
| Infrastructure | Refrigerated containers, cold storage warehouses, temperature-controlled vehicles. | Container yards, intermodal terminals, standardized containers. |
| Key Benefits | Minimized spoilage, extended shelf life, compliance with safety standards. | Cost savings, reduced transit time, flexible routing options. |
| Common Industries | Food & Beverage, Pharmaceuticals, Biotechnology. | Manufacturing, Retail, Automotive, Consumer Goods. |
| Challenges | Maintaining uninterrupted cold chain, high energy costs, equipment reliability. | Coordination among different carriers, container compatibility, scheduling complexities. |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products, such as pharmaceuticals and perishable foods, maintain quality and safety through refrigerated storage and transport. Intermodal logistics combines multiple transportation modes like rail, truck, and ship to optimize cost-efficiency and flexibility in delivering goods across long distances. The choice between cold chain and intermodal logistics depends on whether temperature control or multi-modal transport efficiency is the primary requirement for the supply chain.
Connection
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive goods are maintained within precise thermal conditions throughout transport and storage, which often requires specialized containers and equipment. Intermodal logistics enhances this process by combining multiple transportation modes--such as rail, road, and sea--facilitating seamless transfers while preserving cold chain integrity. Together, they optimize supply chain efficiency for perishable products by minimizing temperature fluctuations during multimodal transit.
Key Terms
**Intermodal Logistics:**
Intermodal logistics integrates multiple transportation modes such as rail, road, sea, and air to optimize efficiency and reduce transit times, particularly for long-haul shipments. This approach leverages containerization to enhance cargo security and minimize handling costs, driving improved supply chain sustainability. Explore further to understand the strategic advantages and applications of intermodal logistics in global commerce.
Containerization
Intermodal logistics leverages containerization to seamlessly transfer goods across multiple transportation modes, enhancing efficiency and reducing handling risks. Cold chain logistics integrates specialized refrigerated containers within containerization to maintain strict temperature controls essential for perishable goods during transit. Explore how innovative container solutions optimize both intermodal and cold chain logistics processes for global supply chains.
Multimodal Transport
Intermodal logistics integrates multiple modes of transport such as rail, road, and sea to optimize the movement of goods, while cold chain logistics specifically manages temperature-sensitive products throughout the supply chain to preserve quality. Multimodal transport in intermodal logistics enhances efficiency and flexibility by using standardized containers for seamless transfer between transportation modes, contrasting with cold chain logistics that requires specialized refrigerated vehicles and storage units. Discover how multimodal transport innovations are transforming logistics strategies in both sectors by exploring the latest industry insights.
Source and External Links
Intermodal Transportation 101: Benefits & How It Works - Intermodal logistics involves moving freight in the same container across multiple transport modes (truck, rail, ship), improving efficiency, reducing handling, and providing real-time shipment visibility throughout the journey.
Intermodal transportation - Logistics of Things - DHL - This logistics method uses a single container compatible with different transport modes to ship cargo cost-effectively, lowering lead times, minimizing damage risk, and reducing the carbon footprint by optimizing routes.
Intermodal Logistics & Services - Intermodal logistics integrate multiple transport modes using standardized ISO containers to ensure smooth, secure cargo transport with reduced delays and optimized costs from origin to final delivery.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com