Predictive fleet maintenance leverages IoT sensors and machine learning algorithms to anticipate vehicle breakdowns, reduce downtime, and optimize operational efficiency within logistics networks. Warehouse automation employs robotics, AI-powered sorting systems, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to enhance inventory management, speed up order fulfillment, and minimize human error. Explore how integrating predictive maintenance and warehouse automation can transform your supply chain performance.
Why it is important
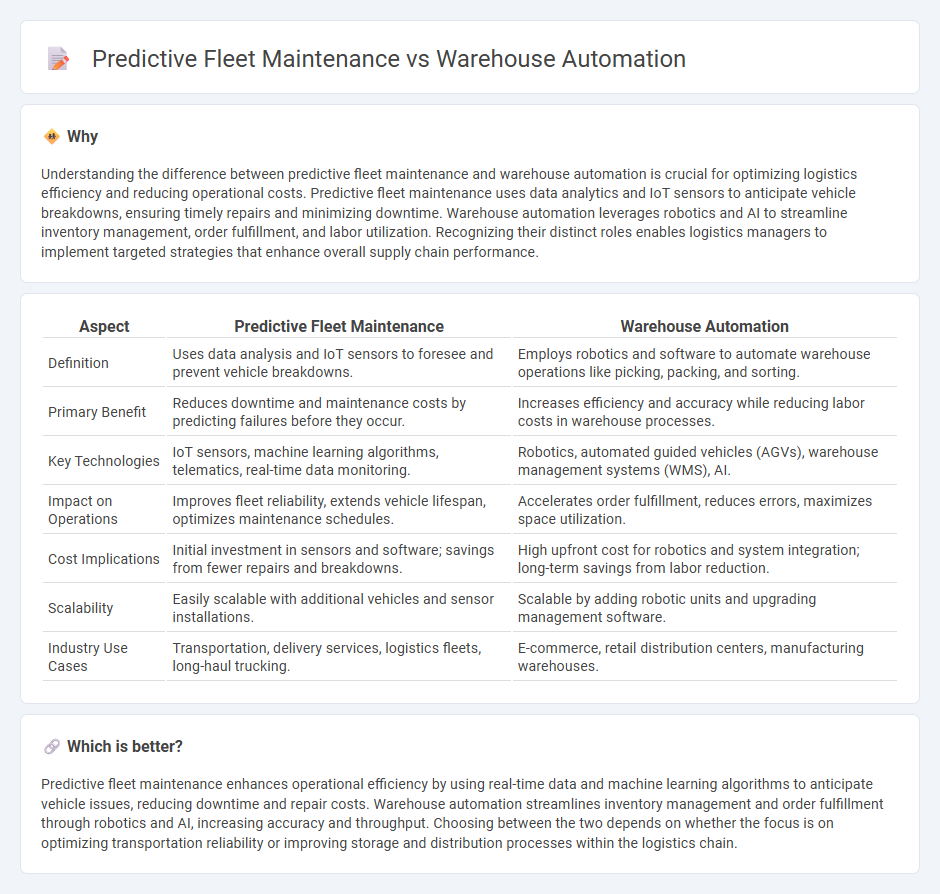
Understanding the difference between predictive fleet maintenance and warehouse automation is crucial for optimizing logistics efficiency and reducing operational costs. Predictive fleet maintenance uses data analytics and IoT sensors to anticipate vehicle breakdowns, ensuring timely repairs and minimizing downtime. Warehouse automation leverages robotics and AI to streamline inventory management, order fulfillment, and labor utilization. Recognizing their distinct roles enables logistics managers to implement targeted strategies that enhance overall supply chain performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Predictive Fleet Maintenance | Warehouse Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses data analysis and IoT sensors to foresee and prevent vehicle breakdowns. | Employs robotics and software to automate warehouse operations like picking, packing, and sorting. |
| Primary Benefit | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs by predicting failures before they occur. | Increases efficiency and accuracy while reducing labor costs in warehouse processes. |
| Key Technologies | IoT sensors, machine learning algorithms, telematics, real-time data monitoring. | Robotics, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), warehouse management systems (WMS), AI. |
| Impact on Operations | Improves fleet reliability, extends vehicle lifespan, optimizes maintenance schedules. | Accelerates order fulfillment, reduces errors, maximizes space utilization. |
| Cost Implications | Initial investment in sensors and software; savings from fewer repairs and breakdowns. | High upfront cost for robotics and system integration; long-term savings from labor reduction. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable with additional vehicles and sensor installations. | Scalable by adding robotic units and upgrading management software. |
| Industry Use Cases | Transportation, delivery services, logistics fleets, long-haul trucking. | E-commerce, retail distribution centers, manufacturing warehouses. |
Which is better?
Predictive fleet maintenance enhances operational efficiency by using real-time data and machine learning algorithms to anticipate vehicle issues, reducing downtime and repair costs. Warehouse automation streamlines inventory management and order fulfillment through robotics and AI, increasing accuracy and throughput. Choosing between the two depends on whether the focus is on optimizing transportation reliability or improving storage and distribution processes within the logistics chain.
Connection
Predictive fleet maintenance leverages IoT sensors and data analytics to anticipate vehicle issues, thereby reducing downtime and improving delivery schedules critical to warehouse operations. Warehouse automation integrates automated systems like robotics and AI to streamline inventory management, which depends on timely fleet performance for supply chain efficiency. The connection between predictive maintenance and warehouse automation enhances overall logistics by synchronizing vehicle reliability with automated material handling, minimizing disruptions and boosting operational productivity.
Key Terms
**Warehouse Automation:**
Warehouse automation leverages advanced robotics, IoT sensors, and AI-driven systems to streamline inventory management, reduce human errors, and enhance operational efficiency. Technologies such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and conveyor systems enable faster order fulfillment while minimizing labor costs. Discover how integrating these innovations can transform your warehouse operations for maximum productivity.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Warehouse automation leverages Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) to enhance inventory handling, reduce labor costs, and increase operational efficiency through autonomous navigation and real-time data integration. Predictive fleet maintenance for AGVs uses IoT sensors and machine learning algorithms to anticipate mechanical failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and extend vehicle lifespan, minimizing downtime and improving reliability. Explore how integrating AGV technology with predictive maintenance transforms warehouse logistics and fleet management strategies.
Conveyor Systems
Warehouse automation enhances conveyor systems by integrating advanced robotics and sensors to streamline material handling and reduce manual labor. Predictive fleet maintenance applies real-time data analytics and IoT technology to monitor conveyor system components, anticipating failures and minimizing downtime. Explore in-depth strategies for optimizing conveyor systems through automation and predictive maintenance.
Source and External Links
Warehouse Automation Explained: Trends, Types & Best Practices - Warehouse automation automates inventory movement in warehouses with minimal human input, involving steps such as forming an implementation committee, collecting critical data, evaluating inventory control, implementing a warehouse management system (WMS), and determining the appropriate automation type based on company goals.
13 Warehouse Automation Trends in 2025 - Implementing warehouse automation requires careful preparation like feasibility studies, defining goals, budget planning, stakeholder involvement, and selecting solutions such as automated material handling, ASRS, autonomous robots, and seamless software integration with existing WMS or ERP systems to enhance efficiency and accuracy.
Warehouse Automation | SSI SCHAEFER - Warehouse automation integrates hardware, software, and control systems including conveyor belts, robotics, AS/RS, and automated guided vehicles to optimize storage, picking, packing, and shipping processes, aiming to reduce manual labor, increase productivity, and improve supply chain performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com