Grey market shipping involves the unauthorized but legal distribution of genuine products through unofficial channels, often bypassing manufacturer controls and warranties. Black market shipping, by contrast, entails the illegal transportation of counterfeit, stolen, or prohibited goods, violating customs and trade laws. Explore the key differences and implications of these shipping methods to understand their impact on global logistics.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between grey market shipping and black market shipping is crucial for businesses to ensure legal compliance and protect brand integrity. Grey market shipping involves the distribution of genuine products through unauthorized channels, which may affect warranty and support but is generally legal. Black market shipping deals with illegal goods that violate laws, posing severe risks including fines, seizures, and reputational damage. Recognizing these distinctions helps companies manage supply chains effectively and avoid financial and legal penalties.
Comparison Table
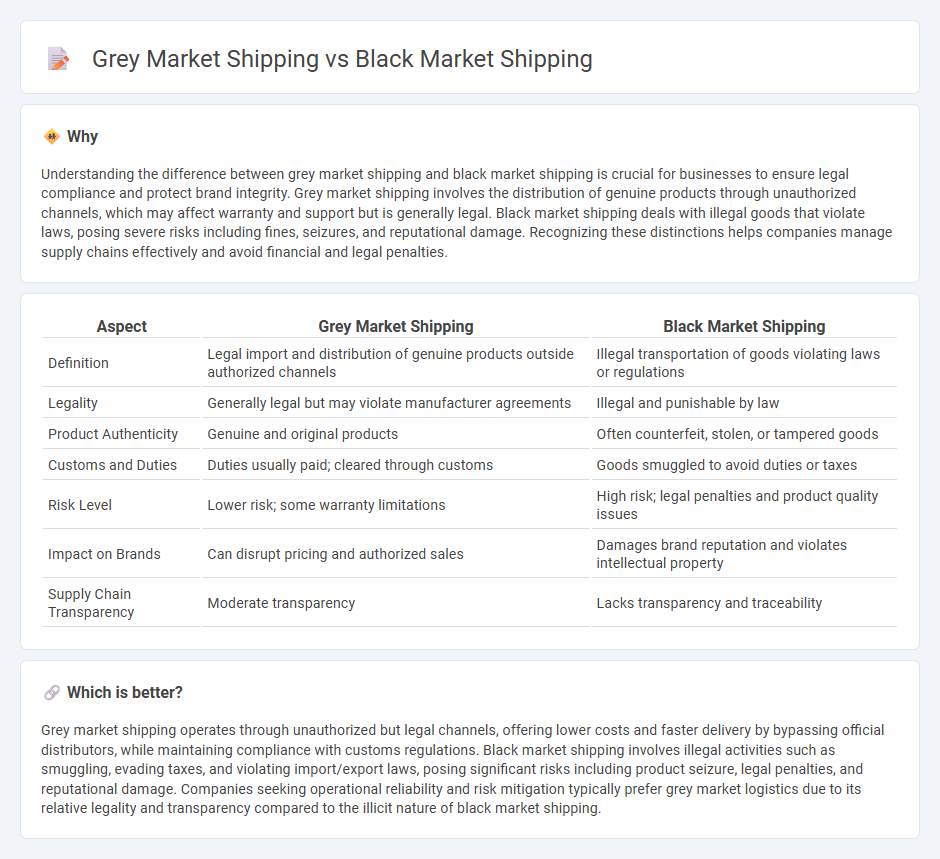
| Aspect | Grey Market Shipping | Black Market Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal import and distribution of genuine products outside authorized channels | Illegal transportation of goods violating laws or regulations |
| Legality | Generally legal but may violate manufacturer agreements | Illegal and punishable by law |
| Product Authenticity | Genuine and original products | Often counterfeit, stolen, or tampered goods |
| Customs and Duties | Duties usually paid; cleared through customs | Goods smuggled to avoid duties or taxes |
| Risk Level | Lower risk; some warranty limitations | High risk; legal penalties and product quality issues |
| Impact on Brands | Can disrupt pricing and authorized sales | Damages brand reputation and violates intellectual property |
| Supply Chain Transparency | Moderate transparency | Lacks transparency and traceability |
Which is better?
Grey market shipping operates through unauthorized but legal channels, offering lower costs and faster delivery by bypassing official distributors, while maintaining compliance with customs regulations. Black market shipping involves illegal activities such as smuggling, evading taxes, and violating import/export laws, posing significant risks including product seizure, legal penalties, and reputational damage. Companies seeking operational reliability and risk mitigation typically prefer grey market logistics due to its relative legality and transparency compared to the illicit nature of black market shipping.
Connection
Grey market shipping involves the unauthorized distribution of goods through unofficial channels, bypassing manufacturers' authorized networks. Black market shipping escalates this by trading goods illegally, often evading customs and regulatory controls, leading to severe legal and economic consequences. Both disrupt legitimate logistics operations, causing challenges in supply chain transparency, inventory management, and compliance enforcement.
Key Terms
Legality
Black market shipping involves illegal trade of goods bypassing customs regulations, resulting in fines, seizures, and criminal charges. Grey market shipping refers to the trade of genuine products through unauthorized channels, legal but often violating trademark or warranty terms. Discover the key distinctions to safeguard your business and ensure compliance.
Parallel Importation
Parallel importation involves importing genuine products through unauthorized channels without the manufacturer's consent, distinguishing it from black market shipping, which deals in counterfeit or illicit goods. Grey market shipping exploits price differentials across regions by distributing authentic items outside official distribution networks, often causing warranty and regulatory issues. Discover more about how parallel importation shapes global trade dynamics and consumer access.
Regulatory Compliance
Black market shipping involves the illegal transportation of goods without adherence to customs regulations, tariff laws, or product safety standards, often resulting in severe legal penalties. Grey market shipping, while involving the importation of genuine products through unauthorized channels, frequently skirts formal regulatory compliance but operates in a legal gray area with risks related to warranties and quality assurance. Explore detailed insights into regulatory compliance challenges in both shipping markets to understand their impact on global trade.
Source and External Links
Shipping policy | BlackMarketLabs.com - BLACKMARKET ships to all U.S. states including Hawaii and Alaska, using economical FedEx 2Day shipping to ensure delivery by the end of the second business day.
Shipping & Payment | BlackMarketMiniatures.net - They provide worldwide shipping with delivery times ranging from 21 to 29 days, with varying shipping costs based on order amount and secure packaging.
Where can I find delivery and shipping info? - Back Market - Back Market ships orders within 1 business day, offers tracking for all shipments, and operates in multiple countries including the U.S. and Europe.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com