Cross docking minimizes storage time by directly transferring inbound shipments to outbound carriers, enhancing supply chain speed and reducing inventory costs. The hub and spoke model centralizes distribution through a main hub, optimizing route efficiency and consolidating shipments for broader reach. Explore the strengths and applications of each method to improve your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
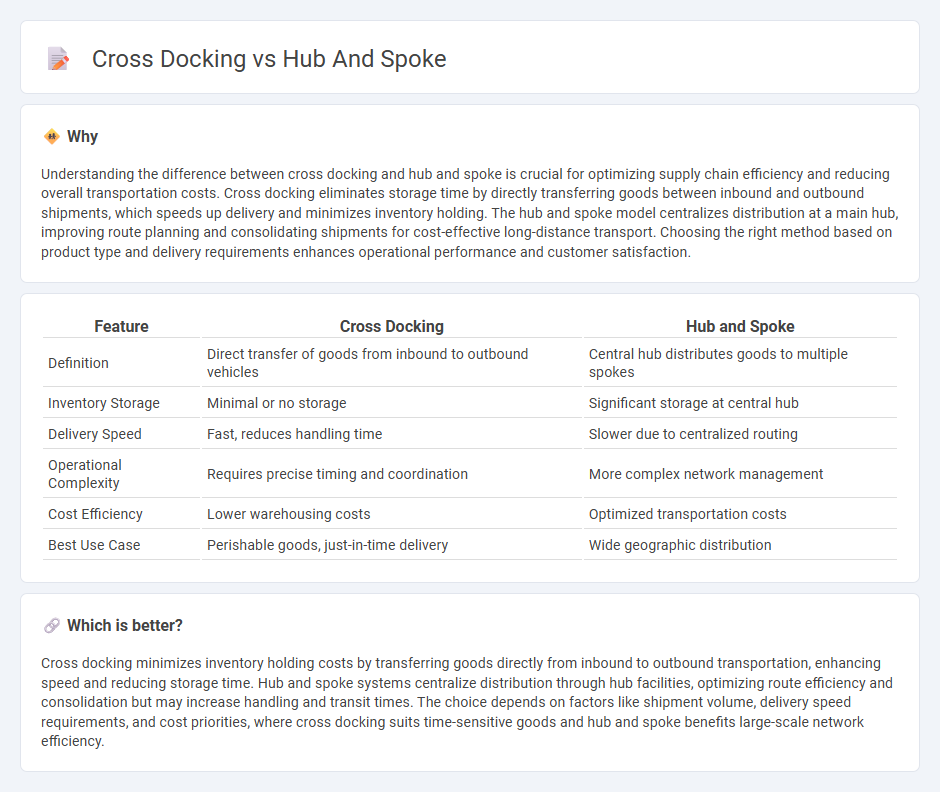
Understanding the difference between cross docking and hub and spoke is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing overall transportation costs. Cross docking eliminates storage time by directly transferring goods between inbound and outbound shipments, which speeds up delivery and minimizes inventory holding. The hub and spoke model centralizes distribution at a main hub, improving route planning and consolidating shipments for cost-effective long-distance transport. Choosing the right method based on product type and delivery requirements enhances operational performance and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cross Docking | Hub and Spoke |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct transfer of goods from inbound to outbound vehicles | Central hub distributes goods to multiple spokes |
| Inventory Storage | Minimal or no storage | Significant storage at central hub |
| Delivery Speed | Fast, reduces handling time | Slower due to centralized routing |
| Operational Complexity | Requires precise timing and coordination | More complex network management |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower warehousing costs | Optimized transportation costs |
| Best Use Case | Perishable goods, just-in-time delivery | Wide geographic distribution |
Which is better?
Cross docking minimizes inventory holding costs by transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound transportation, enhancing speed and reducing storage time. Hub and spoke systems centralize distribution through hub facilities, optimizing route efficiency and consolidation but may increase handling and transit times. The choice depends on factors like shipment volume, delivery speed requirements, and cost priorities, where cross docking suits time-sensitive goods and hub and spoke benefits large-scale network efficiency.
Connection
Cross docking streamlines the transfer of goods by minimizing storage time, aligning closely with the hub and spoke model that centralizes distribution through a main hub to optimize routing. Both strategies enhance supply chain efficiency by reducing inventory holding costs and accelerating delivery times. Integrating cross docking within a hub and spoke system maximizes throughput and improves overall logistics network responsiveness.
Key Terms
Centralized Distribution
Centralized distribution leverages the hub and spoke model by consolidating inventory in a central hub, enhancing efficiency through streamlined inbound and outbound shipments. Cross docking in centralized distribution minimizes storage time by directly transferring goods from incoming to outgoing transportation, reducing inventory holding costs and speeding up delivery. Explore how combining these methods can optimize supply chain performance and reduce operational expenses.
Direct Transfer
Direct transfer in hub and spoke logistics involves consolidating shipments at a central hub before redistribution, enhancing route efficiency but potentially increasing handling time. Cross docking eliminates storage by immediately transferring goods from inbound to outbound transport, minimizing inventory holding and speeding up delivery. Explore the benefits and operational differences between these methods to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Transportation Efficiency
Hub and spoke systems consolidate shipments at central hubs to optimize transportation routes and reduce overall costs, making them ideal for managing large-scale distribution networks. Cross docking minimizes storage time by directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound transport, significantly speeding up delivery and improving inventory turnover. Explore these logistics strategies in detail to enhance your supply chain's transportation efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is a Hub-and-Spoke Network: 9 Tips, Benefits & Limitations - A hub-and-spoke network is a centralized structure where a central "hub" coordinates with multiple "spoke" partners, streamlining communication and resource allocation by having spokes communicate only through the hub.
Spoke-hub distribution paradigm - Wikipedia - The hub-and-spoke system is a transport and logistics model that optimizes routes by connecting multiple outlying points (spokes) to a central hub, widely used in airlines and package delivery since the 1950s.
Hub-spoke network topology in Azure - Azure Architecture Center - In cloud networking, the hub-spoke topology connects multiple spoke virtual networks to a central hub network that hosts shared services and manages cross-network communication, traffic control, and gateway access.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com