Grey market shipping involves importing products through unauthorized channels, often resulting in lower costs but potentially lacking manufacturer warranties and support. Direct shipping guarantees authentic products with full manufacturer backing, ensuring reliability and compliance with regional regulations. Explore the key differences and benefits of each shipping method to optimize your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between grey market shipping and direct shipping is crucial for logistics professionals to ensure compliance with international trade regulations and avoid legal risks. Grey market shipping involves the unauthorized distribution of genuine products, often bypassing official channels, which can lead to warranty issues and intellectual property infringements. Direct shipping guarantees products are sourced through official suppliers, ensuring authenticity, quality control, and reliable customer service. Efficient logistics management relies on distinguishing these channels to optimize supply chain integrity and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
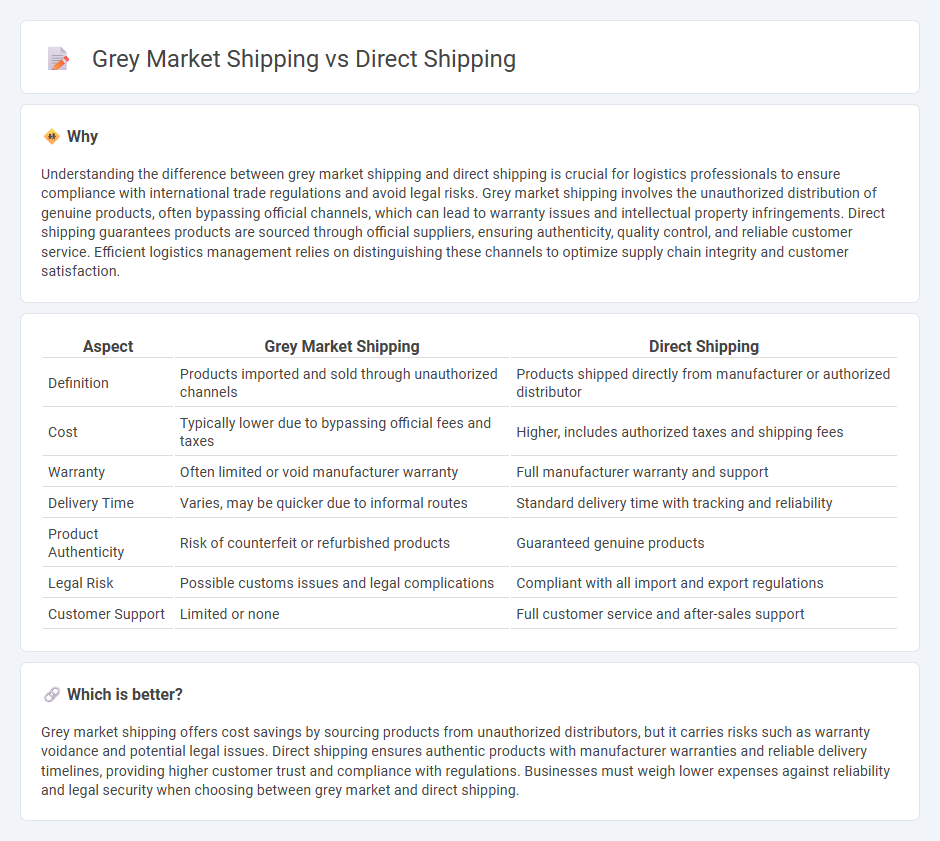
| Aspect | Grey Market Shipping | Direct Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Products imported and sold through unauthorized channels | Products shipped directly from manufacturer or authorized distributor |
| Cost | Typically lower due to bypassing official fees and taxes | Higher, includes authorized taxes and shipping fees |
| Warranty | Often limited or void manufacturer warranty | Full manufacturer warranty and support |
| Delivery Time | Varies, may be quicker due to informal routes | Standard delivery time with tracking and reliability |
| Product Authenticity | Risk of counterfeit or refurbished products | Guaranteed genuine products |
| Legal Risk | Possible customs issues and legal complications | Compliant with all import and export regulations |
| Customer Support | Limited or none | Full customer service and after-sales support |
Which is better?
Grey market shipping offers cost savings by sourcing products from unauthorized distributors, but it carries risks such as warranty voidance and potential legal issues. Direct shipping ensures authentic products with manufacturer warranties and reliable delivery timelines, providing higher customer trust and compliance with regulations. Businesses must weigh lower expenses against reliability and legal security when choosing between grey market and direct shipping.
Connection
Grey market shipping involves the unauthorized distribution of genuine goods through unofficial channels, often bypassing standard logistics protocols and customs regulations. Direct shipping, wherein products are sent straight from manufacturer to consumer, can inadvertently facilitate grey market activities by reducing oversight and increasing the risk of unauthorized reselling. Both practices impact supply chain control, making robust tracking and compliance measures essential to mitigate risks associated with counterfeit or diverted products.
Key Terms
Distribution Channels
Direct shipping leverages authorized distribution channels to ensure products move from manufacturers directly to customers, maintaining brand integrity and warranty support. Grey market shipping exploits unauthorized distribution networks, often resulting in lower costs but potential risks such as lack of official warranty and variable product authenticity. Explore the differences in distribution strategies and their impacts on consumer trust and product availability for deeper insights.
Authorized Dealers
Authorized dealers utilize direct shipping to guarantee product authenticity, warranty validation, and adherence to brand standards, enhancing consumer trust and satisfaction. In contrast, grey market shipping bypasses official distribution channels, often resulting in voided warranties and questionable product provenance. Explore the key differences to safeguard your purchases and ensure genuine buying experiences.
Parallel Importation
Parallel importation involves purchasing genuine products from authorized markets and selling them in unauthorized markets without the brand owner's approval, often leading to price differences and varied warranty conditions. Direct shipping typically ensures products come straight from the official manufacturer or authorized distributor, guaranteeing product authenticity and full warranty support. Explore the implications of parallel importation on consumer rights and product quality to better understand its impact on global trade.
Source and External Links
Direct Shipping: Definition, Advantages, Disadvantages - Direct shipping is a method where goods are shipped directly from the supplier to the customer, bypassing intermediaries like warehouses, saving logistics costs but with no quality guarantee from the seller's side.
What Is Direct Shipping? Pros and Cons of Direct Shipping - Direct shipping is an in-house fulfillment method where sellers handle inventory and ship products directly to customers, providing faster delivery and more control over packaging compared to indirect shipping.
Direct Shipping: A Comprehensive Guide - Direct shipping involves suppliers shipping products directly to customers on behalf of retailers, reducing storage costs and offering better control over branding compared to dropshipping, which involves no inventory ownership.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com