Quick commerce focuses on ultra-fast delivery of everyday essentials within minutes, leveraging localized micro-fulfillment centers and advanced inventory management systems. Grocery delivery typically involves larger order volumes with scheduled delivery windows, supported by centralized warehouses and optimized routing algorithms. Explore the key differences and innovations driving efficiency in both logistics models.
Why it is important
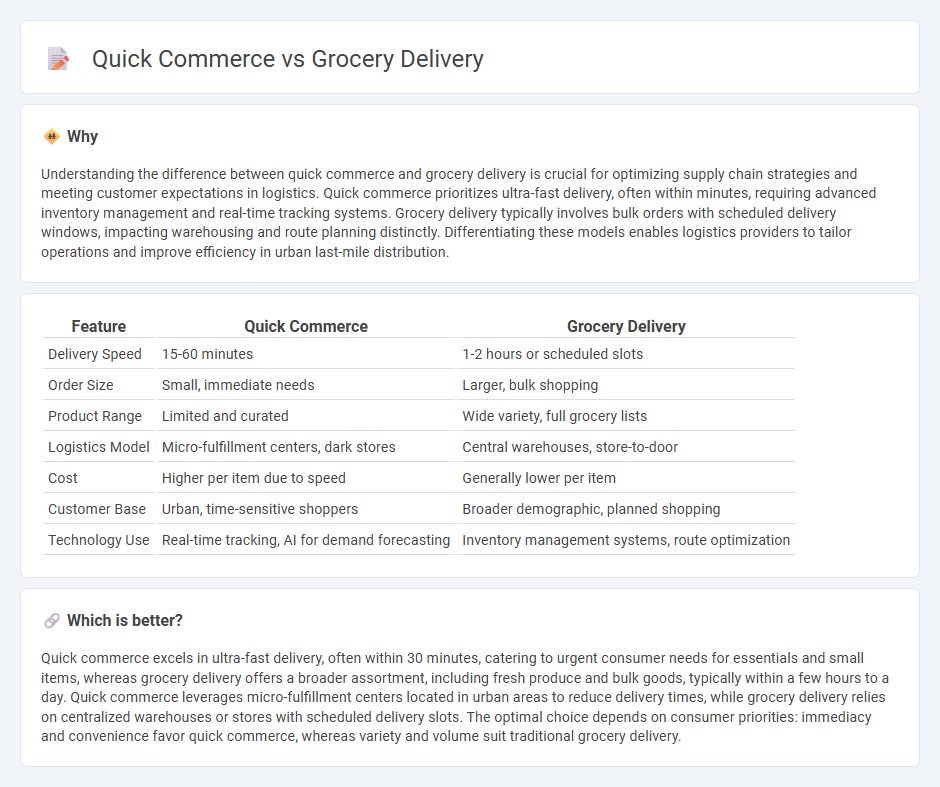
Understanding the difference between quick commerce and grocery delivery is crucial for optimizing supply chain strategies and meeting customer expectations in logistics. Quick commerce prioritizes ultra-fast delivery, often within minutes, requiring advanced inventory management and real-time tracking systems. Grocery delivery typically involves bulk orders with scheduled delivery windows, impacting warehousing and route planning distinctly. Differentiating these models enables logistics providers to tailor operations and improve efficiency in urban last-mile distribution.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Quick Commerce | Grocery Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Speed | 15-60 minutes | 1-2 hours or scheduled slots |
| Order Size | Small, immediate needs | Larger, bulk shopping |
| Product Range | Limited and curated | Wide variety, full grocery lists |
| Logistics Model | Micro-fulfillment centers, dark stores | Central warehouses, store-to-door |
| Cost | Higher per item due to speed | Generally lower per item |
| Customer Base | Urban, time-sensitive shoppers | Broader demographic, planned shopping |
| Technology Use | Real-time tracking, AI for demand forecasting | Inventory management systems, route optimization |
Which is better?
Quick commerce excels in ultra-fast delivery, often within 30 minutes, catering to urgent consumer needs for essentials and small items, whereas grocery delivery offers a broader assortment, including fresh produce and bulk goods, typically within a few hours to a day. Quick commerce leverages micro-fulfillment centers located in urban areas to reduce delivery times, while grocery delivery relies on centralized warehouses or stores with scheduled delivery slots. The optimal choice depends on consumer priorities: immediacy and convenience favor quick commerce, whereas variety and volume suit traditional grocery delivery.
Connection
Quick commerce accelerates grocery delivery by leveraging advanced logistics networks and real-time inventory systems that reduce order fulfillment time to minutes. Dark stores and micro-fulfillment centers located close to urban areas enable rapid last-mile delivery, enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Integration of AI-driven route optimization and demand forecasting further streamlines the supply chain, minimizing costs and ensuring fresh product availability.
Key Terms
Last-mile delivery
Grocery delivery services prioritize scheduled shipments with bulk orders, optimizing routes for cost-efficiency in last-mile delivery, while quick commerce emphasizes ultra-fast, on-demand delivery often within minutes, relying on micro-fulfillment centers and real-time route adjustments. The last-mile delivery in quick commerce faces challenges such as higher operational costs and the need for dense urban infrastructure to ensure speed and customer satisfaction. Explore how innovations in logistics and technology are transforming last-mile delivery in both sectors.
Fulfillment centers
Fulfillment centers in grocery delivery are typically larger facilities designed to store and manage a broad range of products, enabling efficient batch processing and scheduled deliveries. Quick commerce fulfillment centers, by contrast, operate as smaller, strategically located dark stores aimed at rapid order picking and immediate last-mile delivery within minutes. Discover more about how these fulfillment models transform urban logistics and consumer expectations.
Delivery time window
Quick commerce offers ultra-fast delivery typically within 30 minutes, surpassing traditional grocery delivery time windows that range from one to several hours. This tight delivery window is powered by localized micro-fulfillment centers designed to rapidly handle frequent, small baskets. Explore how these innovative logistics models are transforming consumer expectations and operational efficiency in retail.
Source and External Links
ALDI Grocery Delivery - ALDI offers same-day grocery delivery, where a personal shopper selects your items and notifies you about replacements or out-of-stock items, with final charges adjusted based on actual weight, substitutions, and availability.
DoorDash Grocery Delivery Near Me - DoorDash provides on-demand delivery from national and local grocery stores, allowing you to choose substitutions or get refunds for out-of-stock items, with DashPass members enjoying $0 delivery fees on eligible orders.
Walmart Food & Online Groceries - Walmart.com offers a wide range of groceries for online purchase with options for pickup or delivery the next day, featuring fresh produce, dairy, meat, and pantry staples.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com