Empty miles reduction focuses on minimizing the distance trucks travel without cargo, significantly cutting fuel costs and carbon emissions. Co-loading leverages shared transportation resources by combining multiple shipments into a single vehicle, enhancing load efficiency and reducing overall freight expenses. Explore how integrating these strategies can optimize your logistics operations and boost sustainability.
Why it is important
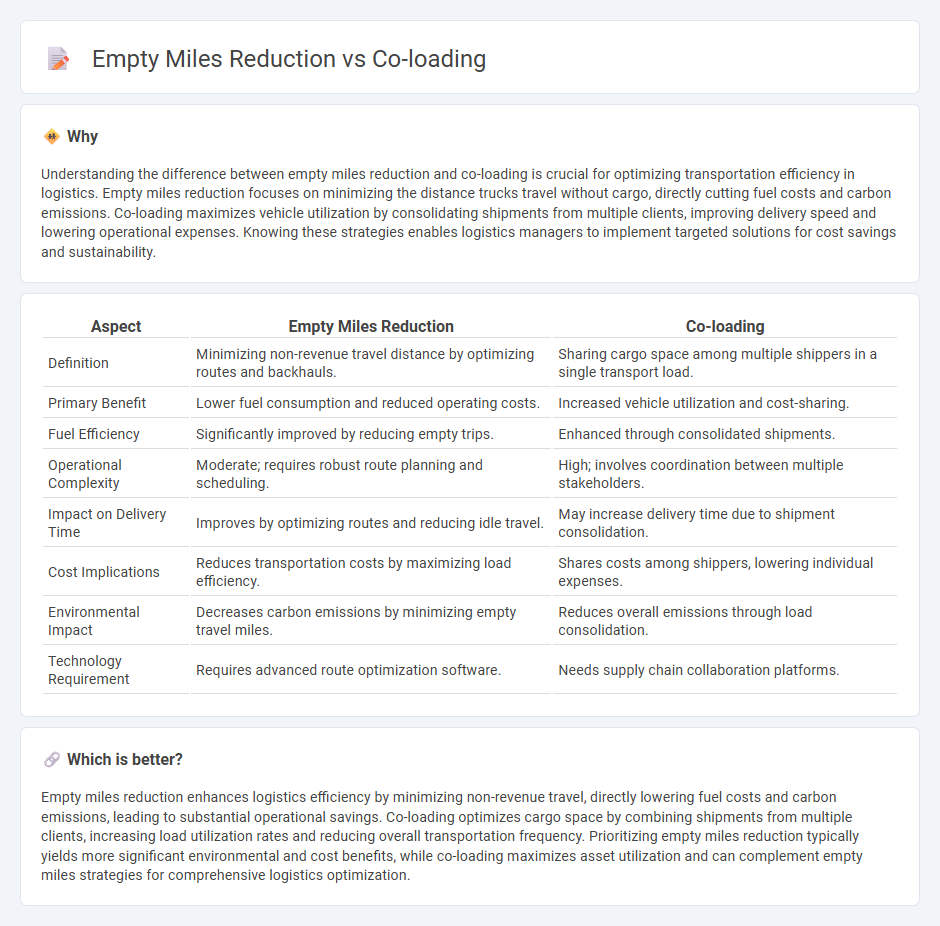
Understanding the difference between empty miles reduction and co-loading is crucial for optimizing transportation efficiency in logistics. Empty miles reduction focuses on minimizing the distance trucks travel without cargo, directly cutting fuel costs and carbon emissions. Co-loading maximizes vehicle utilization by consolidating shipments from multiple clients, improving delivery speed and lowering operational expenses. Knowing these strategies enables logistics managers to implement targeted solutions for cost savings and sustainability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Empty Miles Reduction | Co-loading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimizing non-revenue travel distance by optimizing routes and backhauls. | Sharing cargo space among multiple shippers in a single transport load. |
| Primary Benefit | Lower fuel consumption and reduced operating costs. | Increased vehicle utilization and cost-sharing. |
| Fuel Efficiency | Significantly improved by reducing empty trips. | Enhanced through consolidated shipments. |
| Operational Complexity | Moderate; requires robust route planning and scheduling. | High; involves coordination between multiple stakeholders. |
| Impact on Delivery Time | Improves by optimizing routes and reducing idle travel. | May increase delivery time due to shipment consolidation. |
| Cost Implications | Reduces transportation costs by maximizing load efficiency. | Shares costs among shippers, lowering individual expenses. |
| Environmental Impact | Decreases carbon emissions by minimizing empty travel miles. | Reduces overall emissions through load consolidation. |
| Technology Requirement | Requires advanced route optimization software. | Needs supply chain collaboration platforms. |
Which is better?
Empty miles reduction enhances logistics efficiency by minimizing non-revenue travel, directly lowering fuel costs and carbon emissions, leading to substantial operational savings. Co-loading optimizes cargo space by combining shipments from multiple clients, increasing load utilization rates and reducing overall transportation frequency. Prioritizing empty miles reduction typically yields more significant environmental and cost benefits, while co-loading maximizes asset utilization and can complement empty miles strategies for comprehensive logistics optimization.
Connection
Empty miles reduction and co-loading are interconnected strategies that enhance logistics efficiency by minimizing unproductive transportation. Reducing empty miles lowers fuel consumption and operational costs by ensuring trucks carry loads more consistently, while co-loading optimizes vehicle capacity by combining shipments from multiple customers. Together, these practices improve route planning, decrease carbon emissions, and increase overall supply chain sustainability.
Key Terms
Load Optimization
Load optimization directly impacts reducing empty miles by ensuring vehicles are maximally utilized through strategic co-loading, which pairs compatible shipments to fill truck capacity efficiently. Implementing advanced load optimization software can decrease operational costs and carbon emissions by minimizing underutilized routes. Discover innovative load optimization techniques to enhance your logistics performance and reduce empty miles.
Backhauling
Backhauling efficiently reduces empty miles by transporting freight on return trips, maximizing truck utilization and cutting operational costs. Co-loading consolidates multiple shipments into a single load, enhancing route optimization and minimizing unnecessary mileage. Explore how strategic backhauling and co-loading synergize to revolutionize logistics efficiency.
Freight Consolidation
Freight consolidation significantly reduces empty miles by optimizing load capacity and combining shipments from multiple clients into a single transport, enhancing operational efficiency. Co-loading strategies leverage this by sharing truck space, cutting down on partial loads and minimizing fuel consumption across supply chains. Explore more insights on how freight consolidation drives sustainability and cost savings in logistics.
Source and External Links
What is a Co-Loader? - Co-loading is a logistics service where a provider consolidates cargo from multiple shippers into one shipment under a single bill of lading, enabling cost savings and efficient transport by sharing container space among smaller shipments.
Definition of Co-Loading - Co-loading refers to sharing space on a trailer or container and splitting the shipping cost, often used for less-than-truckload (LTL) shipments or vehicles to reduce time and expenses by bypassing hub-and-spoke networks.
Co-Loading: Ride-Sharing for Freight - Co-loading is the freight equivalent of ride-sharing where multiple companies share space in the same vehicle or container to split costs, improve operational efficiency, reduce carbon footprint, and better utilize trailer capacity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com