Crowdsourced delivery platforms leverage a decentralized network of independent contributors to fulfill last-mile logistics, optimizing flexibility and reducing operational costs. Gig economy delivery apps utilize a similar model but focus on providing app-based, on-demand workforce solutions primarily for food and parcel delivery, emphasizing speed and user experience. Explore the differences and benefits of each model to understand their impact on modern logistics.
Why it is important
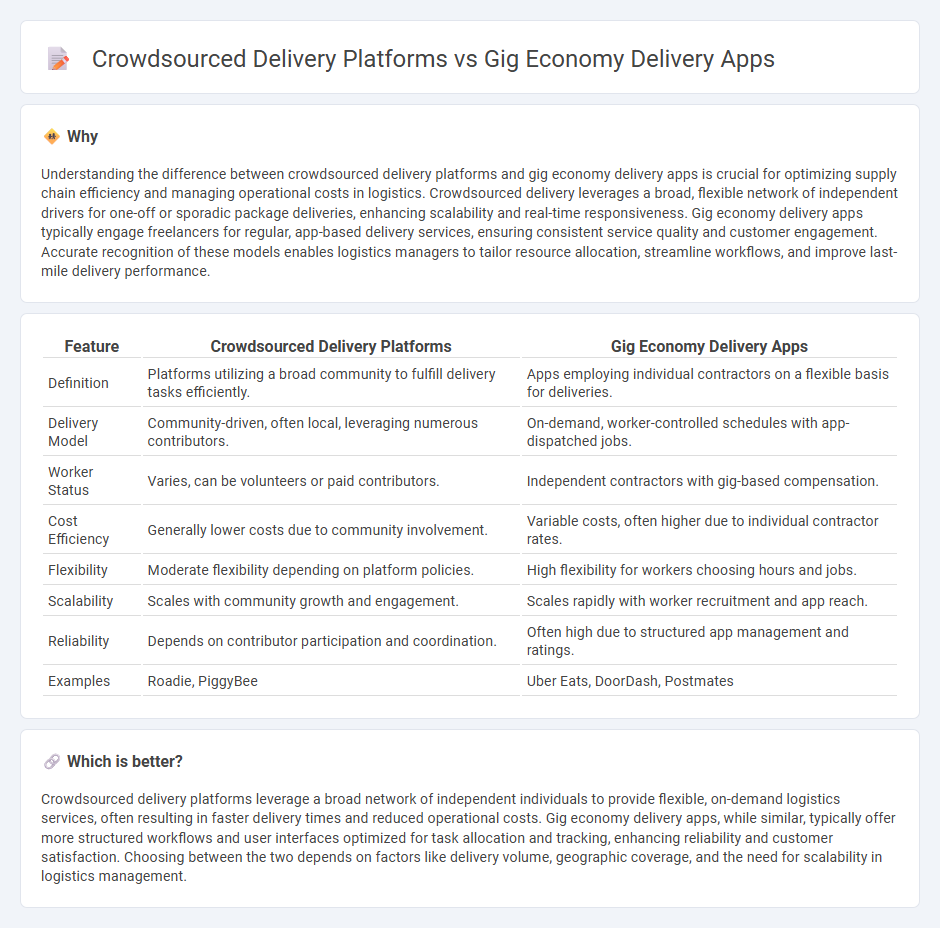
Understanding the difference between crowdsourced delivery platforms and gig economy delivery apps is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and managing operational costs in logistics. Crowdsourced delivery leverages a broad, flexible network of independent drivers for one-off or sporadic package deliveries, enhancing scalability and real-time responsiveness. Gig economy delivery apps typically engage freelancers for regular, app-based delivery services, ensuring consistent service quality and customer engagement. Accurate recognition of these models enables logistics managers to tailor resource allocation, streamline workflows, and improve last-mile delivery performance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Crowdsourced Delivery Platforms | Gig Economy Delivery Apps |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Platforms utilizing a broad community to fulfill delivery tasks efficiently. | Apps employing individual contractors on a flexible basis for deliveries. |
| Delivery Model | Community-driven, often local, leveraging numerous contributors. | On-demand, worker-controlled schedules with app-dispatched jobs. |
| Worker Status | Varies, can be volunteers or paid contributors. | Independent contractors with gig-based compensation. |
| Cost Efficiency | Generally lower costs due to community involvement. | Variable costs, often higher due to individual contractor rates. |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility depending on platform policies. | High flexibility for workers choosing hours and jobs. |
| Scalability | Scales with community growth and engagement. | Scales rapidly with worker recruitment and app reach. |
| Reliability | Depends on contributor participation and coordination. | Often high due to structured app management and ratings. |
| Examples | Roadie, PiggyBee | Uber Eats, DoorDash, Postmates |
Which is better?
Crowdsourced delivery platforms leverage a broad network of independent individuals to provide flexible, on-demand logistics services, often resulting in faster delivery times and reduced operational costs. Gig economy delivery apps, while similar, typically offer more structured workflows and user interfaces optimized for task allocation and tracking, enhancing reliability and customer satisfaction. Choosing between the two depends on factors like delivery volume, geographic coverage, and the need for scalability in logistics management.
Connection
Crowdsourced delivery platforms leverage gig economy delivery apps to connect businesses with independent drivers, enabling flexible, on-demand shipment fulfillment. These apps optimize route efficiency and enable real-time tracking, improving delivery speed and transparency in logistics operations. The synergy between crowdsourced models and gig platforms lowers operational costs while expanding access to a distributed workforce.
Key Terms
On-demand fulfillment
Gig economy delivery apps leverage independent contractors to provide rapid, flexible on-demand fulfillment, enabling businesses to scale delivery capacity without fixed costs. Crowdsourced delivery platforms utilize a large network of local drivers, optimizing route efficiency and reducing delivery times through real-time data and algorithm-driven dispatch. Explore how these models reshape logistics and customer experience in dynamic, on-demand fulfillment environments.
Independent contractors
Gig economy delivery apps and crowdsourced delivery platforms both rely heavily on independent contractors to fulfill delivery tasks, offering flexible work arrangements without traditional employee benefits. Independent contractors on these platforms manage their schedules and use personal vehicles, but they face challenges such as income variability and lack of job security. Explore the evolving dynamics of contractor rights and platform policies to better understand this shifting labor landscape.
Dynamic routing
Dynamic routing in gig economy delivery apps leverages real-time data and advanced algorithms to optimize delivery paths and reduce transit times, enhancing efficiency for independent contractors. Crowdsourced delivery platforms utilize dynamic routing to adapt fluidly to fluctuating demand and driver availability, often increasing scalability and responsiveness. Explore how these dynamic routing strategies redefine last-mile delivery performance and customer satisfaction.
Source and External Links
The Ultimate Guide to the Best Gig Apps in 2024 - shiftNOW - Popular gig economy delivery apps include DoorDash (best for food delivery), Instacart (grocery delivery), and Postmates (variety of delivery options), all offering flexible hours but variable income and physical demands.
11 Best Gig Economy Apps for Making Extra Cash in 2025 - Millo.co - Postmates stands out for delivering many types of items beyond food, offering drivers flexible schedules, on-demand earnings, and keeping all tips; Uber remains the largest ride-share but is less profitable for drivers after expenses.
35 Highest Paying Gig Economy Jobs ' Gig Apps that Pay Well | Para - High-paying delivery apps include ParaWorks (up to $50/hour with guaranteed earnings), ChowBus (Asian food delivery up to $32/hour), and Dlivrd (up to $32/hour), showing diverse opportunities in the gig economy food delivery sector.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com