Green corridors focus on establishing environmentally sustainable transportation routes by minimizing carbon emissions through optimized logistics and cleaner energy use. Freight forwarding involves managing and coordinating shipments from origin to destination, prioritizing speed, cost-efficiency, and reliability. Explore more to understand how green corridors and freight forwarding reshape modern supply chains for sustainability and efficiency.
Why it is important
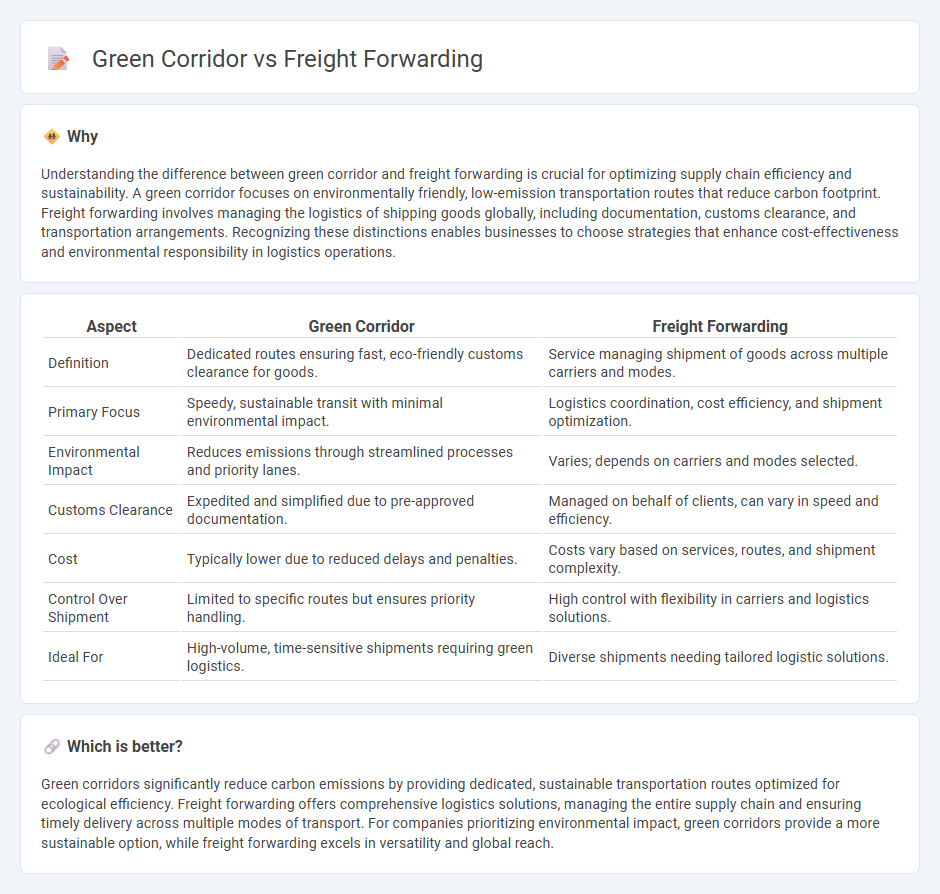
Understanding the difference between green corridor and freight forwarding is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and sustainability. A green corridor focuses on environmentally friendly, low-emission transportation routes that reduce carbon footprint. Freight forwarding involves managing the logistics of shipping goods globally, including documentation, customs clearance, and transportation arrangements. Recognizing these distinctions enables businesses to choose strategies that enhance cost-effectiveness and environmental responsibility in logistics operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Corridor | Freight Forwarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dedicated routes ensuring fast, eco-friendly customs clearance for goods. | Service managing shipment of goods across multiple carriers and modes. |
| Primary Focus | Speedy, sustainable transit with minimal environmental impact. | Logistics coordination, cost efficiency, and shipment optimization. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces emissions through streamlined processes and priority lanes. | Varies; depends on carriers and modes selected. |
| Customs Clearance | Expedited and simplified due to pre-approved documentation. | Managed on behalf of clients, can vary in speed and efficiency. |
| Cost | Typically lower due to reduced delays and penalties. | Costs vary based on services, routes, and shipment complexity. |
| Control Over Shipment | Limited to specific routes but ensures priority handling. | High control with flexibility in carriers and logistics solutions. |
| Ideal For | High-volume, time-sensitive shipments requiring green logistics. | Diverse shipments needing tailored logistic solutions. |
Which is better?
Green corridors significantly reduce carbon emissions by providing dedicated, sustainable transportation routes optimized for ecological efficiency. Freight forwarding offers comprehensive logistics solutions, managing the entire supply chain and ensuring timely delivery across multiple modes of transport. For companies prioritizing environmental impact, green corridors provide a more sustainable option, while freight forwarding excels in versatility and global reach.
Connection
Green corridors in logistics optimize freight forwarding by establishing dedicated routes that minimize environmental impact through reduced emissions and energy consumption. Freight forwarders leverage these eco-friendly pathways to enhance supply chain sustainability and meet regulatory standards for green transportation. Integrating green corridors into freight forwarding operations promotes efficient cargo movement while supporting carbon footprint reduction goals.
Key Terms
**Freight Forwarding:**
Freight forwarding involves coordinating and shipping goods from origin to destination using various transportation modes while managing logistics, customs clearance, and documentation. It optimizes supply chain efficiency by selecting cost-effective routes and ensuring timely delivery through experienced carriers and freight networks. Explore how freight forwarding streamlines global trade and reduces shipping complexities for businesses.
Shipment Consolidation
Freight forwarding involves coordinating shipments from various suppliers to optimize transportation routes and costs, whereas green corridors emphasize streamlined, eco-friendly pathways that reduce emissions and improve sustainability in logistics. Shipment consolidation in freight forwarding maximizes container utilization by combining multiple smaller shipments into a single load, lowering freight expenses and carbon footprint. Explore how shipment consolidation within green corridors strengthens efficiency and environmental impact in modern supply chains.
Customs Brokerage
Freight forwarding streamlines the transport of goods by coordinating shipments across multiple carriers and handling documentation, including customs brokerage services that ensure compliance with import-export regulations. In contrast, the Green Corridor initiative simplifies customs procedures by eliminating physical inspections and reducing paperwork, expediting clearance for specific goods under agreed guidelines. Explore how these customs brokerage strategies impact supply chain efficiency and regulatory adherence to learn more.
Source and External Links
What is freight forwarding? - Freight forwarding is the strategic planning and coordination of international goods movement via multiple transport modes, with freight forwarders acting as logistics experts who arrange shipping, customs clearance, and ensure shipments arrive on time and in good condition.
What Is Freight Forwarding? Definition, Benefits and Key ... - Freight forwarding involves key stages such as export haulage, export customs clearance, and origin handling, whereby the freight forwarder coordinates moving goods from the point of origin to destination, navigating regulatory and logistical challenges.
About Freight Forwarding - Freight forwarding facilitates international trade by managing the carriage, consolidation, storage, handling, and documentation of goods, aiming to deliver shipments economically, on time, undamaged, and to the right location.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com