Cold chain logistics maintains temperature-sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals and perishable foods within controlled environments, ensuring product efficacy and freshness during transportation and storage. Dry chain logistics focuses on protecting moisture-sensitive goods like grains, seeds, and spices by maintaining low humidity conditions throughout the supply chain. Explore the key differences and benefits of cold chain versus dry chain solutions to optimize your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cold chain and dry chain logistics is crucial for ensuring the proper storage and transportation of temperature-sensitive and moisture-sensitive products, respectively. Cold chain logistics maintain products like vaccines and perishable foods at controlled low temperatures to prevent spoilage. Dry chain logistics protect goods such as pharmaceuticals and electronics from humidity damage during transit. Proper differentiation optimizes supply chain efficiency and preserves product integrity, reducing financial losses and health risks.
Comparison Table
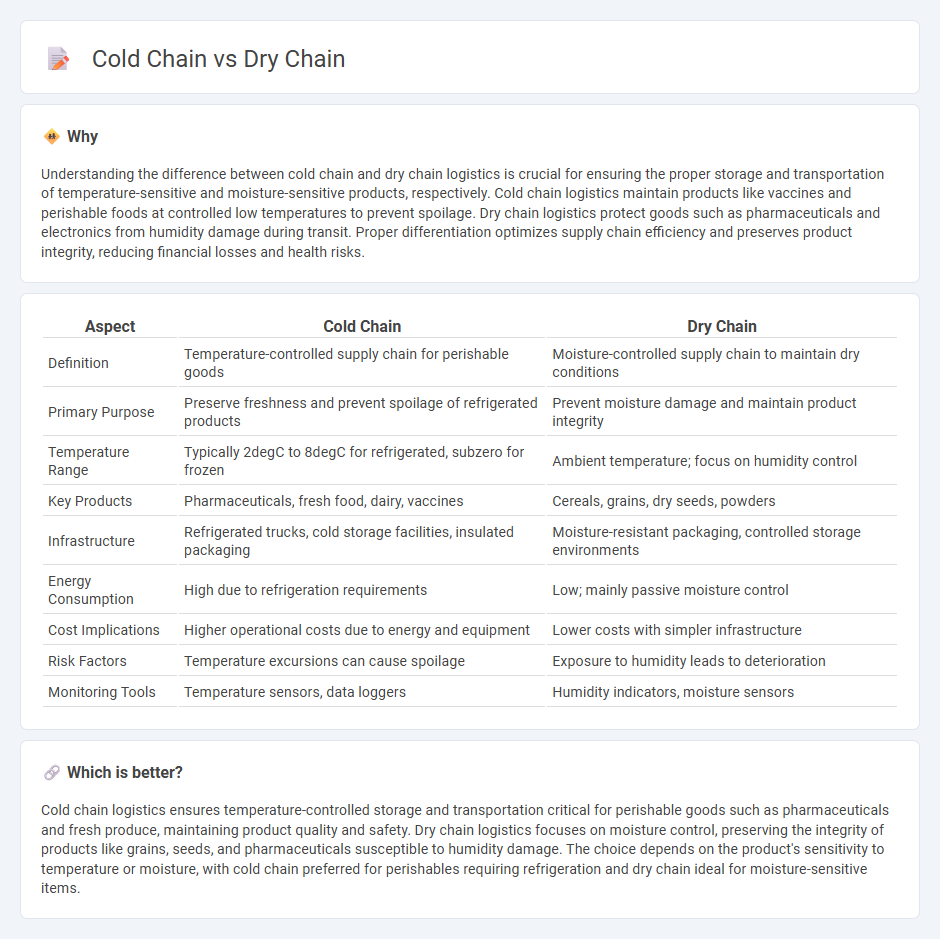
| Aspect | Cold Chain | Dry Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods | Moisture-controlled supply chain to maintain dry conditions |
| Primary Purpose | Preserve freshness and prevent spoilage of refrigerated products | Prevent moisture damage and maintain product integrity |
| Temperature Range | Typically 2degC to 8degC for refrigerated, subzero for frozen | Ambient temperature; focus on humidity control |
| Key Products | Pharmaceuticals, fresh food, dairy, vaccines | Cereals, grains, dry seeds, powders |
| Infrastructure | Refrigerated trucks, cold storage facilities, insulated packaging | Moisture-resistant packaging, controlled storage environments |
| Energy Consumption | High due to refrigeration requirements | Low; mainly passive moisture control |
| Cost Implications | Higher operational costs due to energy and equipment | Lower costs with simpler infrastructure |
| Risk Factors | Temperature excursions can cause spoilage | Exposure to humidity leads to deterioration |
| Monitoring Tools | Temperature sensors, data loggers | Humidity indicators, moisture sensors |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-controlled storage and transportation critical for perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals and fresh produce, maintaining product quality and safety. Dry chain logistics focuses on moisture control, preserving the integrity of products like grains, seeds, and pharmaceuticals susceptible to humidity damage. The choice depends on the product's sensitivity to temperature or moisture, with cold chain preferred for perishables requiring refrigeration and dry chain ideal for moisture-sensitive items.
Connection
Cold chain and dry chain logistics both focus on maintaining product quality through temperature and moisture control during transportation and storage. Cold chain ensures perishable goods like pharmaceuticals and food remain within specific temperature ranges, while dry chain prevents moisture damage to goods such as seeds and electronics. Together, these supply chains optimize product integrity by managing environmental factors critical to shelf life and efficacy.
Key Terms
Temperature Control
Dry chain and cold chain both emphasize temperature control but serve different purposes; the dry chain maintains low humidity and moisture levels to protect products like seeds and pharmaceuticals from degradation, while the cold chain strictly regulates low temperatures to preserve perishable items such as food and vaccines. Temperature stability in the cold chain is critical to prevent spoilage and maintain efficacy, whereas the dry chain focuses on preventing moisture-induced damage by avoiding condensation and humidity fluctuations. Explore detailed strategies and technologies used in temperature control for dry and cold chains to optimize product safety and quality.
Moisture Management
Moisture management in the dry chain involves controlling humidity levels to prevent mold growth and preserve product quality, particularly for grains and pharmaceuticals. The cold chain focuses on maintaining low temperatures to inhibit microbial activity and biochemical reactions, effective for perishable foods and vaccines. Explore detailed differences and best practices to optimize storage and transportation efficacy.
Product Shelf Life
Dry chain technology preserves product shelf life by controlling moisture content from production to storage, significantly reducing spoilage and quality degradation in moisture-sensitive goods like grains and pharmaceuticals. Unlike the cold chain, which requires continuous refrigeration to maintain low temperatures for perishable items, the dry chain offers energy-efficient moisture control without temperature dependence. Discover how implementing dry chain solutions can enhance your product's longevity and quality by exploring detailed comparisons and case studies.
Source and External Links
Dry chain | Feed the Future Innovation Lab for Horticulture - The dry chain refers to drying agricultural products and keeping them dry with hermetic storage to prevent mold, food loss, and mycotoxin contamination.
Dry Lube - Chain Lubricants - Finish Line - Finish Line Dry Lube is a bicycle chain lubricant designed for dry, dusty conditions, forming a clean, wax-like film that reduces friction and repels dirt.
Stan's Biobased Dry Chain Lube - Stan's Biobased Dry Lube is an eco-friendly, biodegradable chain lubricant for bicycles, ideal for dry to moderate riding conditions and made from natural ingredients.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com