Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals and perishable foods remain within required temperature ranges throughout transportation and storage. Containerization revolutionizes cargo handling by using standardized containers that enhance security, reduce damage, and streamline global shipping processes. Explore how integrating cold chain technology with containerization optimizes supply chain efficiency and product integrity.
Why it is important
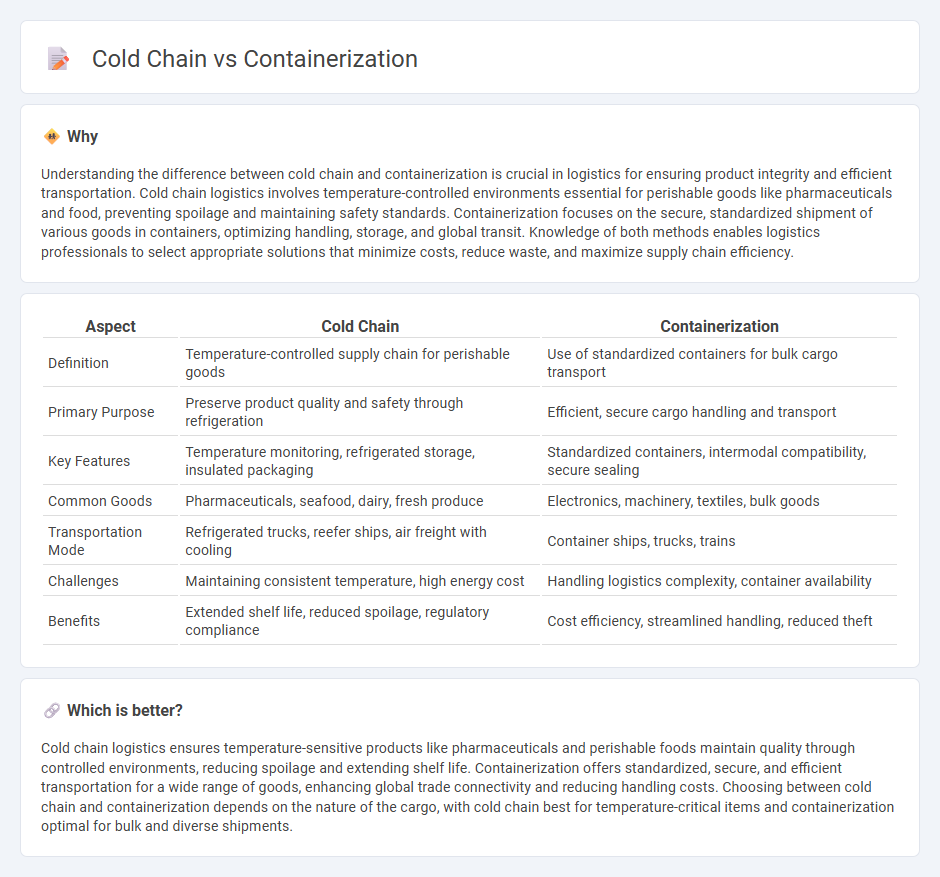
Understanding the difference between cold chain and containerization is crucial in logistics for ensuring product integrity and efficient transportation. Cold chain logistics involves temperature-controlled environments essential for perishable goods like pharmaceuticals and food, preventing spoilage and maintaining safety standards. Containerization focuses on the secure, standardized shipment of various goods in containers, optimizing handling, storage, and global transit. Knowledge of both methods enables logistics professionals to select appropriate solutions that minimize costs, reduce waste, and maximize supply chain efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain | Containerization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods | Use of standardized containers for bulk cargo transport |
| Primary Purpose | Preserve product quality and safety through refrigeration | Efficient, secure cargo handling and transport |
| Key Features | Temperature monitoring, refrigerated storage, insulated packaging | Standardized containers, intermodal compatibility, secure sealing |
| Common Goods | Pharmaceuticals, seafood, dairy, fresh produce | Electronics, machinery, textiles, bulk goods |
| Transportation Mode | Refrigerated trucks, reefer ships, air freight with cooling | Container ships, trucks, trains |
| Challenges | Maintaining consistent temperature, high energy cost | Handling logistics complexity, container availability |
| Benefits | Extended shelf life, reduced spoilage, regulatory compliance | Cost efficiency, streamlined handling, reduced theft |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics ensures temperature-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals and perishable foods maintain quality through controlled environments, reducing spoilage and extending shelf life. Containerization offers standardized, secure, and efficient transportation for a wide range of goods, enhancing global trade connectivity and reducing handling costs. Choosing between cold chain and containerization depends on the nature of the cargo, with cold chain best for temperature-critical items and containerization optimal for bulk and diverse shipments.
Connection
Cold chain logistics relies heavily on containerization to maintain temperature-controlled environments during transit, ensuring perishable goods remain fresh and safe. Specialized refrigerated containers, known as reefers, are designed to regulate temperature precisely, preserving the integrity of pharmaceuticals, food, and other temperature-sensitive items. Efficient containerization streamlines handling, reduces spoilage, and extends shelf life in global cold supply chains.
Key Terms
**Containerization:**
Containerization revolutionizes logistics by using standardized containers to enhance the efficiency and security of cargo transport across multiple modes, including ships, trains, and trucks. This method significantly reduces handling time and damage while improving tracking and inventory management through advanced technologies like GPS and RFID. Explore how containerization optimizes supply chains and supports global trade growth.
Intermodal Containers
Intermodal containers play a pivotal role in containerization by enabling seamless cargo transfer across ships, trucks, and trains without unloading the cargo, significantly boosting efficiency and reducing handling risks. In contrast, cold chain logistics within these containers ensure temperature-sensitive goods remain within precise thermal ranges through advanced refrigeration technologies and insulated container designs. Explore the intricacies of intermodal containerization and cold chain integration to optimize global supply chains effectively.
TEU (Twenty-foot Equivalent Unit)
Containerization revolutionizes cargo transport by standardizing shipments into TEU units, ensuring efficient stacking, loading, and tracking across global supply chains. Cold chain logistics within TEUs require specialized refrigerated containers (reefers) to maintain precise temperature controls for perishable goods during transit. Explore detailed comparisons of containerization strategies and cold chain innovations to optimize your TEU utilization and cargo integrity.
Source and External Links
What Is Containerization? Applications and Technologies - Containerization is a cloud resource method that bundles an application and all its OS libraries and dependencies into isolated, portable containers managed by a container engine over the host OS and hardware infrastructure, ensuring consistent performance and security across environments.
What is Containerization? - Containerization packages an application's code with all necessary files and libraries into a container image that runs consistently on any infrastructure via a container engine interfacing with the OS and hardware.
What Is Containerization? | IBM - Containerization packages software code with essential OS libraries into lightweight, portable containers that run reliably on any platform, speeding deployment and preventing environment-related bugs, popularized by Docker since 2013.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com